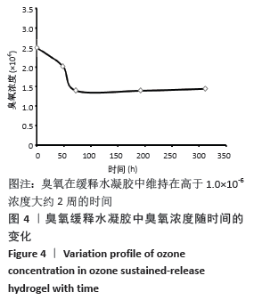
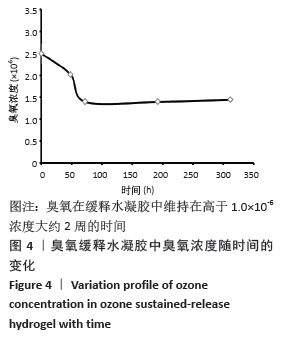
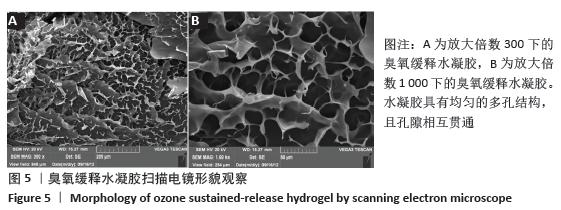
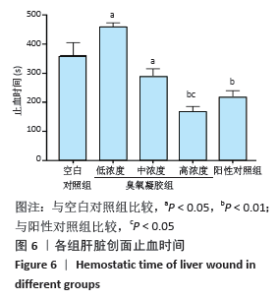
[1] BORGES GA, ELIAS ST, SILVA SM, et al. In vitro evaluation of wound healing and antimicrobial potential of ozone therapy. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2017; 45(3):364-370.
[2] KHATRI I, MOGER G, KUMAR NA. Evaluation of effect of topical ozone therapy on salivary Candidal carriage in oral candidiasis. Indian J Dent Res. 2015;26(2):158-162.
[3] ALSAADI H, POTAPOVA I, ROCHFORD ET, et al. Ozonated saline shows activity against planktonic and biofilm growing Staphylococcus aureus in vitro: a potential irrigant for infected wounds. Int Wound J. 2016;13(5):936-942.
[4] 李云恺,陈丽艳,王惠,等.臭氧、臭氧水对感染性创面修复作用的分子生物学研究[J].海南医学,2014,25(10):1409-1411.
[5] 王韬.壳聚糖纳米粒水凝胶的制备及其对皮肤伤口修复的研究[D].锦州:锦州医科大学,2019.
[6] ZENG J, LU J. Mechanisms of action involved in ozone-therapy in skin diseases. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;56:235-241.
[7] 倪高荣.臭氧自血疗法对患者凝血功能影响的自身对比研究[D].昆明医科大学,2017.
[8] SAKAII D, MAKITA Y, MASUNO K, et al. Local Hemostatic Effect of Aqueous Ozone in Cutting Wound Surface. J Hard Tissue Biol. 2014;23(2):245-248.
[9] 陈静.药用辅料卡波姆在药物制剂中的应用探讨[J].企业科技与发展, 2019(9):150-151,153.
[10] 何银舟.卡波姆的特性及其在药剂学中应用的研究进展[J].临床合理用药杂志,2019,12(15):180-181.
[11] LUND RG, SILVA AF, PIVA E, et al. Clinical evaluation of two desensitizing treatments in southern Brazil: A 3-month follow-up. Acta Odontol Scand. 2013;71(6):1469-1474.
[12] XU M, SUN M, QIAO H, et al. Preparation and evaluation of colon adhesive pellets of 5-aminosalicylic acid. Int J Pharm. 2014;468(1-2):165-171.
[13] MESHALI MM, ELSAYED GM, ELSAID Y, et al. Preparation and Evaluation of Theophylline Sustained-Release Tablets. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 1996;22(4): 373-376.
[14] DURRANI MJ, WHITAKER R, ANDREWS A, et al. Studies on drug release kinetics from Carbopol 934 Ptablets. Pharm Res. 1991;8 (10Suppl):s135.
[15] 孟勇涛,饶丽平.卡波姆在凝胶制剂中使用的问题探讨[J].齐鲁药事, 2010,29(12):708-709.
[16] 李成蓉,黄筱萍.卡波姆的性质和应用[J].华西药学杂志,1999,14(2):50.
[17] 许伟坚.臭氧缓释水溶胶的制备及条件研究[D].北京:北京化工大学,2017.
[18] 孟志云,窦桂芳,刘敏霞.纤维蛋白胶干粉对大鼠出血模型的止血作用[J].军事医学科学院院刊,2002,26(1):51-53.
[19] 王建坤,赵黎黎,刘文婕.蒙脱石在肝脏出血模型大鼠的止血作用[J].江苏医药,2018,44(5):484-487.
[20] 王景文.京万红软膏治疗皮肤损伤的临床应用研究进展[J].药物评价研究,2014,37(4):375-380.
[21] 白爽,侯登勇,沈先荣.新型静电纺丝伤口敷料的止血性能及促愈合作用研究[J].中国海洋药物,2019, 38(2):1-10.
[22] 秦承玲.海藻酸盐基水凝胶的制备及其性能研究[D].上海:东华大学,2017.
[23] WALTER RH, SHERMAN RM. Duration of ozone in water in the upper solubility range. J Food Sci. 1976;41:993-995.
[24] 郭红叶,伊博文,闫小平,等.新型辅料卡波姆在凝胶剂中应用现状[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2013,19(17):371-374.
[25] 王敏,薛晓东.卡波姆凝胶剂的临床应用研究进展[J].医学综述,2013, 19(6):1078-1080.
[26] BOCCI V. Biological and clinical effects of ozone. Has ozone therapy a future in medicine. Brit J Biomed Sci. 1999;56(4):270-279.
[27] GÓRNICKI A, GUTSZE A. In vitro effects of ozone on human erythrocyte membranes: An EPR study. Acta Biochim Pol. 2000;47(4):963-971.
[28] BOCCI V, ALDINUCCI C. Rational bases for using oxygen-ozonetherapy as a biological response modifier in sickle cell anemia and beta-thalassemia: A therapeutic perspective. J Biol Reg Homeos Ag. 2004;18(1):38-44.
[29] ROSENFELD MA, BYCHKOVA V, SHCHEGOLKHIN AN, et al. Ozone-induced oxidative modification of plasma fibrin-stabilizing factor. Bba-Proteins Proteom. 2013;1834(12):2470-2479.
[30] ROSENFELD MA, BYCHKOVA V, SHCHEGOLKHIN AN, et al. Fibrin self-assembly is adapted to oxidation. Free Radical Bio Med. 2016;(95):55-64.
[31] ROSENFELD MA, SHCHEGOLKHIN AN, BYCHKOVA V, et al. Ozone-induced oxidative modification of fibrinogen: role of the D regions. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014;(77):106-120.
[32] BOCCI V. Ozone as Janus: this controversial gas can be either toxic or medically useful. Mediat Inflamm. 2004;13(1):3-11.
[33] 万筱玲,谢运华,叶毓粦,等.慢性伤口应用臭氧外部充气疗法的效果观察[J].护理学报,2009,16(14):57-58.
[34] 陈晓红.臭氧治疗仪对肛周脓肿术后伤口愈合的临床研究[J].全科医学临床与教育,2019,17(3):287-288.
[35] 童化军.医用臭氧在皮肤疾病中的创新性应用[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2018,18(89):40-41.
|