Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (18): 2881-2887.doi: 10.12307/2022.698
Previous Articles Next Articles
Screening of differential genes and validation of key genes in synovial tissue of osteoarthritis
Yao Jiawei1, Xu Xiongfeng1, Yi Peng1, Qiu Bo2
- 1Wuhan University, Wuhan 430000, Hubei Province, China; 2Second Department of Orthopedics, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430000, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2021-01-13Accepted:2021-04-12Online:2022-06-28Published:2022-01-30 -
Contact:Qiu Bo, MD, Chief physician, Second Department of Orthopedics, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430000, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Yao Jiawei, Master candidate, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430000, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81071494 (to QB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yao Jiawei, Xu Xiongfeng, Yi Peng, Qiu Bo. Screening of differential genes and validation of key genes in synovial tissue of osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(18): 2881-2887.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
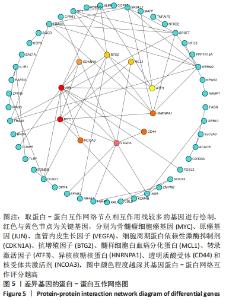
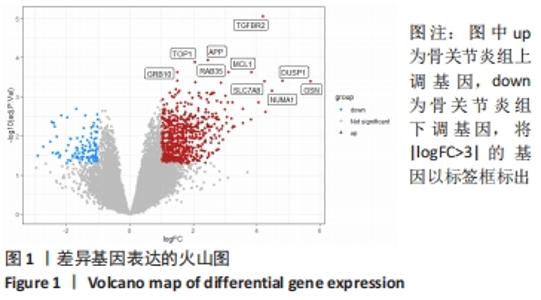
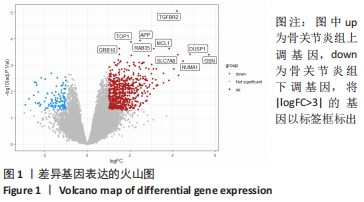
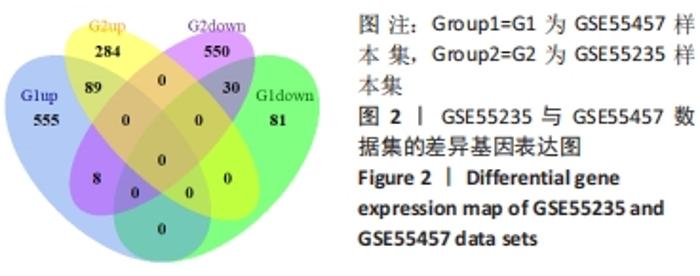
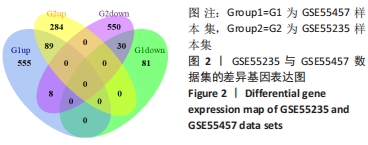
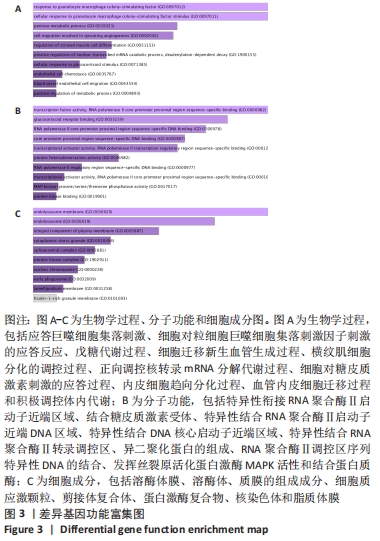
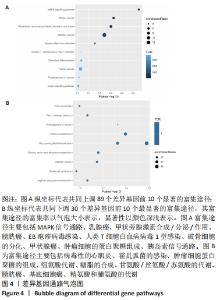
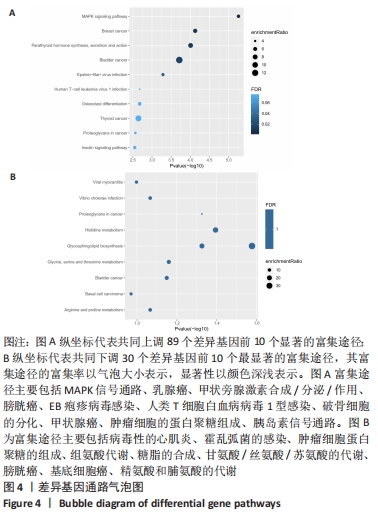
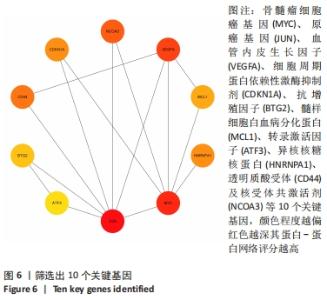
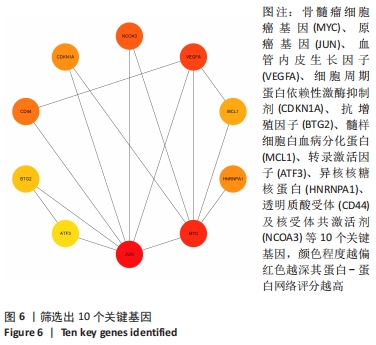
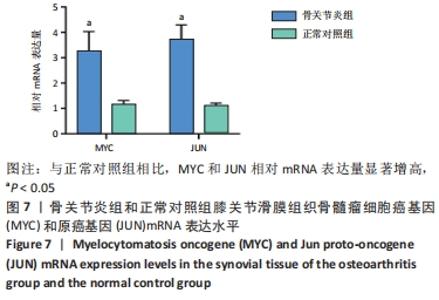
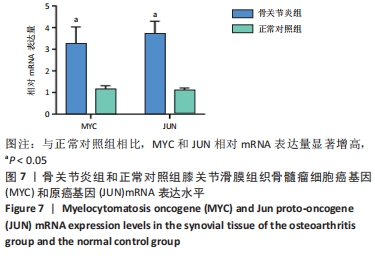
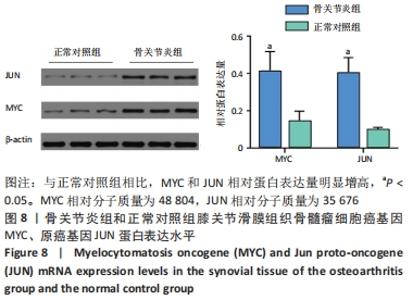
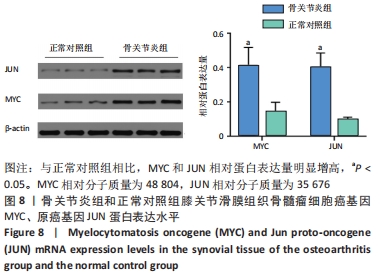
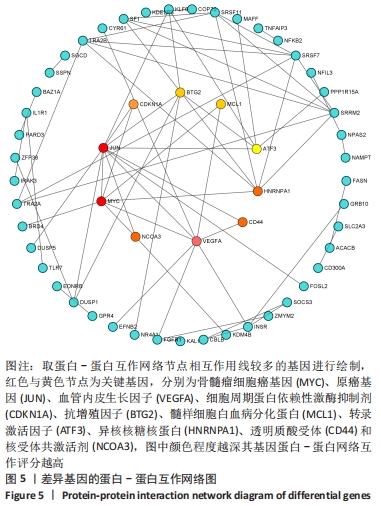
2.3 PPI网络的构建与Hub基因的鉴定结果 向Sting数据库输入共同上调与下调的基因,最低置信度为>0.7(“minimum required interaction score > 0.7”)为条件,得到116个节点,66条蛋白-蛋白互作线的网络。从该数据库下载结果并以Cytoscape 3.8.0软件构建更为清晰的蛋白-蛋白互作网络图,见图5,根据蛋白网络互作图采用EPC、Radialty、 Closeness共3种算法综合分析出前10个Hub基因(Hub gene),见图6。Hub基因包括上调基因:JUN,MYC,VEGFA,MCL1,NCOA3,CDKN1A,HNRNPA1,BTG2,ATF3和CD44,未发现下调基因。"
| [1] WATT FE. Osteoarthritis biomarkers: year in review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(3):312-318. [2] ISHIJIMA M, WATARI T, NAITO K, et al. Relationships between biomarkers of cartilage, bone, synovial metabolism and knee pain provide insights into the origins of pain in early knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011; 13(1):R22. [3] WANG P, SONG J, QIAN D. CTX-II and YKL-40 in early diagnosis and treatment evaluation of osteoarthritis. Exp Ther Med. 2019;17(1):423-431. [4] BARRETT T, WILHITE SE, LEDOUX P, et al. NCBI GEO: archive for functional genomics data sets--update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41(Database issue): D991-D995. [5] 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组,骨关节炎诊疗指南(2018年版)[J].