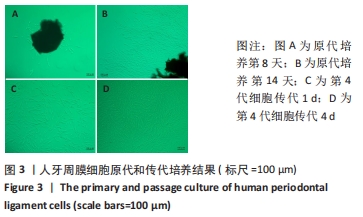
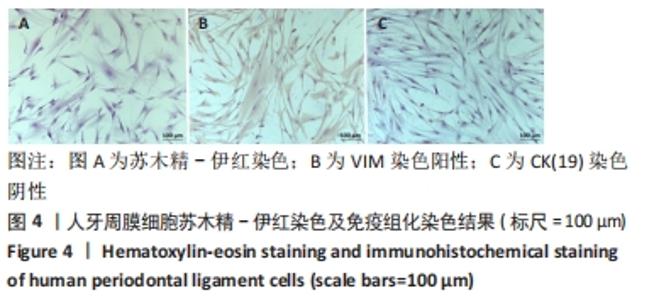
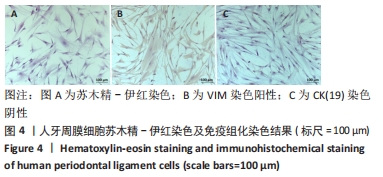
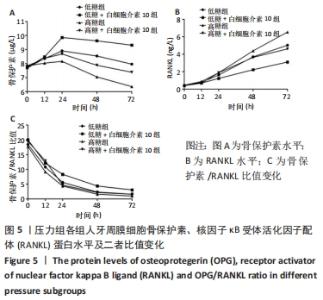
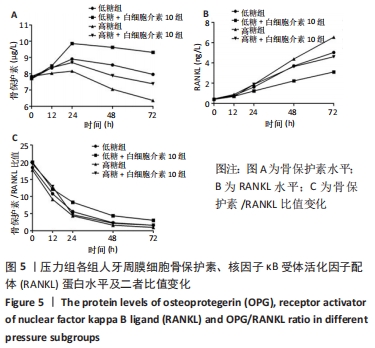
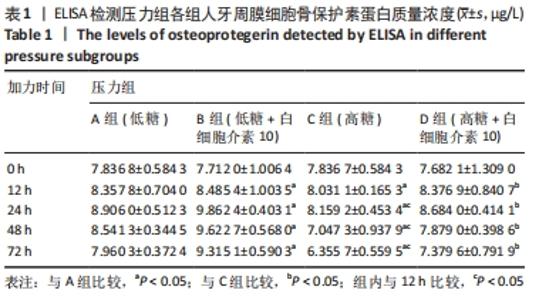
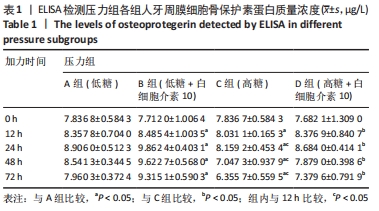
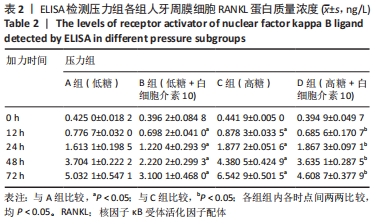
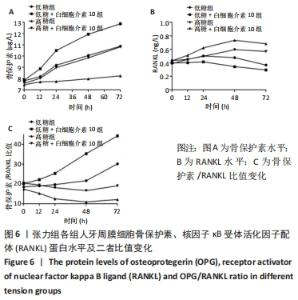
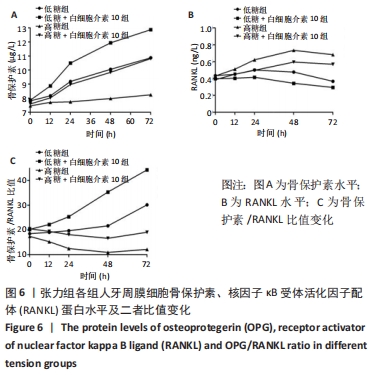
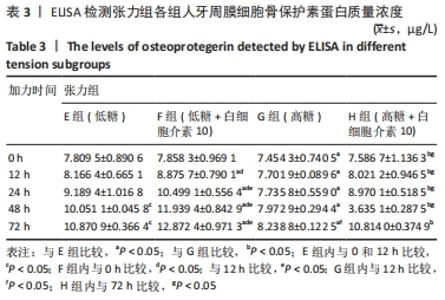
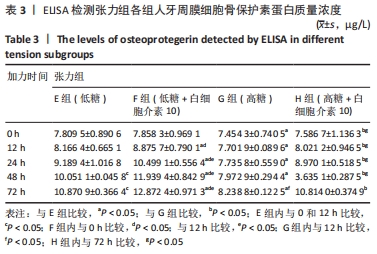
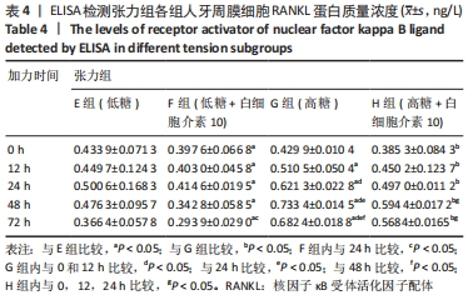
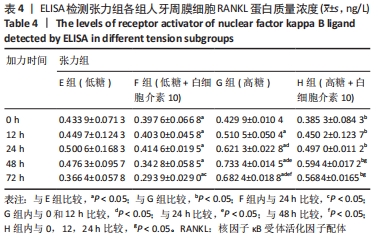
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (26): 4180-4185.doi: 10.12307/2022.821
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of interleukin-10 on alveolar bone remodeling under orthodontic force in a high glucose condition
Han Yu, Li Wenjing, Wu Jie, Cui Zhanqin
- The Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050000, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2021-04-16Accepted:2021-06-01Online:2022-09-18Published:2022-03-07 -
Contact:Cui Zhanqin, Master, Professor, The Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050000, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Han Yu, Master, Physician, The Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050000, Hebei Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Han Yu, Li Wenjing, Wu Jie, Cui Zhanqin. Effects of interleukin-10 on alveolar bone remodeling under orthodontic force in a high glucose condition[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(26): 4180-4185.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] GRAVES DT, DING Z, YANG Y. The impact of diabetes on periodontal diseases. Periodontol 2000. 2020;82(1):214-224. [2] PICKE AK, CAMPBELL G, NAPOLI N, et al. Update on the impact of type 2 diabetes mellitus on bone metabolism and material properties. Endocr Connect. 2019;8(3):55-70. [3] NAJEEB S, SIDDIQUI F, QASIM SB, et al. Influence of uncontrolled diabetes mellitus on periodontal tissues during orthodontic tooth movement: a systematic review of animal studies. Prog Orthod. 2017;18(1):5-12. [4] 迟家敏. 实用糖尿病学[M].4版.北京:人民卫生出版社, 2015. [5] 勾忠平,李秀钧. 糖尿病属慢性炎症性疾病——慢性炎病新概念释义与讨论[J].实用糖尿病杂志,2007,3(2): 5-7. [6] ACHARYA AB, THAKUR S, MUDDAPUR MV. Evaluation of serum interleukin-10 levels as a predictor of glycemic alteration in chronic periodontitis and type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2015;19(4):388-392. [7] RODIC T, WÖLFEL EM, MILOVANOVIC P, et al. Bone quality analysis of jaw bones in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus-post mortem anatomical and microstructural evaluation. Clin Oral Investig. 