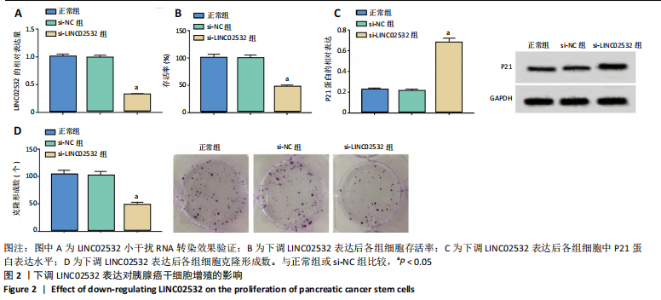
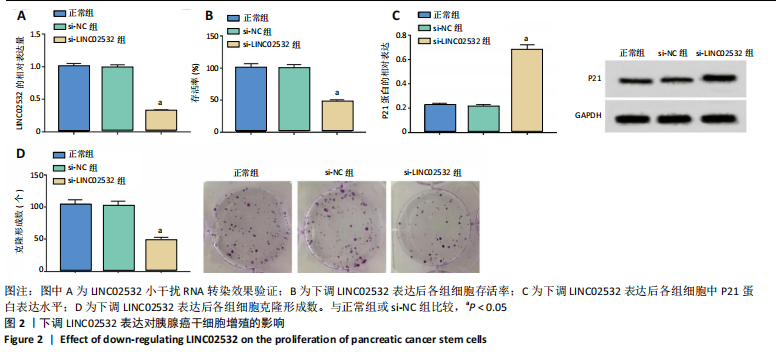
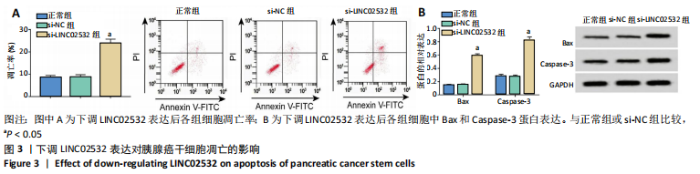
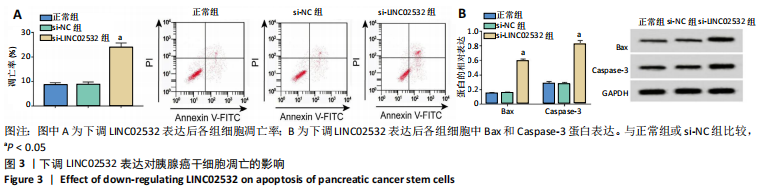
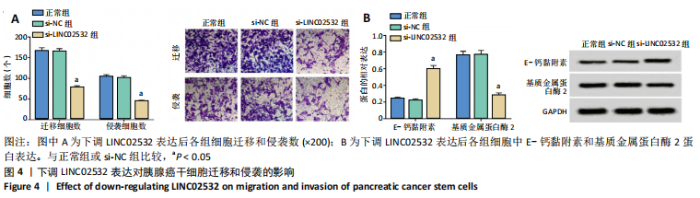
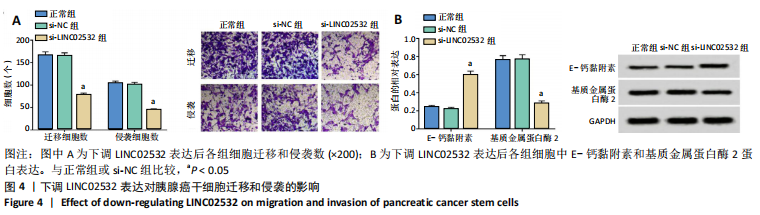
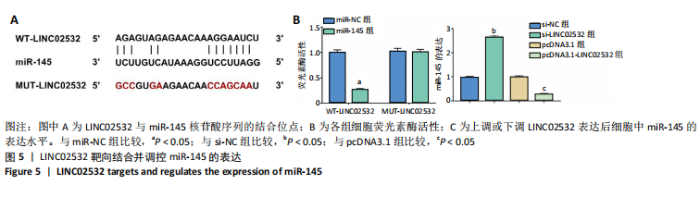
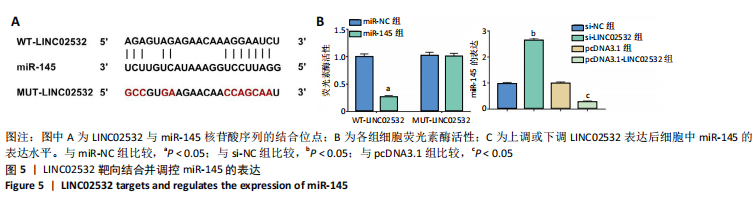
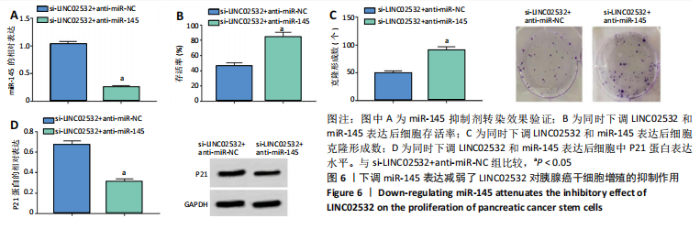
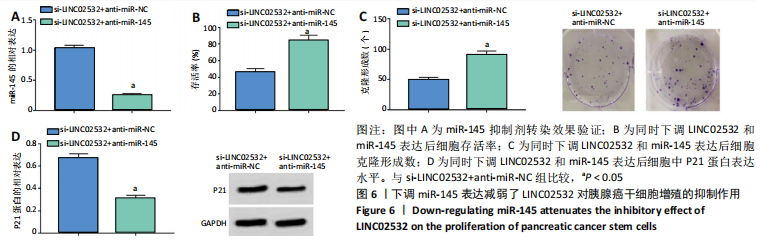
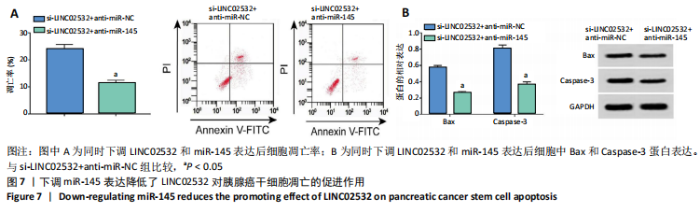
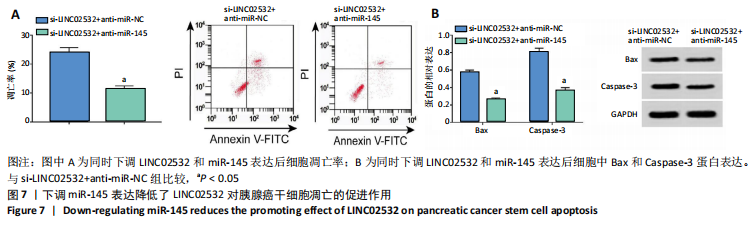
[1] 王冰一,施宝民.外泌体在胰腺癌中的研究进展[J].中华实验外科杂志,2019,36(4):779-782.
