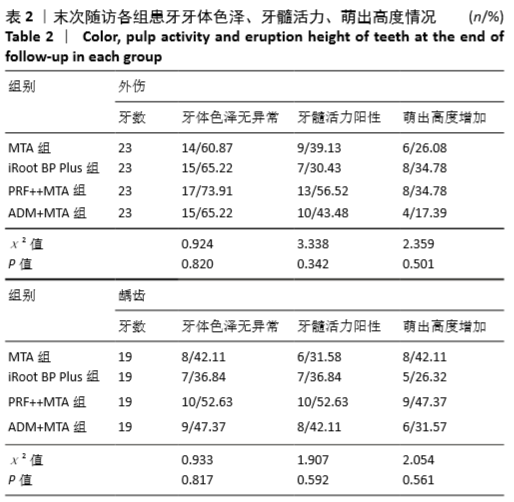
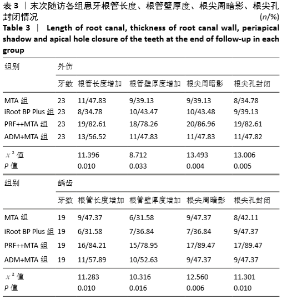
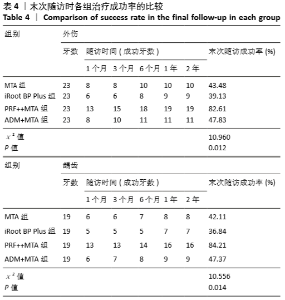
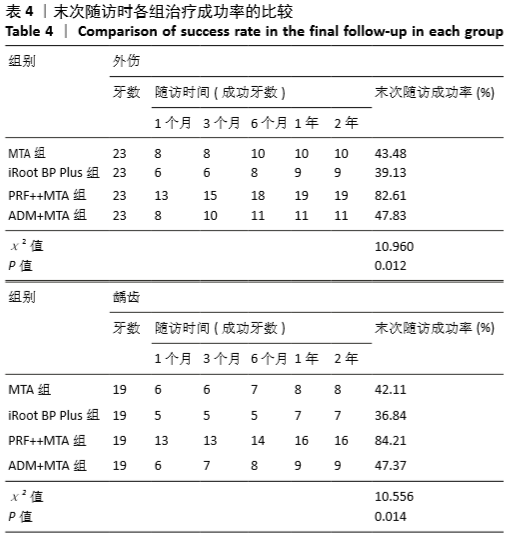
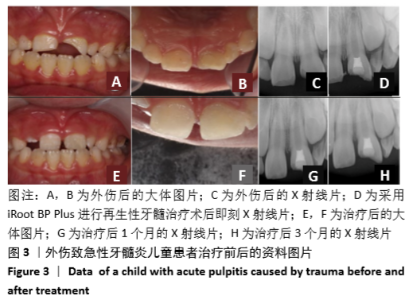
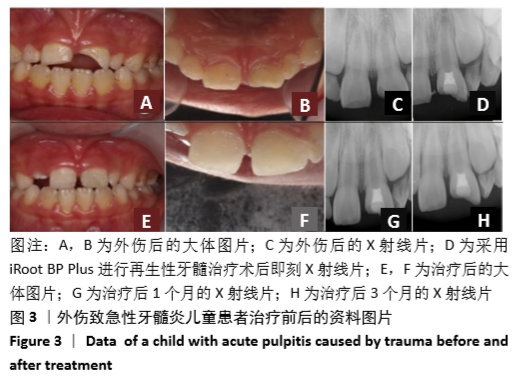
[1] 陈宜辉,刘岚,朱咏.两种根尖诱导成形剂对年轻恒牙牙髓根尖周炎根尖孔闭合的影响[J].现代医学,2017,45(11):1598-1603.
[2] LINSUWANONT P, WIMONSUTTHIKUL K, POTHIMOKE U, et al. Treatment Outcomes of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Pulpotomy in Vital Permanent Teeth with Carious Pulp Exposure: The Retrospective Study.J Endod.2017;43(2):225-230.
[3] 周媛,武瑾,程靖,等.氢氧化钙和洗必泰在年轻恒牙外伤后牙髓血运重建中的疗效[J].安徽医学, 2018,39(1):57-59.
[4] SILUJJAI J, LINSUWANONT P. Treatment Outcomes of Apexification or Revascularization in Nonvital Immature Permanent Teeth: A Retrospective Study.J Endod.2017;43(2):238-245.
[5] 胡晓燕,马丽琼,潘莉.牙髓血管再生治疗牙髓坏死伴根尖周病变的年轻恒牙的两年疗效观察[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2017,33(4): 469-474.
[6] 姜力铭,夏商,宋戈,等.明胶纤维支架促进人牙髓干细胞的成纤维分化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(13):1981-1986.
[7] 肖文,汪俊.牙髓再生治疗临床进展的循证医学研究[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2018,11(3):150-155.
[8] 徐丹,何旭顺,高志雄,等.微创牵引复位外伤挫入年轻恒牙的临床疗效观察[J].中华口腔医学研究杂志(电子版),2018,12(1):37-47.
[9] 李静,王尔慧,王宇.牙髓血管再生治疗年轻恒牙牙髓坏死的安全性和有效性:单中心、随机、对照临床试验方案[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(24):3809-3814.
[10] TAHA NA,ABDULKHADER SZ.Full Pulpotomy with Biodentine in Symptomatic Young Permanent Teeth with Carious Exposure.J Endod. 2018;44(6):932-936.
[11] 胡晓燕,马丽琼,潘莉.牙髓血管再生治疗牙髓坏死伴根尖周病变的年轻恒牙的两年疗效观察[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2017,33(4): 469-474.
[12] 雷期音,陈柯.年轻恒牙牙髓再生的临床应用进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2017,44(3):267-272.
[13] 刘金凤,牛雪微,超博,等.牙髓再生的研究现状[J].口腔医学研究, 2017,33(1):108-111.
[14] ERFANPARAST L, IRANPARVAR P, VAFAEI A. Direct pulp capping in primary molars using a resin-modified Portland cement-based material (TheraCal) compared to MTA with 12-month follow-up: a randomised clinical trial.Eur Arch Paediatr Dent.2018;19(3):197-203.
[15] 邱小玲,贾搏,韩久松,等.显微根尖手术联合MTA治疗难治性慢性根尖周炎的研究[J].口腔医学研究,2017,33(7):770-773.
[16] 战园,刘鹤.iRoot BP对人乳牙牙髓细胞增殖、矿化的影响[J].山东医药,2017,57(28):85-87.
[17] 李娇娇,黎淑芳.富血小板纤维蛋白应用于牙髓再生的研究进展[J].医学综述,2018,24(1):107-111.
[18] 王颖莹,张少衡.脱细胞真皮基质膜联合改良隧道术在牙龈退缩治疗的应用[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2018,33(1):84-87.
[19] AMINE K,AMRANI YE,CHEMLALI S,et al.Alternatives to connective tissue graft in the treatment of localized gingival recessions: a systematic review.J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018;119(1):25-32.
[20] 宋光泰,靳秋晨.年轻恒牙牙髓再生性治疗的研究进展[J].口腔疾病防治,2016,24(12):681-687.
[21] 黄伟曼,张栋杰,胡旭初,等.iRoot BP Plus和MTA用于年轻恒牙直接盖髓的临床疗效观察[J].中华口腔医学研究杂志(电子版), 2017,11(6):366-370.
[22] 陈燕,王燚虹,陈婷.年轻恒牙牙髓血管再生治疗效果观察及评估[J].当代医学,2017,23(13):71-72. |