Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (28): 4539-4545.doi: 10.12307/2021.070
Previous Articles Next Articles
Role and characteristics of tissue-engineered cartilage in the treatment of growth plate injuries
Wang Xianggang, Wan Qian, Liu He, Li Ronghang, Zhang Yan, Li Zuhao, Wang Jincheng
- Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130041, Jilin Province, China
-
Received:2020-10-15Revised:2020-10-17Accepted:2020-11-25Online:2021-10-08Published:2021-05-21 -
Contact:Wang Jincheng, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130041, Jilin Province, China Li Zuhao, PhD, Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130041, Jilin Province, China -
About author:Wang Xianggang, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130041, Jilin Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82001971 (to LH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Xianggang, Wan Qian, Liu He, Li Ronghang, Zhang Yan, Li Zuhao, Wang Jincheng. Role and characteristics of tissue-engineered cartilage in the treatment of growth plate injuries[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(28): 4539-4545.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
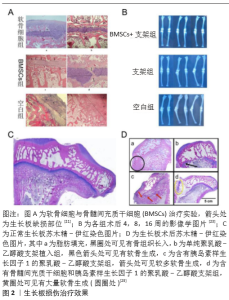
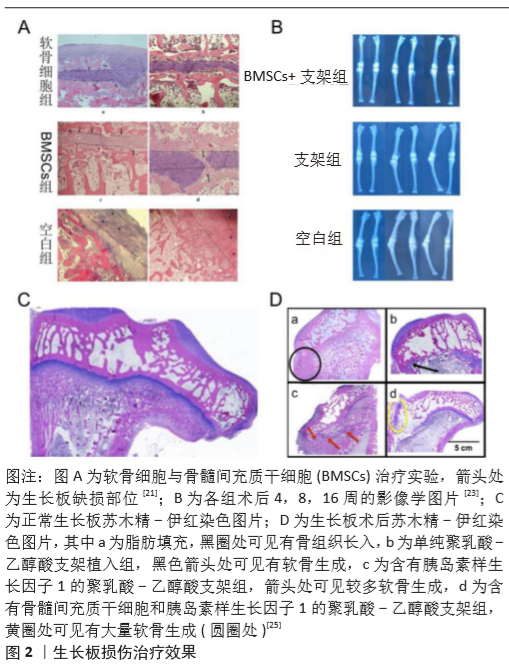
在治疗生长板损伤实验时,骨髓间充质干细胞的表现优异。GULTEKIN等[21]将骨髓间充质干细胞细胞薄层植入家兔胫骨近端生长板缺损处,结果发现骨髓间充质干细胞能够有效抑制受损生长板的骨化,并促进长骨继续生长,见图2A。虽然单纯的骨髓间充质干细胞植入有一定的效果,但是由于生长板损伤处再生微环境较差,治疗效果有限,加入支架和活性物质提供支撑和再生微环境,效果会更好[6]。AZARPIRA等[26]通过切除家兔股骨远端50%的生长板进行造模,在壳聚糖支架上加入骨髓间充质干细胞并将复合支架植入缺损处,3个月后,空白对照组有骨桥形成,提示造模成功;而相比于仅植入壳聚糖支架组,支架与骨髓间充质干细胞细胞结合组的患肢成角畸形明显减轻,显示骨髓间充质干细胞与支架结合能更好地治疗缺损。LI等[23]使用生长板细胞外基质制备的支架搭载自体骨髓间充质干细胞植入家兔生长板缺损处,4,8和16周影像学结果显示,对比空白对照组和单纯支架植入组,含有骨髓间充质干细胞的治疗组家兔患肢成角畸形明显减轻,如图2B。更进一步的研究显示,加入软骨分化诱导因子后,通过定向诱导骨髓间充质干细胞的分化可以更有针对性地治疗软骨类损伤。CLARK等[25]通过使用胰岛素样生长因子1作为活性物质定向诱导骨髓间充质干细胞的分化,以聚乳酸-乙醇酸支架作为载体,植入家兔生长板骨桥形成处,结果显示相较于空白支架组和胰岛素样生长因子1支架组,加入了骨髓间充质干细胞和胰岛素样生长因子1的支架组更好地减轻了患肢畸形,并且组织染色分析显示有更多的新生软骨细胞形成,预示着临床应用时在支架和诱导因子的作用下,骨髓间充质干细胞能更好地治愈生长板损伤,见图2C,D。"
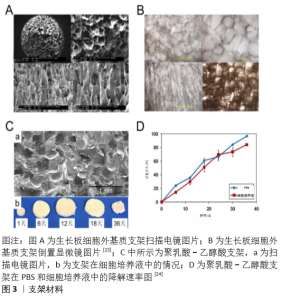
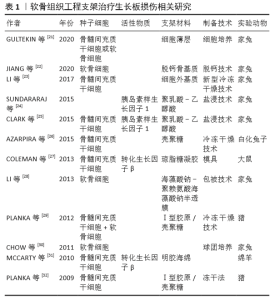
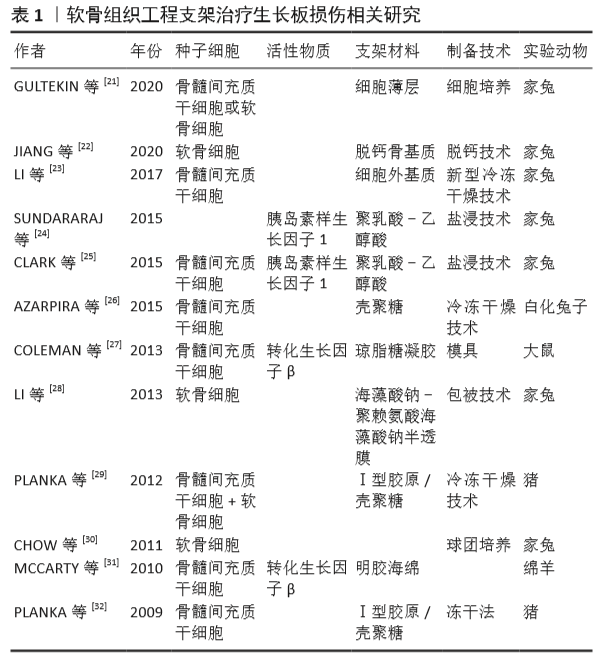
2.3.1 天然材料 天然材料一般由动物体内分离纯化获得,生物相容性较好,能够为植入细胞提供适宜的再生微环境。最典型的天然材料是生长板处获得的细胞外基质,LI等[23]将生长板切除分离,经过去细胞化得到主要成分为Ⅱ型胶原和糖胺聚糖的细胞外基质,再通过冷冻干燥法制备成支架,实验结果证实这种细胞外基质支架具有一定的孔隙结构,见图3A,B。 2.3.2 合成材料 虽然天然生物材料能更好地模拟软骨组织微环境,但是来源有限且制成的支架支撑强度不够,而人工合成的超分子聚合物却能够提供足够的力学强度,并且来源广泛、价格低廉,已被大量应用在软骨组织工程之中[58-59]。在合成高分子中,聚乳酸-乙醇酸能够在体内相关酶作用下通过正常代谢途径被降解为乳酸和乙醇酸[60-61],是美国食品药品监督管理局批准的药物载体,见图3C,D。 "

| [1] RACINE HL, SERRAT MA. The Actions of IGF-1 in the Growth Plate and Its Role in Postnatal Bone Elongation. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2020; 18(3):210-227. [2] AGIRDIL Y. The growth plate: a physiologic overview. EFORT Open Rev. 2020;5(8):498-507. [3] MATSUSHITA Y, ONO W, ONO N. Growth plate skeletal stem cells and their transition from cartilage to bone. Bone. 2020;136:115359. [4] HUNZIKER EB. Elongation of the Long Bones in Humans by the Growth Plates. Nestle NutrInst Workshop Ser. 2018;89:13-23. [5] MIZUHASHI K, ONO W, MATSUSHITA Y, et al. Resting zone of the growth plate houses a unique class of skeletal stem cells. Nature. 2018;563 (7730):254-258. [6] SHAW N, ERICKSON C, BRYANT SJ, et al. Regenerative Medicine Approaches for the Treatment of Pediatric Physeal Injuries. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2018;24(2):85-97. [7] EID AM, HAFEZ MA. Traumatic injuries of the distal femoral physis.Retrospective study on 151 cases.Injury. 2002;33(3):251-255. [8] 陈劲松,王中汉,常非,等.多种特殊状态下关节软骨缺损修复的组织工程技术[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(8):1272-1279. [9] SALTER RB, HARRIS WR. Injuries involving the epiphyseal plate. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83a(11):1753-1753. [10] SYURAHBIL AH, MUNAJAT I, MOHD EF, et al. Displaced Physeal and Metaphyseal Fractures of Distal Radius in Children. Can Wire Fixation Achieve Better Outcome at Skeletal Maturity than Cast Alone? Malays Orthop J. 2020;14(2):28-38. [11] BELLAMY JT, WARD LA, FLETCHER ND. Evaluation of pediatric distal femoral physeal fractures and the factors impacting poor outcome requiring further corrective surgery. J PediatrOrthop B. 2020. doi: 10.1097/BPB.0000000000000733. [12] STENROOS A, PUHAKKA J, JALKANEN J, et al. Risk of premature physeal closure in fractures of distal tibia. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2020. doi: 10.1097/BPB.0000000000000744. [13] SHALABY-RANA E, HINDS TS, DEYE K, et al. Proximal femoral physeal fractures in children: a rare abusive injury. PediatrRadiol. 2020;50(8): 1115-1122. [14] BADINA A, VIALLE R, FITOUSSI F, et al. Case reports: Treatment of traumatic triradiate cartilage epiphysiodesis: what is the role of bridge resection? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(11):3701-3705. [15] DAS P, SINGH YP, MANDAL BB, et al. Tissue-derived decellularized extracellular matrices toward cartilage repair and regeneration. Methods Cell Biol. 2020;157:185-221. [16] UZ U, GUNHAN K, VATANSEVER S, et al. Novel Simple Strategy for Cartilage Tissue Engineering Using Stem Cells and Synthetic Polymer Scaffold. J Craniofac Surg. 2019;30(3):940-943. [17] CHEN L, LIU J, GUAN M, et al. Growth Factor and Its Polymer Scaffold-Based Delivery System for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:6097-6111. [18] MATAI I, KAUR G, SEYEDSALEHI A, et al. Progress in 3D bioprinting technology for tissue/organ regenerative engineering. Biomaterials. 2020;226:119536. [19] ZHAO ZY, FAN CJ, CHEN F, et al. Progress in Articular Cartilage Tissue Engineering: A Review on Therapeutic Cells and Macromolecular Scaffolds. Macromol Biosci. 2020;20(2):1900278. [20] SABHARWAL S, SABHARWAL S. Growth Plate Injuries of the Lower Extremity: Case Examples and Lessons Learned. Indian J Orthop. 2018;52(5):462-469. [21] GULTEKIN A, AGIRDIL Y, ONCEL DUMAN B, et al. Comparison of mesenchymal stem cell sheets and chondrocyte sheets in a rabbit growth plate injury model. Turk J Med Sci. 2020;50(4):1082-1096. [22] JIANG F, QIAO F, HU H, et al. Early Closure of Growth Plate Due to Avascular Necrosis of the Femoral Head After Displaced Fracture of the Femoral Neck in Children. Nanosci Nanotech Let. 2020;12(1):34-38. [23] LI WC, XU RJ, HUANG JX, et al. Treatment of rabbit growth plate injuries with oriented ECM scaffold and autologous BMSCs. Sci Rep. 2017;7:44140. [24] SUNDARARAJ SKC, CIEPLY RD, GUPTA G, et al. Treatment of growth plate injury using IGF-I-loaded PLGA scaffolds. J Tissue EngRegen Med. 2015;9(12):E202-E209. [25] CLARK A, HILT JZ, MILBRANDT TA, et al. Treating Proximal Tibial Growth Plate Injuries Using Poly(Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid) Scaffolds. Biores Open Access. 