中华骨科杂志,2018,38(12):705-715. [6] PALAZZO C, NGUYEN C, LEFEVRE-COLAU M, et al. Risk factors and burden of osteoarthritis. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2016;59(3):134-138. [7] MUNJAL A, BAPAT S, HUBBARD D, et al. Advances in molecular biomarker for early diagnosis of osteoarthritis. Biomol Concepts. 2019;10(1):111-119. [8] GRIFFIN TM, SCANZELLO CR. Innate inflammation and synovial macrophages in osteoarthritis pathophysiology. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2019;37 Suppl 120(5):57-63. [9] SAVVIDOU O, MILONAKI M, GOUMENOS S, et al. Glucocorticoid signaling and osteoarthritis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2019;480:153-166. [10] NISHIMURA R, HATA K, TAKAHATA Y, et al. Role of signal transduction pathways and transcription factors in cartilage and joint diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(4):1340. [11] MATSUZAKI T, ALVAREZ-GARCIA O, MOKUDA S, et al. FoxO transcription factors modulate autophagy and proteoglycan 4 in cartilage homeostasis and osteoarthritis. Sci Transl Med. 2018;10(428):eaan0746. [12] ZHENG G, ZHAN Y, LI X, et al. TFEB, a potential therapeutic target for osteoarthritis via autophagy regulation. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(9):858. [13] ZHOU F, MEI J, HAN X, et al. Kinsenoside attenuates osteoarthritis by repolarizing macrophages through inactivating NF-kappaB/MAPK signaling and protecting chondrocytes. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2019;9(5):973-985. [14] GNANAPRAKASAM JN, AND WANG R. MYC in regulating immunity: metabolism and beyond. Genes (Basel). 2017;8(3):88. [15] WU YH, LIU W, ZHANG L, et al. Effects of microRNA-24 targeting C-myc on apoptosis, proliferation, and cytokine expressions in chondrocytes of rats with osteoarthritis via MAPK signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2018; 119(10):7944-7958. [16] RHEE J, PARK SH, KIM SK, et al. Inhibition of BATF/JUN transcriptional activity protects against osteoarthritic cartilage destruction. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017; 76(2):427-434. [17] RAMSEY HE, FISCHER MA, LEE T, et al. A novel MCL1 inhibitor combined with venetoclax rescues venetoclax-resistant acute myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Discov. 2018;8(12):1566-1581. [18] FATIMA LA, CAMPELLO RS, SANTOS RS, et al. Estrogen receptor 1 (ESR1) regulates VEGFA in adipose tissue. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):16716. [19] GUAN M, ZHU Y, LIAO B, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound inhibits VEGFA expression in chondrocytes and protects against cartilage degeneration in experimental osteoarthritis. FEBS Open Biol. 2020;10(3): 434-443. [20] DUCOUX M, URBACH S, BALDACCI G, et al. Mediation of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA)-dependent DNA replication through a conserved p21(Cip1)-like PCNA-binding motif present in the third subunit of human DNA polymerase delta. