Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (7): 1085-1092.doi: 10.12307/2022.149
Previous Articles Next Articles
Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke
Fang Xiaolei¹, Leng Jun², Zhang Chen¹, Liu Huimin¹, Guo Wen¹
- 1Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, Shandong Province, China; 2Second Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250001, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2021-04-26Revised:2021-04-27Accepted:2021-05-26Online:2022-03-08Published:2021-10-29 -
Contact:Leng Jun, Associate chief physician, Second Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250001, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Fang Xiaolei, Master candidate, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:Research Fund of National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. JDZX201915 (to LJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
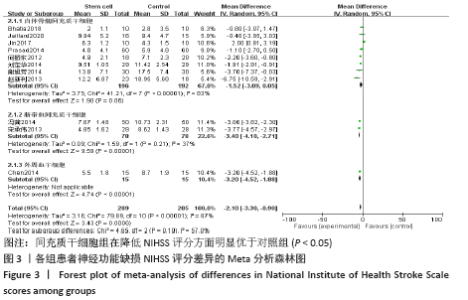
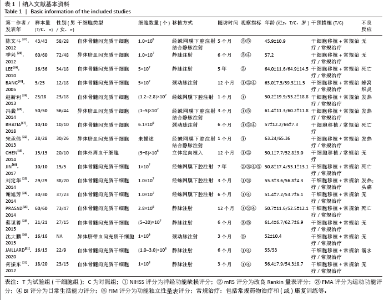
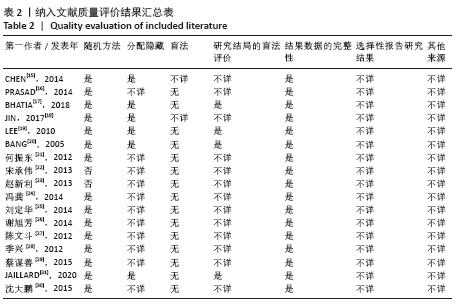
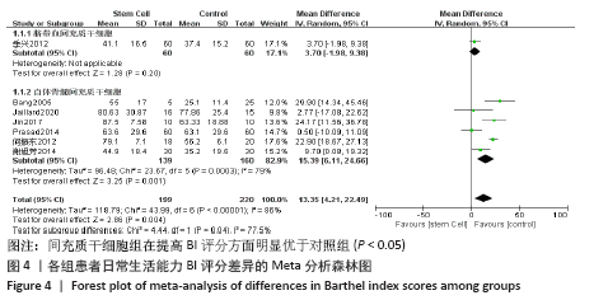
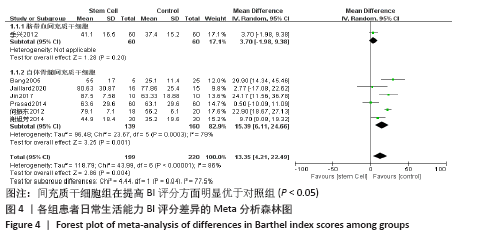
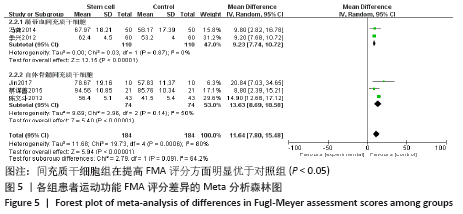
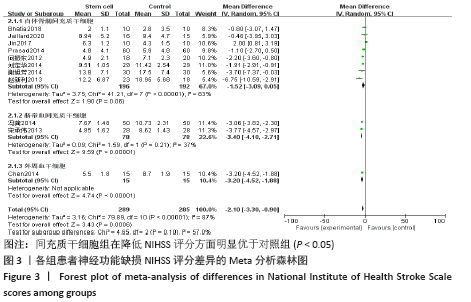
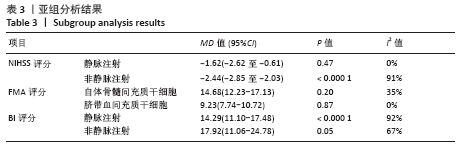
2.4 Meta分析结果 2.4.1 各组NIHSS评分差异 有11篇文献报道NIHSS作为结局指标[15-17,20-26,31],其中8项研究使用自体骨髓间充质干细胞[16-17,20-21,23,25-26,31],2项研究使用脐血间充质干细胞[22,24],1项研究使用外周血干细胞[15],Meta分析异质性检验结果显示:I2=87%,P < 0.00 001,提示有异质性,故采用随机效应模型,结果显示间充质干细胞组在降低NIHSS评分方面明显优于对照组(MD=-2.10,95%Cl:-3.30至-0.90,P < 0.000 01)。亚组分析显示,脐血间充质干细胞组和外周血干细胞移植组NIHSS评分均优于对照组(P < 0.000 01),见图3。"
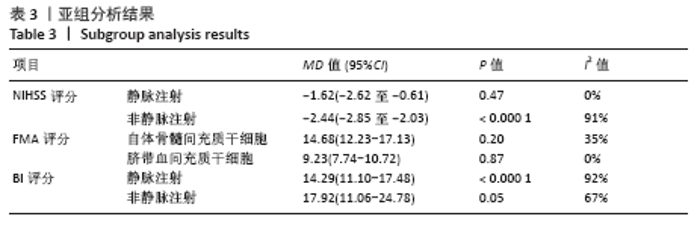
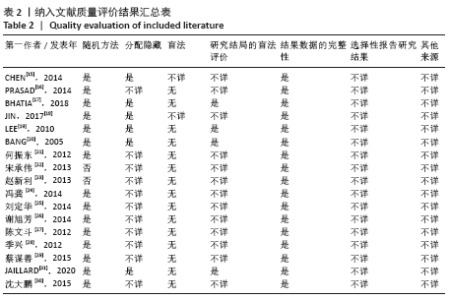
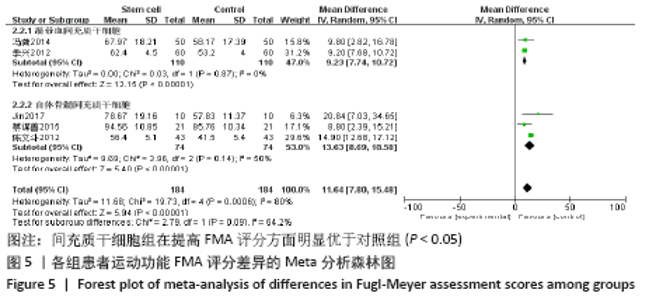
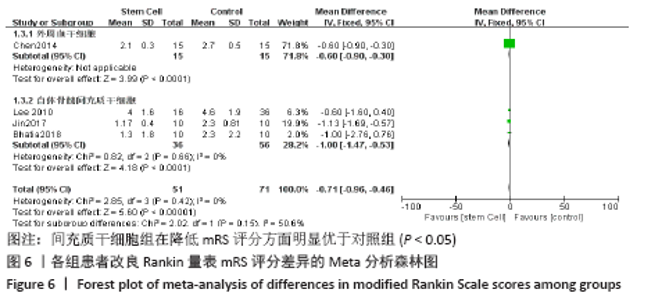
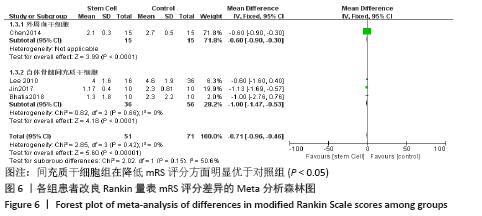
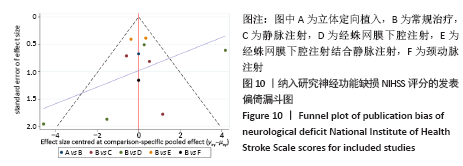
2.4.6 安全性评价结果 有4篇文献报告了死亡病例[16-19],为严重不良结局。异质性检验结果显示:I2=39%,P=0.18,提示异质性较小,Meta分析表明干细胞移植与死亡事件的发生之间差异无显著性意义(P=0.31),两者之间无直接联系。 刘定华等[25]报告术后3例患者出现发热,1例患者出现头痛;冯龚等[24]报告1例发热病例;宋承伟等[22]报告4例发热患者;赵新利等[23]报告1例发热;以上症状出现后均得到及时治疗,治疗后以上症状痊愈。JAILLARD等[31]报告1例患者出现溺水,与干细胞移植无关;BANG等[20]报告1例蜂窝织炎,但是由足癣引起,与干细胞移植无直接联系。 2.5 文献异质性分析结果 2.5.1 亚组分析结果 NIHSS评分的亚组分析显示,根据不同注射方式分组,静脉注射I2=0%,非静脉注射I2=61%,提示使用不同移植途径可能为异质性的来源。FMA评分的亚组分析显示,根据不同间充质干细胞分组,自体骨髓间充质干细胞I2=50%,脐血间充质干细胞I2=0%,可见使用不同间充质干细胞可能为异质性的来源。BI亚组分析显示,根据不同注射方式分组,静脉注射I2=67%,P=0.05;非静脉注射:I2=92%,P < 0.000 01,提示非静脉注射可能是异质性来源,但不能完全降低异质性,见表3。"

