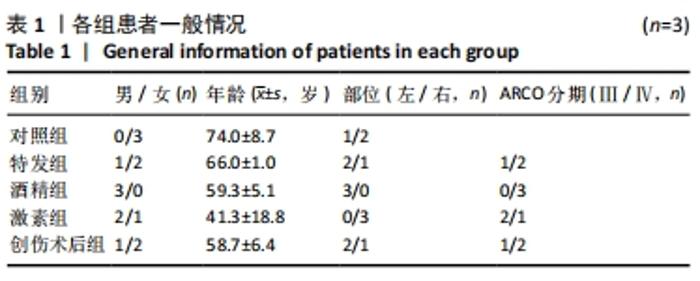
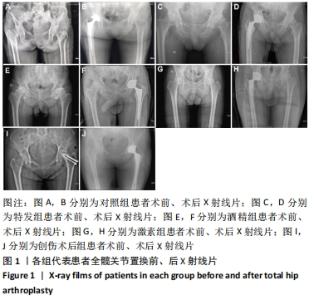
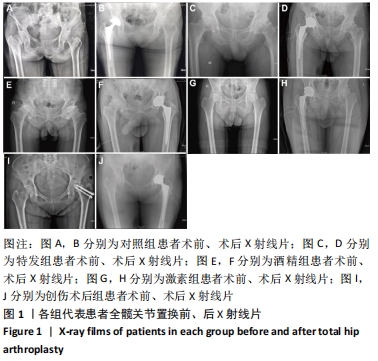
[1] 中国成人股骨头坏死临床诊疗指南(2020)[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2020, 40(20):1365-1376.
[2] MONT MA, SALEM HS, PIUZZI NS, et al. Nontraumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: Where Do We Stand Today? A 5-Year Update. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020;102(12): 1084-1099.
[3] 崔立强. 中国大陆地区股骨头坏死病因学调查及危险因素初步分析[D]. 北京:北京协和医学院,2014.
[4] 周占国, 郭浩山, 关涛, 等. 股骨头坏死病因的相关因素分析[J]. 中医正骨,2020,32(1):7-10.
[5] 王义生, 李劲峰. 股骨头坏死发病机制的研究现状与展望[J]. 中华实验外科杂志,2020,37(6):1001-1010.
[6] 梁学振. 补肾活血胶囊通过Hedgehog信号通路调控BMSCs成骨-成脂分化治疗激素性股骨头坏死的机制研究[D].济南:山东中医药大学,2019.
[7] 汪瑜, 熊德建, 罗梅懿, 等. 葛根素联合阿托伐他汀用药对激素性股骨头缺血性坏死Hedgehog信号通路的影响[J]. 四川医学,2019, 40(6):552-557.
[8] 中华医学会骨科分会显微修复学组, 中国修复重建外科专业委员会骨缺损及骨坏死学组. 成人股骨头坏死诊疗标准专家共识(2012年版)[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2012,32(6):606-610.
[9] 郑筱萸. 中药新药临床研究指导原则(试行)[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社,2002.
[10] 孙伟, 李子荣. 2019国际骨循环研究协会股骨头坏死分期[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2020,40(13):889-892.
[11] 中国医药生物技术协会生物样本库标准(试行)[J]. 中国医药生物技术,2011,6(1):71-79.
[12] 郑小龙, 何晓铭, 龚水帝, 等. 酒精性股骨头坏死患者的骨转换特点[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(5):657-661.
[13] 王荣田, 陈卫衡, 林娜, 等. 股骨头坏死的病因构成及发病特征分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2009,24(9):792-795.
[14] 晏涛, 郜玉忠. 非创伤性股骨头坏死与潜在关键基因表达谱的相关研究[J]. 暨南大学学报(自然科学与医学版),2018,39(3):198-207.
[15] KUBO T, UESHIMA K, SAITO M, et al. Clinical and basic research on steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in Japan. J Orthop Sci. 2016;21(4):407-413.
[16] 黄荣兰, 胡文彬, 詹庆昊. 中医药通过调控骨代谢相关信号通路治疗股骨头坏死的研究进展[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2021,27(8): 241-250.
[17] 李时斌, 赖渝, 周毅, 等. 激素性股骨头坏死发病机制及相关信号通路的靶点效应[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(6):935-941.
[18] 程继强,刘彬.激素性股骨头坏死的细胞生物学机制研究综述[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘(连续型电子期刊), 2019,19(35):77-78,81.
[19] 彭普基,龙林生,彭昊. 酒精性股骨头坏死的发病机制及治疗进展[J]. 医学综述,2021,27(4):637-642.
[20] 周龙涛, 韦标方, 任金钊, 等. 酒精性股骨头坏死发病机制的研究进展[J]. 风湿病与关节炎, 2015,4(4):67-71.
[21] 汪瑜, 熊德建, 罗梅懿, 等. 葛根素联合阿托伐他汀用药对激素性股骨头缺血性坏死Hedgehog信号通路的影响[J]. 四川医学,2019, 40(6):552-557.
[22] 李立东, 白俊清. 创伤性股骨头坏死的研究进展[J]. 中国煤炭工业医学杂志,2008,11(3):430-433.
[23] BOSE R, MOORS M, TOFIGHI R, et al. Glucocorticoids induce long-lasting effects in neural stem cells resulting in senescence-related alterations. Cell Death Dis. 2010;1(11):e92.
[24] 岳国阳. 骨肉瘤患者血清碱性磷酸酶和肿瘤特异性生长因子水平检测及其临床意义[J]. 肿瘤基础与临床,2020,33(3):239-241.
[25] 宋玉文, 李梅. Ⅰ型胶原蛋白代谢异常导致成骨不全症机制研究进展[J]. 中国实用内科杂志,2017,37(7):667-670.
[26] 陈伟健, 晋大祥, 谢炜星, 等. Runx2基因参与骨代谢相关通路的研究进展[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(4):557-560.
[27] YANG D, OKAMURA H, QIU L. Upregulated osterix expression elicited by Runx2 and Dlx5 is required for the accelerated osteoblast differentiation in PP2A Cα-knockdown cells. Cell Biol Int. 2018;42(4):403-410.
[28] SHICHAO T, JIMIN Y, JI L. Platelet-rich plasma has beneficial effects in mice with osteonecrosis of the femoral head by promoting angiogenesis. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(2):1781-1788.
[29] QUAN R, DU W, ZHENG X, et al. VEGF165 induces differentiation of hair follicle stem cells into endothelial cells and plays a role in in vivo angiogenesis. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(8):1593-1604.
[30] 张启栋, 岳聚安. 激素性股骨头坏死相关因子的研究进展[J]. 中日友好医院学报,2017,31(4):242-244.
[31] LI C, SHEN L, YANG Y, et al. Plasma ghrelin and von Willebrand Factor levels in patients with non-traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Hip Int. 2015;25(1):76-81.
[32] 李长有, 原银栋, 宋今丹. 血管内皮生长因子在骨折愈合中的自分泌作用[J]. 中华实验外科杂志,2005,22(11):107-108.
[33] 赵忠泽. 血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)及其受体在胶质瘤血管生成及侵袭中的作用[J]. 中国医药导报,2008,5(3):18-20.
[34] 徐练, 孔清泉. 调控成骨细胞分化及骨形成关键信号通路的研究进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2014,28(12):1484-1489.
[35] 迟博婧, 刘光源, 邢磊, 等. Hedgehog信号通路调控骨形成及BMSCs成骨分化的研究进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2016, 30(12):1545-1550.
|