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(52):49258-49266. [21] GANG X, XU H, SI L, et al. Treatment effect of CDKN1A on rheumatoid arthritis by mediating proliferation and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 2018;194(2):220-230. [22] ROY R, HUANG Y, SECKL MJ, et al. Emerging roles of hnRNPA1 in modulating malignant transformation. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2017. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1431. [23] LI M, ZHUANG Y, BATRA R, et al. HNRNPA1-induced spliceopathy in a transgenic mouse model of myotonic dystrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(10):5472-5477. [24] GEE F, RUSHTON MD, LOUGHLIN J, et al. Correlation of the osteoarthritis susceptibility variants that map to chromosome 20q13 with an expression quantitative trait locus operating on NCOA3 and with functional variation at the polymorphism rs116855380. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67(11):2923-2932. [25] IEZAKI T, OZAKI K, FUKASAWA K, et al. ATF3 deficiency in chondrocytes alleviates osteoarthritis development. J Pathol. 2016;239(4):426-437. [26] MAO B, ZHANG Z, AND WANG G. BTG2: a rising star of tumor suppressors (review). Int J Oncol. 2015;46(2):459-464. [27] MELLOR L, KNUDSON CB, HIDA D, et al. Intracellular domain fragment of CD44 alters CD44 function in chondrocytes. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(36): 25838-25850. [28] HO LJ, HUNG LF, LIU FC, et al. Ginkgo biloba extract individually inhibits JNK activation and induces c-Jun degradation in human chondrocytes: potential therapeutics for osteoarthritis. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e82033. [29] SUI X, KONG N, YE L, et al. p38 and JNK MAPK pathways control the balance of apoptosis and autophagy in response to chemotherapeutic agents. Cancer Lett. 2014;344(2):174-179. [30] ZHU J, ZHENG Y, ZHANG H, et al. Galectin-1 induces metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in human ovarian cancer cells via activation of the MAPK JNK/p38 signalling pathway. Am J Transl Res. 2019; 11(6):3862-3878. |
| [1] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [2] | Zhang Jichao, Dong Yuefu, Mou Zhifang, Zhang Zhen, Li Bingyan, Xu Xiangjun, Li Jiayi, Ren Meng, Dong Wanpeng. Finite element analysis of biomechanical changes in the osteoarthritis knee joint in different gait flexion angles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1357-1361. |
| [3] | Wang Baojuan, Zheng Shuguang, Zhang Qi, Li Tianyang. Miao medicine fumigation can delay extracellular matrix destruction in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1180-1186. |
