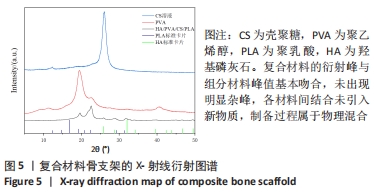
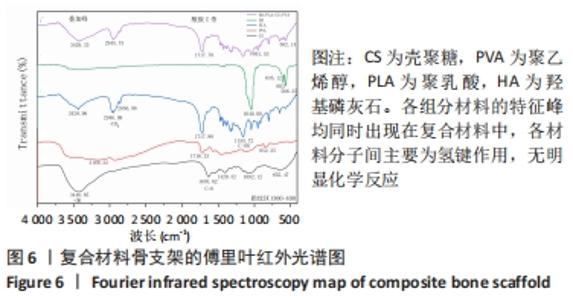
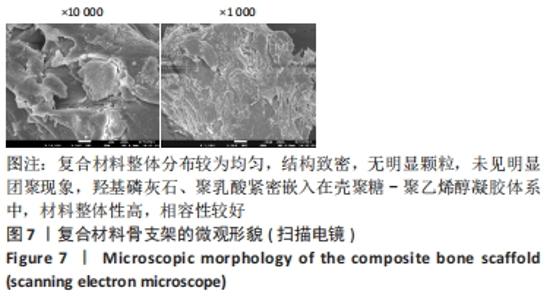
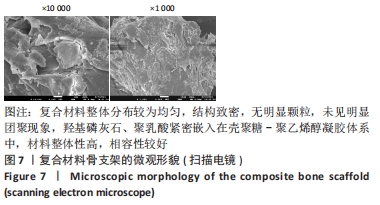
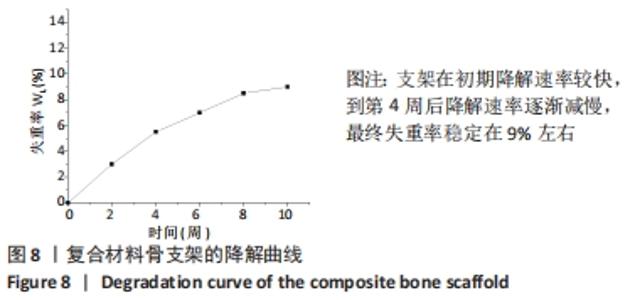
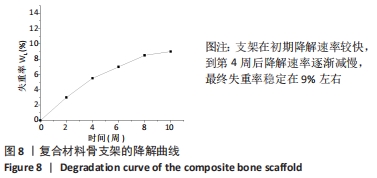
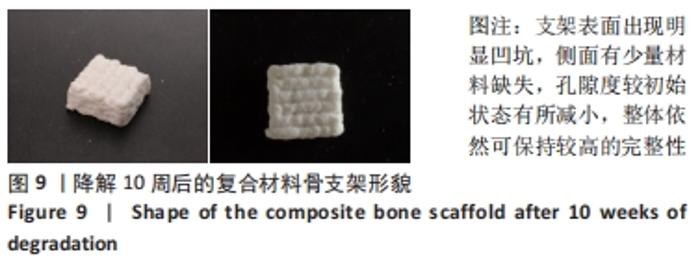
[1] BOZORGI A, SABOURI L. Osteosarcoma, personalized medicine, and tissue engineering; an overview of overlapping fields of research. Cancer Treat Res Commun. 2021;27:100324.
[2] 张健烽,刘云霞.骨肉瘤治疗的研究进展[J].浙江医学,2019,41(7): 723-727+730.
[3] 王凯,郑爽,潘肃,张恒,等.制备3D打印骨组织工程支架修复骨缺损的特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(34):5516-5522.
[4] REZWAN K, CHEN QZ, BLAKER JJ, et al. Biodegradable and bioactive porous polymer/inorganic composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2006;27(18):3413-3431
[5] 赵宝林,罗民,马洪顺.国人股骨下端松质骨力学性质实验研究[J].北京生物医学工程,2004,23(2):143-146.
[6] 龚明明,谭丽丽,杨柯.骨组织工程支架材料及其力学性能[J].材料导报,2007,21(10):43-46+54.
[7] SUN X, WANG T, GUO S. Applications of 3D printed bone tissue engineering scaffolds in the stem cell field. Regen Ther. 2021;16:63-72.
[8] 秦瑞冰,乌日开西·艾依提,滕勇.FDM式3D打印技术研究进展[J].制造技术与机床,2020(2):40-44.
[9] 王阮彬,程丽乾,陈凯.高分子材料在3D打印生物骨骼及支架中的应用与价值[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(4):636-643.