2015;4(1):65-74. [26] AZARPIRA MR, SHAHCHERAGHI GH, AYATOLLAHI M, et al. Tissue engineering strategy usingmesenchymal stem cell-based chitosan scafolds in growth plate surgery: a preliminary study in rabbits. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015;101(5):601-605. [27] COLEMAN RM, SCHWARTZ Z, BOYAN BD, et al. The Therapeutic Effect of Bone Marrow-Derived Stem Cell Implantation After Epiphyseal Plate Injury Is Abrogated by Chondrogenic Predifferentiation. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(3-4):475-483. [28] LI WC, XU RJ, XUE YL, et al. Treatment of growth plate injury with microencapsulated chondrocytes.Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng. 2013; 18(4):655-662. [29] PLANKA L, SRNEC R, RAUSER P, et al. Nanotechnology and mesenchymal stem cells with chondrocytes in prevention of partial growth plate arrest in pigs. Biomed Pap Med FacUnivPalacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2012;156(2):128-134. [30] CHOW SKH, LEE KM, QIN L, et al. Restoration of longitudinal growth by bioengineered cartilage pellet in physeal injury is not affected by low intensity pulsed ultrasound. J Biomed Mater Res B ApplBiomater. 2011;99(1):36-44. [31] MCCARTY RC, XIAN CJ, GRONTHOS S, et al. Application of autologous bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells to an ovine model of growth plate cartilage injury. Open Orthop J. 2010;4:204-210. [32] PLANKA L, STARY D, HLUCILOVA J, et al. Comparison of Preventive and Therapeutic Transplantations of Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Healing of the Distal Femoral Growth Plate Cartilage Defects in Miniature Pigs. Acta Vet Brno. 2009;78(2):293-U122. [33] CHOI JR, YONG KW, CHOI JY. Effects of mechanical loading on human mesenchymal stem cells for cartilage tissue engineering. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(3):1913-1928. [34] ISOBE Y, KOYAMA N, NAKAO K, et al. Comparison of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow, synovial fluid, adult dental pulp, and exfoliated deciduous tooth pulp. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016;45(1):124-131. [35] KHALILIFAR MA, ESLAMINEJAD MB, GHASEMZADEH M, et al. In Vitro and In Vivo Comparison of Different Types of Rabbit Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Cartilage Repair. Cell J. 2019;21(2):150-160. [36] CONTENTIN R, DEMOOR M, CONCARI M, et al. Comparison of the Chondrogenic Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from Bone Marrow and Umbilical Cord Blood Intended for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2020;16(1):126-143. [37] CARON MM, EMANS PJ, COOLSEN MM, et al. Redifferentiation of dedifferentiated human articular chondrocytes: comparison of 2D and 3D cultures. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(10):1170-1178. [38] HAMAMOTO S, CHIJLMATSU R, SHIMOMURA K, et al. Enhancement of chondrogenic differentiation supplemented by a novel small compound for chondrocyte-based tissue engineering. J Exp Orthop. 