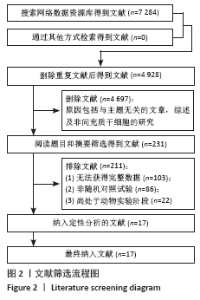
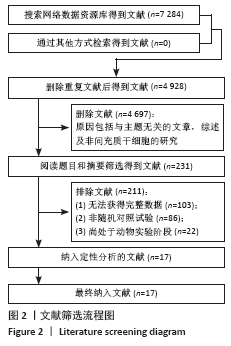
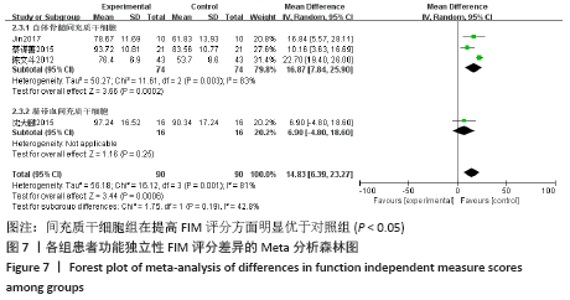
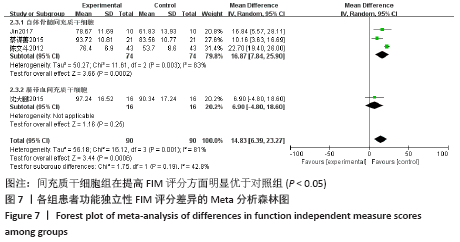
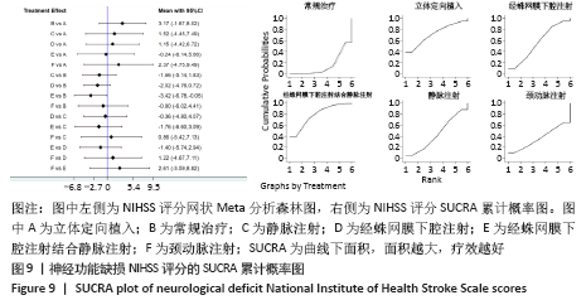
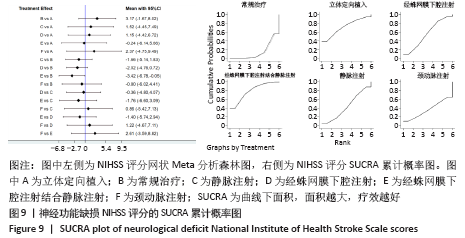
2.5.2 敏感性分析结果 针对FIM评分,尝试去除陈文斗等[27]的研究,异质性降到I2=0%,P=0.46,通过对该文献的认真剖析,发现异质性的来源可能与该文献质量较低有关。在剔除该研究后重新合并效应量,剔除前后合并结果未发生大的变化,剔除前合并效应量(MD=14.83,95%CI:6.39-23.27,P=0.000 6);剔除后合并效应量(MD=10.90,95%CI:5.82-15.99,P < 0.000 19) 。说明敏感性低,此meta分析结果稳健可信。 2.6 网状Meta分析结果 2.6.1 网状证据关系 纳入研究中有11项研究报道了NIHSS评分作为结局指标,网状Meta分析中有5种移植方式,分别是立体定向植入、静脉注射、颈动脉注射、经蛛网膜下腔注射、经蛛网膜下腔注射结合静脉注射和常规治疗(未移植)。此5种不同的移植方式和常规治疗未形成闭环,见图8。"

| [1] RICHARDS LG, CRAMER SC. Advances in stroke: therapies targeting stroke recovery. Stroke. 2021;52(1):348-350. [2] WANG W, JIANG B, SUN H, et al. Prevalence, incidence, and mortality of stroke in China: results from a nation wide population based survey of 480 687 adults. Circulation. 2017,135(8):759-771. [3] WU S, WU B, LIU M, et al. Stroke in China: advances and challenges in epidemiology, prevention, and management. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(4):394-405. [4] LI Z, PANDIAN J, SYLAJA PN, et al. Quality of care for ischemic stroke in China vs India: findings from national clinical registries. Neurology. 2018;91(14):e1348-e1354. [5] JOHNSON CO, NGUYEN M, ROTH GA, et al. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(5):439-458. [6] DETANTE O, MUIR K, JOLKKONEN J. Cell therapy in stroke-cautious steps towards a clinical treatment. Transl Stroke Res. 2018;9(4):321-332. [7] VAN VELTHOVEN CT, DZIETKO M, WENDLAND MF, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells attenuate MRI-identifiable injury, protect white matter, and improve long-term functional outcomes after neonatal focal stroke in rats. J Neurosci Res. 2017; 95(5):1225-1236. [8] OH SH, CHOI C, CHANG DJ, et al. Early neuroprotective effect with lack of long-term cell replacement effect on experimental stroke after intra-arterial transplantation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Cytotherapy. 2015;17(8):1090-1103. [9] LIAO W, XIE J, ZHONG J, et al. Therapeutic effect of human umbilical cord multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells in a rat model of stroke. Transplantation. 2009;87(3):350-359. [10] 朱尧,汪青松,黄海丽,等.脐带血间充质干细胞改善兔脑梗死神经生长因子和神经元凋亡的研究[J].