| [4] | Tang Wenjing, Wu Siyuan, Yang Chen, Tao Xi. Inflammatory responses in post-stroke depression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1278-1285. |
| [5] | Hu Wei, Xie Xingqi, Tu Guanjun. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve the integrity of the blood-spinal cord barrier after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 992-998. |
| [6] | Liu Dongcheng, Zhao Jijun, Zhou Zihong, Wu Zhaofeng, Yu Yinghao, Chen Yuhao, Feng Dehong. Comparison of different reference methods for force line correction in open wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 827-831. |
| [7] | Zhou Jianguo, Liu Shiwei, Yuan Changhong, Bi Shengrong, Yang Guoping, Hu Weiquan, Liu Hui, Qian Rui. Total knee arthroplasty with posterior cruciate ligament retaining prosthesis in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis with knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 892-897. |
| [8] | He Junjun, Huang Zeling, Hong Zhenqiang. Interventional effect of Yanghe Decoction on synovial inflammation in a rabbit model of early knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 694-699. |
| [9] | Lin Xuchen, Zhu Hainian, Wang Zengshun, Qi Tengmin, Liu Limin, Suonan Angxiu. Effect of xanthohumol on inflammatory factors and articular cartilage in a mouse mode of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 676-681. |
| [10] | Xu Lei, Han Xiaoqiang, Zhang Jintao, Sun Haibiao. Hyaluronic acid around articular chondrocytes: production, transformation and function characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 768-773. |
| [11] | Le Guoping, Zhang Ming, Xi Licheng, Luo Hanwen. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of vancomycin hydrochloride@polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer-chitosan-hyaluronic acid composite sustained-release microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 528-534. |
| [12] | Yang Feng, Zhao Qian, Zhang Shixuan, Zhao Tienan, Feng Bo. Effectiveness and safety of rapamycin combined with CD133 antibody stent in preventing vascular restenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 579-584. |
| [13] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [14] | Liu Shaohua, Zhou Guanming, Chen Xicong, Xiao Keming, Cai Jian, Liu Xiaofang. Changes in kinematic parameters after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty and high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 390-396. |
| [15] | Wang Chong, Zhang Meiying, Zhou Jian, Lao Kecheng. Early gait changes after total hip arthroplasty through direct anterior approach and posterolateral approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 359-364. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||