2020;7(1):10. [39] LEE SU, LEE JY, JOO SY, et al. Transplantation of a Scaffold-Free Cartilage Tissue Analogue for the Treatment of Physeal Cartilage Injury of the Proximal Tibia in Rabbits. Yonsei Med J. 2016;57(2):441-448. [40] TOMASZEWSKI R, BOHOSIEWICZ J, GAP A, et al. Autogenous cultured growth plate chondrocyte transplantation in the treatment of physeal injury in rabbits. Bone Joint Res. 2014;3(11):310-316. [41] CHEN MJ, WHITELEY JP, PLEASE CP, et al. Inducing chondrogenesis in MSC/chondrocyte co-cultures using exogenous TGF-β: a mathematical model. J Theor Biol. 2018;439:1-13. [42] THIELEN NGM, VAN DER KRAAN PM, VAN CAAM APM.TGFbeta/BMP Signaling Pathway in Cartilage Homeostasis.Cells. 2019;8(9):969. [43] GRAFE I, ALEXANDEr S, PETERSON JR, et al. TGF-beta Family Signaling in Mesenchymal Differentiation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018; 10(5):a022202. [44] ROTHWEILER R, BASOLI V, DUTTENHOEFER F, et al. Predicting and Promoting Human Bone Marrow MSC Chondrogenesis by Way of TGFbeta Receptor Profiles: Toward Personalized Medicine. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:618. [45] WANG W, RIGUEUR D, LYONS KM. TGFbeta as a gatekeeper of BMP action in the developing growth plate.Bone. 2020;137:115439. [46] CHEN X, ZHANG RH, ZHANG Q, et al. Microtia patients: Auricular chondrocyte ECM is promoted by CGF through IGF-1 activation of the IGF-1R/PI3K/AKT pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(12):21817-21824. [47] HEILIG J, PAULSSON M, ZAUCKE F. Lack of the chondrocyte IGF-I receptor leads to perinatal death and alterations in extracellular matrix protein expression in vitro. Bone. 2012;50:S64-S64. [48] LUI JC, NILSSON O, BARON J. Recent research on the growth plate: Recent insights into the regulation of the growth plate. J MolEndocrinol. 2014;53(1):T1-T9. [49] COLEMAN RM, CASE ND, GULDBERG RE. Hydrogel effects on bone marrow stromal cell response to chondrogenic growth factors. Biomaterials. 2007;28(12):2077-2086. [50] CUNNIFFE GM, DIAZ-PAYNO PJ, RAMEY JS, et al. Growth plate extracellular matrix-derived scaffolds for large bone defect healing. Eur Cell Mater. 2017;33:130-142. [51] SINGH YP, BHARDWAJ N, MANDAL BB. Potential of Agarose/Silk Fibroin Blended Hydrogel for in Vitro Cartilage Tissue Engineering. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(33):21236-21249. [52] BONHOME-ESPINOSA AB, CAMPOS F, DURAND-HERRERA D, et al.In vitro characterization of a novel magnetic fibrin-agarose hydrogel for cartilage tissue engineering. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2020; 104:103619. [53] CHEN F, HUI JH, CHAN WK, et al. Cultured mesenchymalstem cell transfers in the treatment of partial growth arrest. J Pediatr Orthop. 2003;23(4):425-429. [54] CAMPOS F, BONHOME-ESPINOSA AB, CHATO-ASTRAIN J, et al. Evaluation of Fibrin-Agarose Tissue-Like Hydrogels Biocompatibility for Tissue Engineering Applications. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:596. [55] SHAMEKHI MA, RABIEE A, MIRZADEH H, et al. Fabrication and characterization of hydrothermal cross-linked chitosan porous scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;80:532-542. [56] [56]DEHGHAN-BANIANI D, CHEN Y, WANG D, et al. Injectable in situ forming kartogenin-loaded chitosan hydrogel with tunable rheological properties for cartilage tissue engineering. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020;192:111059. [57] SADEGHIANMARYAN A, NAGHIEH S, SARDROUD HA, et al. Extrusion-based printing of chitosan scaffolds and their in vitro characterization for cartilage tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;164:3179-3192. [58] WEI P, XU Y, GU Y, et al. IGF-1-releasing PLGA nanoparticles modified 3D printed PCL scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering. Drug Deliv. 