中华老年心血管病杂志,2013,15(12):1316-1320. [11] HATANO S. Experience from a multicentre stroke register: a preliminary report. Bull World Health Organ. 1976;54(5):541-553. [12] 曾宪涛,包翠萍,曹世义,等.Meta分析系列之三:随机对照试验的质量评价工具[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2012, 4(3):183-185. [13] 文进,李幼平.Meta分析中效应尺度指标的选择[J].中国循证医学杂志,2007, 7(8):606-613. [14] 王丹,翟俊霞,牟振云,等.Meta分析中的异质性及其处理方法[J].中国循证医学杂志,2009,9(10):1115-1118. [15] CHEN DC, LIN SZ, FAN JR, et al. Intracerebral implantation of autologous peripheral blood stem cells in stroke patients: a randomized phase II study. Cell Transplant. 2014;23(12):1599-1612. [16] PRASAD K, SHARMA A, GARG A, et al. Intravenousautologous bone marrow mononuclear stem cell therapy for ischemic stroke:a multicentric, randomized trial. Stroke. 2014;45(12):3618-3624. [17] BHATIA V, GUPTA V, KHURANA D, et al. Randomized assessment of the safety and efficacy of intra-arterial infusion of autologous stem cells in subacute ischemic stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2018;39(5):899-904. [18] Jin YS, Ying L, Yu G, et al. Analysis of the long-term effect of bone marrow mononuclear cell transplantation for the treatment of cerebral infarction. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2017;10(2):3059-3068. [19] LEE JS, HONG JM, MOON GJ, et al. A long-term follow-up study of intravenous autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in patients with ischemic stroke. Stem Cells. 2010;28(6):1099-1106. [20] BANG OY, LEE JS, LEE PH, et al. Autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in stroke patients. Ann Neurol. 2005;57(6): 874-882. [21] 何振东.骨髓间充质干细胞移植改善脑梗死患者神经功能机制研究[J].亚太传统医药,2012,8(12):126-127. [22] 宋承伟,汪萍,胡晓琴,等.脐带血间充质干细胞移植治疗脑梗死的临床疗效观察[J].临床合理用药,2013,6(2):69-70. [23] 赵新利,王艳,张彩霞,等.骨髓间充质干细胞治疗在脑卒中的研究[J].环球中医药,2013,6(S2):157. [24] 冯龚,田国萍,李莉,等.人脐带血间充质干细胞治疗脑梗死的临床疗效研究[J].实用心脑肺血管病杂志,2014,22(1):28-30. [25] 刘定华,韩伯军,洪珊珊,等.自体骨髓间充质神经干细胞移植治疗脑梗死的疗效观察[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志, 2014,36(6):425-428. [26] 谢旭芳,刘诗英,金光华,等.自体骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗脑梗死的临床分析[J].检验医学与临床,2014,11(21):2955-2957. [27] 陈文斗,李江涛,张效北,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗脑梗死临床分析[J].吉林医学,2012,33(21):4522. [28] 季兴,赵和泰,张效北,等.间充质干细胞治疗老年中风患者60例临床分析[J].咸宁学院学报(医学版),2012,26(1):31-32. [29] 蔡谋善,沈春林,曾令海,等.干细胞移植对缺血性脑卒中患者血清同型半胱氨酸、CRP及BDNF含量影响研究[J].中国生化药物杂志,2015,35(9):91-93. [30] 沈大鹏.