[2] 蔡尚党,蔡满地,娄宁,等. miR-15家族促进CD133+胰腺癌干样细胞的迁移和侵袭[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(21):3316-3321.
[3] 张明辉,樊玉霞,卢秀波.抑癌基因第10号染色体上缺失与张力蛋白同源的磷酸酯酶基因对人甲状腺乳头状癌细胞株生物学行为的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志,2019,36(4):632-634.
[4] THIN KZ, LIU X, FENG X, et al. LncRNA-DANCR: A valuable cancer related long non-coding RNA for human cancers. Pathol Res Pract. 2018; 214(6): 801-805.
[5] LI Y, YAN X, SHI J, et al. Aberrantly expressed miR-188-5p promotes gastric cancer metastasis by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. BMC Cancer. 2019;19(1):505.
[6] JING N, HUANG T, GUO H, et al. LncRNA CASC15 promotes colon cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by regulating the miR‑4310/LGR5/Wnt/β‑catenin signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2018;18(2):2269-2276.
[7] ZHANG C, MA MH, LIANG Y, et al. Novel long non-coding RNA LINC02532 promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in vitro. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2019;11(2):91-101.
[8] WANG H, HANG C, OU XL, et al. MiR-145 functions as a tumor suppressor via regulating angiopoietin-2 in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2016;16(1):65.
[9] 陈锦鹏,王志伟,陆玉华,等.人胰腺癌肿瘤干细胞体外增殖及耐药的研究[J].江苏医药,2013,39(18):2129-2131.
[10] LI D, ZHANG X, YANG Y, et al. Long non-coding RNA SNHG1 promotes Cyclin D1-mediated proliferation in pancreatic cancer by acting as a ceRNA of miR-195. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019;12(3):730-739.
[11] XU DF, WANG LS, ZHOU JH. Long non‑coding RNA CASC2 suppresses pancreatic cancer cell growth and progression by regulating the miR‑24/MUC6 axis. Int J Oncol. 2020;56(2):494-507.
[12] KIM EM, JUNG CH, KIM J, et al. The p53/p21 Complex Regulates Cancer Cell Invasion and Apoptosis by Targeting Bcl-2 Family Proteins. Cancer Res. 2017;77(11):3092-3100.
[13] HAMIVAND Z, HADDADI G, FARDID R. Expression of Bax and Bcl2 Genes in Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes of Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. J Med Phys. 2018;43(1):41-45.
[14] WANG W, ZHU M, XU Z, et al. Ropivacaine promotes apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through damaging mitochondria and activating caspase-3 activity. Biol Res. 2019;52(1):36-47.
[15] KUNTE M, DESAI K. The Protein Extract of Chlorella minutissima Inhibits The Expression of MMP-1, MMP-2 and MMP-9 in Cancer Cells through Upregulation of TIMP-3 and Down Regulation of c-Jun. Cell J. 2018;20(2):211-219.
[16] JANG M, KOH I, LEE JE, et al. Increased extracellular matrix density disrupts E-cadherin/β-catenin complex in gastric cancer cells. Biomater Sci. 2018;6(10):2704-2713.
[17] LI Q, YU X, YANG L. MiR-145 inhibits cervical cancer progression and metastasis by targeting WNT2B by Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019;12(10):3740-3751.
[18] LIU L, ZHANG Y, WANG J, et al. Long non-coding RNA CASC9 knockdown inhibits the progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by regulating miR-145. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019;12(11):4024-4033.
[19] QIAN C, WANG B, ZOU Y, et al. MicroRNA 145 enhances chemosensitivity of glioblastoma stem cells to demethoxycurcumin. Cancer Manag Res. 2019;11:6829-6840.
[20] ZHOU X, YUE Y, WANG R, et al. MicroRNA-145 inhibits tumorigenesis and invasion of cervical cancer stem cells. Int J Oncol. 2017;50(3):853-862.
|