2021; 25(7):4377-4400. [8] THEOLEYRE S, WITTRANT Y, TAT SK, et al. The molecular triad OPG/RANK /RANKL:involvement in the orchestration of pathophysiological bone remodeling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004;5(6):457-475. [9] TROUVIN AP, GOËB V. Receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand and osteoprotegerin: maintaining the balance to prevent bone loss. Clin Interv Aging. 2010;19(5):345-354. [10] BOBHATE A, VISWANATHAN V, ARAVINDHAN V. Anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-27, IL-10, IL-1Ra and TGF-β in subjects with increasing grades of glucose intolerence (DM-LTB-2). Cytokine. 2021;137:155333. [11] RIOS-ARCE ND, DAGENAIS A, FEENSTRA D, et al. Loss of interleukin-10 exacerbates early Type-1 diabetes-induced bone loss. Cell Physiol. 2020;235(3):2350-2365. [12] ZHENG J, CHEN S, ALBIERO ML, et al. Diabetes Activates Periodontal Ligament Fibroblasts via NF-κB In Vivo. Dent Res. 2018;97(5):580-588. [13] JEON HH, TEIXEIRA H, TSAI A. Mechanistic Insight into Orthodontic Tooth Movement Based on Animal Studies: A Critical Review. J Clin Med. 2021;10(8):1733. [14] VAN EXEL E, GUSSEKLOO J, DE CRAEN AJ, et al. Low production capacity of interleukin-10 associates with the metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes: the Leiden 85-Plus Study. Diabetes. 2002;51(4):1088-1092. [15] RIOS-ARCE ND, DAGENAIS A, FEENSTRA D, et al. Loss of interleukin-10 exacerbates early Type-1 diabetes-induced bone loss. Cell Physiol. 2020;235(3):2350-2365. [16] RIBEIRO IS, PEREIRA ÍS, SANTOS DP, et al. Association between body composition and inflammation: A central role of IL-17 and IL-10 in diabetic and hypertensive elderly women. Exp Gerontol. 2019;127: 110734. [17] ZHANG F, YANG Y, LEI H, et al. A meta-analysis about the association between -1082G/A and -819C/T polymorphisms of IL-10 gene and risk of type 2 diabetes. Hum Immunol. 2013;74(5):618-626. [18] TAI N, YASUDA H, XIANG Y, et al. IL-10-conditioned dendritic cells prevent autoimmune diabetes in NOD and humanized HLA-DQ8/RIP-B7.1 mice. Clin Immunol. 2011;139(3):336-349. [19] LI Y, JACOX LA, LITTLE SH, et al. Orthodontic tooth movement: The biology and clinical implications. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2018;34(4):207-214. [20] YANG CY, JEON HH, ALSHABAB A, et al. RANKL deletion in periodontal ligament and bone lining cells blocks orthodontic tooth movement. Int J Oral Sci. 2018;10(1):27-35. [21] NAJEEB S, SIDDIQUI F, QASIM SB, et al. Influence of uncontrolled diabetes mellitus on periodontal tissues during orthodontic tooth movement: a systematic review of animal studies. Prog Orthod. 2017; 18(1):1-7. [22] SANTAMARIA-JR M, DO NASCIMENTO ERA, BAGNE L, et al. Pulpal outcomes in orthodontic tooth movement in diabetes mellitus. Odontology. 