[10] 张旭婧. 3D同轴打印组织工程骨支架成型工艺与实验研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆大学,2017.
[11] 刘洋,王欢,朱晔,等.骨组织工程支架材料研究进展[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2019,35(10):637-639.
[12] 郑磊,崔慧斐.不同分子量和脱乙酰度壳聚糖用作组织工程材料的性质评价[J].中国生化药物杂志,2009,30(2):106-110.
[13] CAO W, JING D, LI J, et al. Effects of the Degree of Deacetylation on the Physicochemical Properties and Schwann Cell Affinity of Chitosan Films. J Biomater Appl. 2005;20(2):157-177.
[14] ANISH B, RAJAGOPAL R, HITOSHI S. Multifaceted Applications of Chitosan in Cancer Drug Delivery and Therapy. Mar Drugs. 2017;15(4):96.
[15] 熊敏剑,李晓峰,闵燕,等.不同脱乙酰度壳聚糖支架制备及降解性能评价[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2012,29(1):107-111.
[16] 康坤龙,王新涛.生物支架材料促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的研究热点[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(4):622-629.
[17] LI M, FU S, CAI Z, et al. Dual regulation of osteoclastogenesis and osteogenesis for osteoporosis therapy by iron oxide hydroxyapatite core/shell nanocomposites. Regen Biomater. 2021;8(5):rbab027. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbab027.
[18] 程思敏. HA/PLA复合材料的制备及其多孔支架成型工艺的研究[D].北京:清华大学,2017.
[19] 沈卫,顾燕芳,刘昌胜,等.羟基磷灰石的表面特性[J].硅酸盐通报, 1996(1):45-52.
[20] SHAN W, SHI K, HAO X, et al. Use 3D printing technology to prepare polylactic acid bone scaffold material and test its physical and chemical properties. SJISR. 2021;3(4):355-362.
[21] 宋颖,邓久鹏,张炜,等.聚乳酸支架材料复合改性的研究进展[J].生物医学工程研究,2020,39(4):431-434.
[22] 尹浩月.聚乳酸/纳米羟基磷灰石复合支架材料的制备与研究[D].唐山:华北理工大学,2019.
[23] 张利,李玉宝,魏杰,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖复合骨修复材料的共沉淀法制备及其性能表征[J].功能材料,2005,36(3):441-444.
[24] 赵秀娟.壳聚糖纤维/羟基磷灰石/聚乳酸三元复合材料的研究[D].广州:暨南大学,2011.
[25] 孙珍珍,蔡汝汝,蒲曦鸣,等.壳聚糖/羟基磷灰石复合骨修复材料的制备及细胞相容性初步研究[J].厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 2010,49(5):671-675.
[26] LALISA B, THANAWADEE L, RIYAJAN SA. Fabrication and physical properties of a novel macroporous poly(vinyl alcohol)/cellulose fibre product. Carbohyd Polym. 2020;240:116215.
[27] GUPTA S, WEBSTER TJ, SINHA A. Correction to: Evolution of PVA gels prepared without crosslinking agents as a cell adhesive surface. J Mater Sci-Mater M. 2020;31(8):63.
[28] 安田田,许燕,周建平,等.基于3D打印技术SF/PVA/HA复合骨支架的制备及表征[J].燕山大学学报,2021,45(5):409-414+423.
[29] 中国科学院数学研究所统计组.方差分析[M].北京:科学出版社, 1977.
[30] BURKHART J. Advanced Common Core Math Explorations: Probability and Statistics (Grades 5-8). New York:Taylor and Francis,2021.
[31] NAVEEN KUMAR HMP, PRABHAKAR MN, PRASAD CV, et al. Compatibility studies of chitosan/PVA blend in 2% aqueous acetic acid solution at 30 °C. Carohyd Polym. 2010;82(2):251-255.
[32] MI F, SHYU S, WU Y, et al. Fabrication and characterization of a sponge-like asymmetric chitosan membrane as a wound dressing. Elsevier. 2001;22(2):165-173.
[33] 卢晓英,王秀红,刘治,等.反应pH值对原位水热沉积法制备纳米羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖复合材料的影响[J].复合材料学报,2009,26(4): 53-58.
[34] 杨辉,张园园.壳聚糖分子对共沉淀法合成羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖粉体材料晶体形貌的影响[J].人工晶体学报,2012(1):215-220.
[35] LIU Y, WEI H, WANG Z, et al. Simultaneous Enhancement of Strength and Toughness of PLA Induced by Miscibility Variation with PVA. Polymers. 2018;10(10):1178.
[36] 潘育松. n-HA/PVA凝胶关节软骨修复材料制备与性能研究[D].南京:南京理工大学,2008.
|