2020;27(1):1106-1114. [59] CHOU SF, WOODROW KA. Relationships between mechanical properties and drug release from electrospun fibers of PCL and PLGA blends. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2017;65:724-733. [60] ABID Z, DALSKOV MOSGAARD M, MANFRONI G, et al. Investigation of Mucoadhesion and Degradation of PCL and PLGA Microcontainers for Oral Drug Delivery. Polymers (Basel). 2019;11(11):1828. [61] MACHATSCHEK R, LENDLEIN A. Fundamental insights in PLGA degradation from thin film studies. J Control Release. 2020;319:276-284. [62] STEFANI RM, LEE AJ, TAN AR, et al. Sustained low-dose dexamethasone delivery via a PLGA microsphere-embedded agarose implant for enhanced osteochondral repair. Acta Biomater. 2020;102:326-340. [63] BOUKARI Y, QUTACHI O, SCURR DJ, et al.A dual-application poly (dl-lactic-co-glycolic) acid (PLGA)-chitosan composite scaffold for potential use in bone tissue engineering. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2017;28(16):1966-1983. [64] 赵守军,熊文化,许柯.细胞因子基因转染的骨骺干细胞复合明胶-硫酸软骨素-透明质酸钠支架修复大鼠骨骺生长板缺损的实验研究[J].中医正骨,2018,30(2):10-15. [65] 徐真然,罗飞宏.生长板的局部调控新进展[J].医学综述,2018, 24(19):3772-3776. |
| [1] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [2] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [3] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [4] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [5] | Wang Debin, Bi Zhenggang. Related problems in anatomy mechanics, injury characteristics, fixed repair and three-dimensional technology application for olecranon fracture-dislocations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [6] | Wu Xun, Meng Juanhong, Zhang Jianyun, Wang Liang. Concentrated growth factors in the repair of a full-thickness condylar cartilage defect in a rabbit [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1166-1171. |
| [7] | Li Jiacheng, Liang Xuezhen, Liu Jinbao, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Differential mRNA expression profile and competitive endogenous RNA regulatory network in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1212-1217. |
| [8] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [9] | Ji Zhixiang, Lan Changgong. Polymorphism of urate transporter in gout and its correlation with gout treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1290-1298. |
| [10] | Yuan Mei, Zhang Xinxin, Guo Yisha, Bi Xia. Diagnostic potential of circulating microRNA in vascular cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1299-1304. |
| [11] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [12] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [13] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [14] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [15] | Zou Gang, Xu Zhi, Liu Ziming, Li Yuwan, Yang Jibin, Jin Ying, Zhang Jun, Ge Zhen, Liu Yi. Human acellular amniotic membrane scaffold promotes ligament differentiation of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells modified by Scleraxis in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1037-1044. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||