2021;109(4):921-929. [23] SASAKI F, HAYASHI M, ONO T, et al. The regulation of RANKL by mechanical force. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021;39(1):34-44. [24] ZHANG L, DING Y, RAO GZ, et al. Effects of IL-10 and glucose on expression of OPG and RANKL in human periodontal ligament fibroblasts. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2016;49(4):e4324. [25] JANJIC M, DOCHEVA D, TRICKOVIC JANJIC O, et al. In Vitro Weight-Loaded Cell Models for Understanding Mechanodependent Molecular Pathways Involved in Orthodontic Tooth Movement: A Systematic Review. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:1-17. [26] KANZAKI H, CHIBA M, SHIMIZU Y, et al. Periodontal ligament cells under mechanical stress induce osteoclastogenesis by receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand up-regulation via prostaglandin E2 synthesis. Bone Miner Res. 2002;17(2):210-220. [27] 黄生高,张建兴,熊培颖,等. 持续静压力对人人牙周膜细胞OPG及ODFmRNA表达的影响[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2006,22(6):347-350. [28] NGAN P, SAITO S, SAITO M, et al. The interactive effects of mechanical stress and interleukin-1 beta on prostaglandin E and cyclic AMP production in human periodontal ligament fibroblasts in vitro: comparison with cloned osteoblastic cells of mouse (MC3T3-E1). Arch Oral Biol. 1990;35(9):717-725. [29] 麻健丰,胡军,张秀华,等. 静态拉伸应变对人牙周膜成纤维细胞的影响[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2003,19(5):439-442. [30] WEIDER M, SCHRÖDER A, DOCHEVA D, et al. A Human Periodontal Ligament Fibroblast Cell Line as a New Model to Study Periodontal Stress. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(21):7961. |
| [1] | Tian Xinbao, Xu Jianfeng, Huang Yuan, Lai Zheying, Li Xiaolong, Liu Xiaoli, Lin Ruizhu, Zhu Ning. Internal heat-type acupuncture inhibits osteoblast viability and promotes bone formation in a rat model of steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(17): 2642-2648. |
| [2] | Huang Zhicai, Xie Liuqin, Wang Guangsu, Zhang Guoxing, Tang Zhenglong. Parathyroid hormone promotes bone healing in rabbits after free reduction of mandibular condyle fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(14): 2172-2178. |
| [3] | Zhong Yulan, Zhou Xiangxiang, Gan Xin. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(13): 1979-1984. |
| [4] | Wang Dong, Ding Hai, Chang Wenju, Wang Jinzi. Biological changes and mechanism of salvianolic acid B in ovariectomized osteoporosis rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(12): 1927-1930. |
| [5] | Liu Keke, Duan Xin, Ma Xiangrui, Zhang Yuntao. Effect of cinnamaldehyde on osteoblasts in high glucose environment with the electrospinning membrane as a carrier [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3500-3504. |