脐带间充质干细胞早期单次移植治疗对急性脑梗死的神经功能恢复[J].中国伤残医学,2015,23(2):26-28. [31] JAILLARD A, HOMMEL M, MOISAN A, et al. Autologous mesenchymal stem cells improve motor recovery in subacute ischemic stroke: a randomized clinical trial. Transl Stroke Res. 2020;11(5):910-923. [32] LINDVALL O, KOKAIA Z. Neurogenesis following stroke affecting the adult brain. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015;7(11): a019034. [33] RUAN L, WANG B, ZHUGE Q, et al. Coupling of neurogenesis and angiogenesis after ischemic stroke. Brain Res. 2015;1623:166-173. [34] FUJIOKA T, KANEKO N, AJIOKA I, et al. β1 integrin signaling promotes neuronal migration along vascular scaffolds in the post-stroke brain. EBioMedicine. 2017; 16:195-203. [35] SHENG GJ. The developmental basis of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSCs). BMC Dev Biol. 2015;15:44. [36] JIAO Y, LIU YW, CHEN WG, et al. Neuroregeneration and functional recovery after stroke: advancing neural stem cell therapy toward clinical application. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(1):80-92. [37] JIN YZ, LEE JH. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for bone regeneration. Clin Orthop Surg. 2018;10(3):271-278. [38] PITTENGER MF, DISCHER DE, PAULT BM, et al.Mesenchymal stem cell perspective: cell biology to clinical progress. NPJ Regen Med. 2019;4:22. [39] CHENG Z, WANG L, QU M,et al. Mesenchymal stem cells attenuate blood-brain barrier leakage after cerebral ischemia in mice. J Neuroinflammation. 2018;15(1):135. [40] HATAKEYAMA M, NINOMIYA I, KANAZAWA M. Angiogenesis and neuronal remodeling after ischemic stroke. Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(1):16-19. [41] KANAZAWA M, TAKAHASHI T, ISHIKAWA M, et al. Angiogenesis in the ischemic core: a potential treatment target? J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2019;39(5):753-769. [42] XIN H, KATAKOWSKI M, WANNG F, et al. MicroRNA cluster miR-17-92 cluster in exosomes enhance neuroplasticity and functional recovery after stroke in rats. Stroke. 2017;48(3):747-753. [43] VU Q, XIE K, ECKERT M, et al. Meta-analysis of preclinical studies of mesenchymal stromal cells for ischemic stroke. Neurology. 2014;82(14):1277-1286. [44] TOYOSHIMA A, YASUHARA T, DATE I. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for ischemic stroke. Acta Med Okayama. 2017;71(4):263-268. [45] 刘玉林,闵瑜,黄臻.骨髓间充质干细胞移植在缺血性脑卒中治疗中的应用研究进展[J].