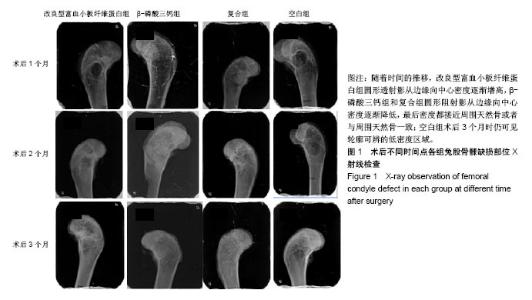
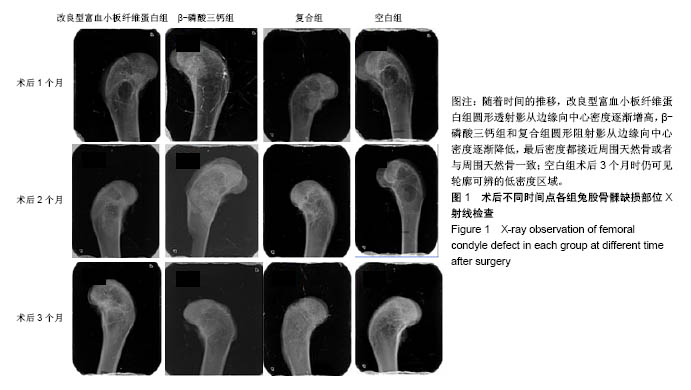
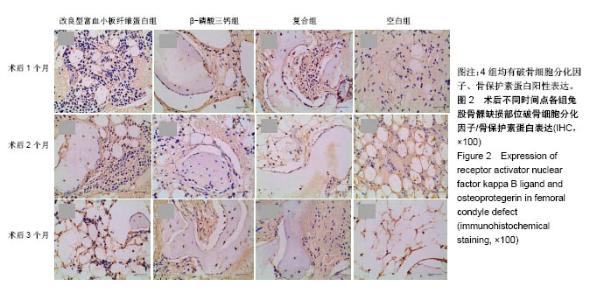
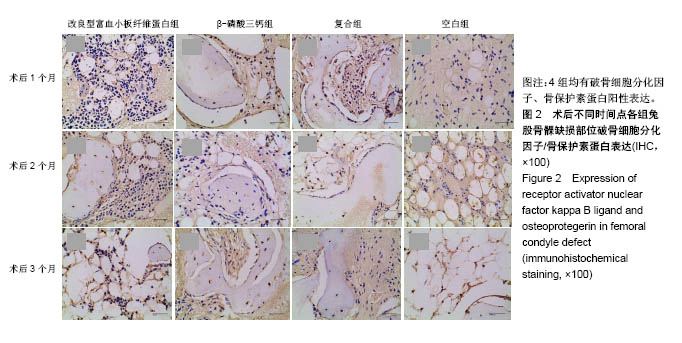
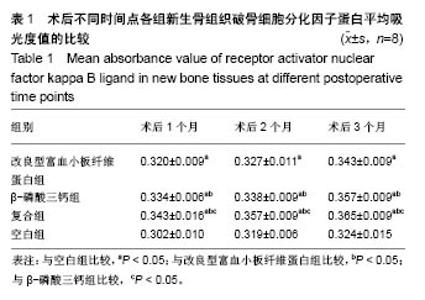
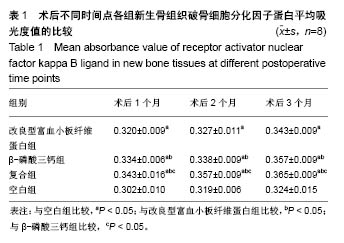
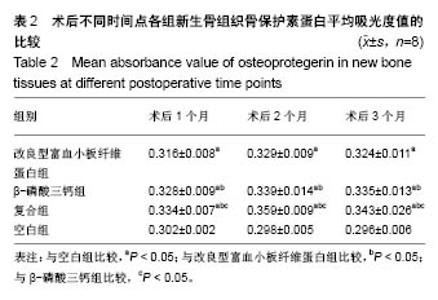
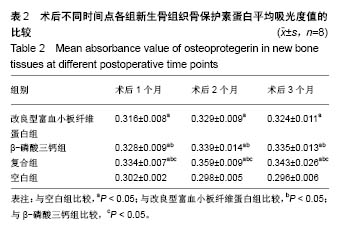
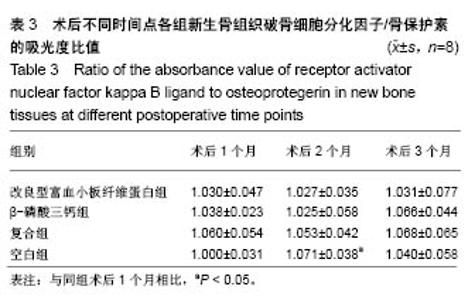
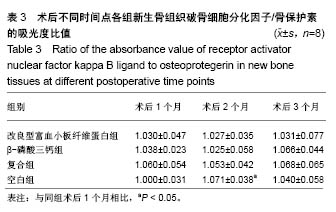
| [1] 胡文军,朱靖恺,马威.植骨材料在口腔种植中的应用概况及进展[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2018,11(1):17-23.[2] Jeon IS, Heo MS, Han KH, et al.Vertical ridge augmentation with simultaneous implant placement using β-TCP and PRP: A report of two cases.J Oral Maxillofac Surg Med Pathol. 2013;25(3):226-231.[3] Sager M, Ferrari D, Wieland M, et al.Immunohis-tochemical characterization of wound healing at two different bone graft substitutes. Int J Oral Maxil-lofac Surg.2012;41(5):657-666.[4] Luo T, Zhang W, Shi B, et al.Enhanced bone regeneration around dental implant with bone mor-phogenetic protein 2 gene and vascular endothelial growth factor protein delivery. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012; 23(4):467-473.[5] 宋乔健.口腔颌面部骨组织缺损修复材料的研究进展[J].临床医药文献电子杂志,2017,4(25):175-177.[6] Walsh W, Vizesi F, Michael D, et al. Beta -TCP bone graft substitutes in a bilateral rabbit tibial defect model. Biomaterials.2008;29(3): 266-271.[7] 孙佳佳,王熙. A-PRF诱导软硬组织再生的研究[J].现代口腔医学杂志, 2018, 32(2):115-117.[8] 毛俊丽,孙勇,赵峰,等.兔PRF、A-PRF制备方法的筛选[J]. 西南国防医药, 2016,26(6):593-596.[9] Schmitz JP,Hollinger JO.The critical size defect as an experimental model for craniomandibulofacial nonunions.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986; (205): 299-308.[10] 周芳,李静,余磊,等.兔桡骨临界骨缺损模型的制备[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2011,15(50):9385-9388.[11] Patel ZS, Young S, Tabata Y, et al.Dual delivery of an angiogenic and an osteogenic growth factor for bone regeneration in a critical size defect model. Bone. 2008;43(5):931-940.[12] Kargozar S, Lotfiakhshaiesh N, Ai J, et al.Osteogenic Evaluation of Stem Cell-Seeded Bioactive Glasses Containing Strontium and Cobalt in a Critical Size Defect in Rabbit Femur: Conference of the European Society for Biomaterials[C]. Conference: 28th ANNUAL CONFERENCE OF THE EUROPEAN SOCIETY FOR BIOMATERIALS (ESB), At ATHENS - GREECE Megaron Athens International Conference Centre, 2017.[13] 李阳.牙龈成纤维细胞成骨能力的体外及体内研究[D].天津:天津医科大学, 2017.[14] Ghanaati S, Booms P, Orlowska A, et al.Advanced platelet-rich fibrin: a new concept for cell-based tissue engineering by mean of inflammatory cells.J Oral Implantol. 2014;40(6):679-689. [15] Kobayashi E, Flückiger L, Fujiokakobayashi M, et al.Comparative release of growth factors from PRP, PRF, and advanced-PRF. Clin Oral Investig. 