| [6] | Li Ping, Lin Yu, Chen Xiang, Liu Zhentao, Xiao Lili, Lin Xueyi, Hua Peng . Characteristics of bone remodeling in female ovariectomized rat models of osteoporosis undergoing Erzhi Pill extract intervention [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 191-195. |
| [7] | Liu Hong, Wan Zhe, Zhang Zhen, Zhang Qin. Relationship between root resorption and intrusive force during maxillary molar intrusion in Beagle dogs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2172-2176. |
| [8] |
Li Xianghe, Luo Wei, Hu Junxian, Yang Jing, Han Xinyun, Dong Shiwu, Yang Xianteng, Li Senlei, Yan Zhihui, Nie Yingjie, Tian Xiaobin, Sun Li.
Chrysin inhibits mouse osteoclastogenesis induced by receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(25): 3978-3986.
|
| [9] | Huang Xiaolin, Liao Jian, Hong Wei, Li Fang, Cheng Yuting, Zhou Qian, Dong Qiang. Zoledronic acid in osteoclastogenesis: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(17): 2716-2721. |
| [10] | Zheng Rui, Xie Jing, Lu Shuai, Sun Yong. Beta-tricalcium phosphate combined with advanced platelet-rich fibrin contributes to bone regeneration: X-ray and immunohistochemical analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(10): 1514-1519. |
| [11] | Zhou Yi-fei, Zheng Qian, Mao Jie, Lv Jia-ling, Wu Xiao-ling, Xu Xiao-mei. Combined oral contraceptives facilitate periodontium remodeling during orthodontic tooth movement in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(4): 542-547. |
| [12] | Wang Ping-ting, Zhou Pan, Zheng Guo-ying, Liu Da-yong. Intervention with pyrrolidine dithioearbamate stimulates expression of RANKL and OPG in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(21): 3365-3370. |
| [13] | Wan Lei1, Huang Hong-xing1, Huang Hong2, Wang Fan3, Chai Shuang4, Wang Ji-li4, Liu Shao-jin4, Huang Jia-chun4. Bushen Jianpi Huoxue decoction increases the proliferation of Sost-overexpressed adenovirus transfected osteoblasts and alkaline phosphatase activity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(16): 2461-2466. |
| [14] | Zhang Shai-lin, Cheng Xiang-yu, Shi Ji-xiang, Zhou Qiang, Shi Wen-jun, Liu Fu-ying, Ji Bin. Osteoclast activity of MG63 cells on silicon doped zirconia films prepared by cathodic arc deposition [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(14): 2227-2232. |
| [15] | Tian Lu-ming1, Xin Zeng-xi1, Ma Yun-sheng2. Effect of concentrated growth factor fibrin membrane during distraction osteogenesis of the rabbit mandible [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(8): 1172-1177. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||