山东医药,2020,60(35):98-101. [46] TREMAIN N, KORKKO J, IBBERSON D, et al. Micro SAGE analysis of 2,353 expressed genes in a single cell-derived colony of undifferentiated human mesenchymal stem cells reveals mRNAs of multiple cell lineages. Stem Cells. 2001;19(5):408-418. [47] 安阳方,曹建华,汤永红.间充质干细胞来源外泌体在缺血性脑卒中的研究进展[J]. 中南医学科学杂志,2019,47(4):442-445. [48] NAKANO M, FUJIMIYA M. Potential effects of mesenchymal stem cell derived extracellular vesicles and exosomal miRNAs in neurological disorders. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(12):2359-2366. |
| [1] | Zhao Jing, Liu Xiaobo, Zhang Yue, Zhang Jiaming, Zhong Dongling, Li Juan, Jin Rongjiang. Visualization analysis of neuromuscular electrical stimulation therapy based on CiteSpace: therapeutic effects, hot spots, and developmental trends [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1290-1297. |
| [2] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1316-1322. |
| [3] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1323-1329. |
| [4] | Tang Wenjing, Wu Siyuan, Yang Chen, Tao Xi. Inflammatory responses in post-stroke depression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1336-1344. |
| [5] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [6] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [7] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [8] | Wang Jifang, Bao Zhen, Qiao Yahong. miR-206 regulates EVI1 gene expression and cell biological behavior in stem cells of small cell lung cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1027-1031. |
| [9] | Liu Feng, Peng Yuhuan, Luo Liangping, Wu Benqing. Plant-derived basic fibroblast growth factor maintains the growth and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1032-1037. |
| [10] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [11] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [12] | Luo Xiaoling, Zhang Li, Yang Maohua, Xu Jie, Xu Xiaomei. Effect of naringenin on osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1051-1056. |
| [13] | Wang Xinmin, Liu Fei, Xu Jie, Bai Yuxi, Lü Jian. Core decompression combined with dental pulp stem cells in the treatment of steroid-associated femoral head necrosis in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1074-1079. |
| [14] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [15] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||