2016;20(9):2353-2360.[16] Masuki H, Okudera T, Watanebe T, et al.Growth factor and pro-inflammatory cytokine contents in platelet-rich plasma (PRP), plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF), advanced platelet-rich fibrin (A-PRF), and concentrated growth factors (CGF). Int J Implant Dent.2016;2(1):19.[17] 何婷婷.两种富血小板纤维蛋白的降解特性研究[D].泸州:西南医科大学, 2017.[18] 焦志立,谢晓玲,付冬梅,等.改良型富血小板纤维蛋白在兔颅骨诱导成骨中的组织学观察[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(14):2208-2214.[19] Gao P, Zhang H, Liu Y, et al.Beta-tricalcium phosphate granules improve osteogenesis in vitro and establish innovative osteo-regenerators for bone tissue engineering in vivo. Sci Rep. 2016;6:23367.[20] Cornell CN.Osteoconductive materials and their role as substitudes for autogenous bone grafts. Orthop Clin North Am. 1999;30(4):591-598.[21] Tanaka T, Kumagae Y, Chazono M, et al.A novel evaluation system to monitor bone formation and β-tricalcium phosphate resorption in opening wedge high tibial osteotomy.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015; 23(7):2007-2011.[22] Meijer HJ, Steen WH, Bosman F.Standarized radiograghs of the alveolar crest around implants in the mandible.J Prosthet Dent. 1992;68:318-321.[23] 于威,李建军.去抗原牛松质骨支架复合骨形态发生蛋白2基因在骨缺损修复过程中的血管化反应[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008, 12(23): 4559-4562.[24] Grzibovskis M,Pilmane M,Urtane I.Today's under-standing about bone aging. Stomatologija.2010;12(4): 99-104.[25] Yu T, Pan H, Hu Y, et al.Autologous platelet-rich plasma induces bone formation of tissue-engineered bone with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on beta-tricalcium phosphate ceramics. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):178.[26] Nelson C, Warren J, Wang MH, et al.RANKL Employs Distinct Binding Modes to Engage RANK and the Osteoprotegerin Decoy Receptor. Structure. 2012; 20(11):1971-1982.[27] Stein NC,Kreutzmann C,Zimmermann SP,et al.Interleukin-4 and interleukin-13 stimulate the osteoclast inhibitor osteoprotegerin by human endothelial cells through the STAT6 pathway.J Bone Miner Res. 2008;23(5):750-758.[28] Kearns AE,Khosla S,Kostenuik PJ.Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand and osteoprotegerin regulation of bone remodeling in health and disease.Endocr Rev. 2008;29(2):155-192.[29] Nakashima T,Takayanagi H.Osteoimmunology: crosstalk between the immune and bone systems. J Clin Immunol. 2009;29(5):555-567.[30] Zhou L,Liu Q,Yang ML,et al.Dihydroartemisinin, an Anti -Malaria drug, suppresses estrogen deficiency - induced osteoporosis, osteoclast formation, and RANKL- Induced signaling pathways.J Bone Miner Res. 2016;31(5):964-974.[31] J Rieu J, Goeuriot P.Ceramic composites for Biomedical applations. Clin Mater.1993;12:211-217. |