Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (20): 3178-3184.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3215
Previous Articles Next Articles
Knowledge mapping analysis on the international research of diabetic foot: a visual analysis based on CiteSpace
Li Wenhui1, Liu Guobin2
- 1Shanghai University of Medicine & Health Sciences, Shanghai 201318, China; 2Shuguang Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China
-
Received:2020-04-22Revised:2020-04-26Accepted:2020-10-09Online:2021-07-18Published:2021-01-15 -
Contact:Liu Guobin, MD, Chief physician, Shuguang Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China -
About author:Li Wenhui, MD, Lecturer, Shanghai University of Medicine & Health Sciences, Shanghai 201318, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Youth Project), No. 81804096 (to LWH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Wenhui, Liu Guobin. Knowledge mapping analysis on the international research of diabetic foot: a visual analysis based on CiteSpace[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3178-3184.
share this article
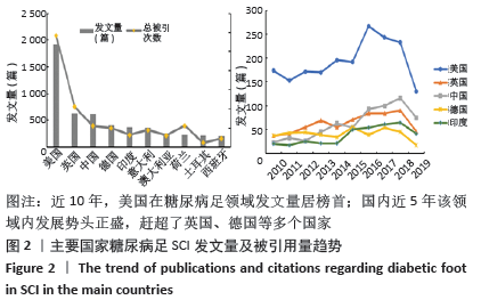
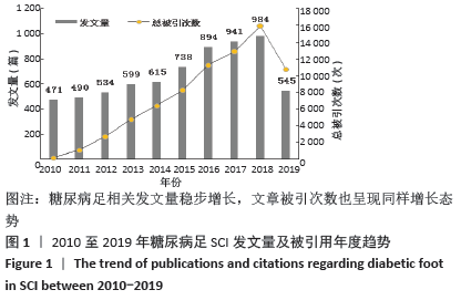
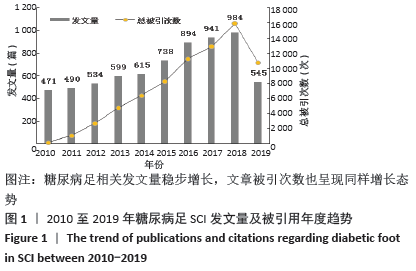
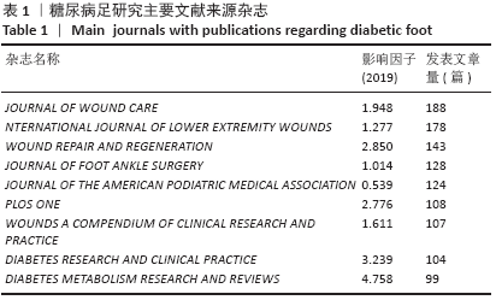
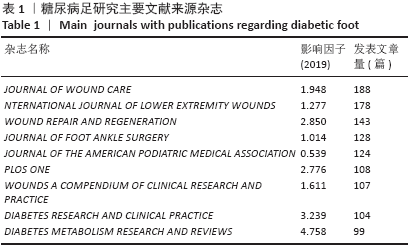
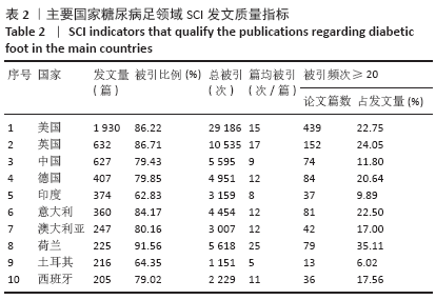
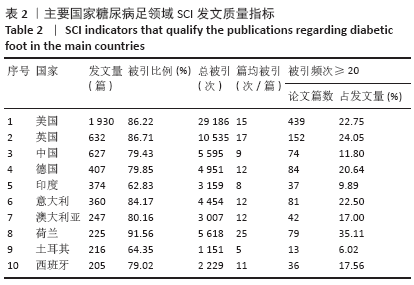
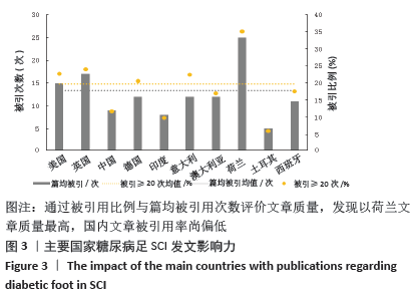
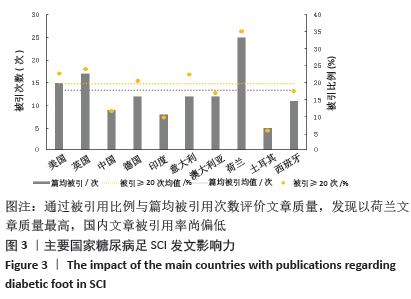
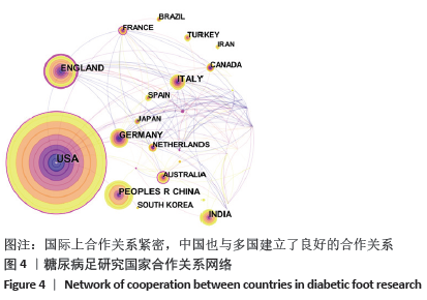
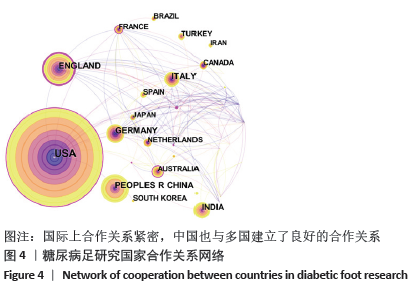
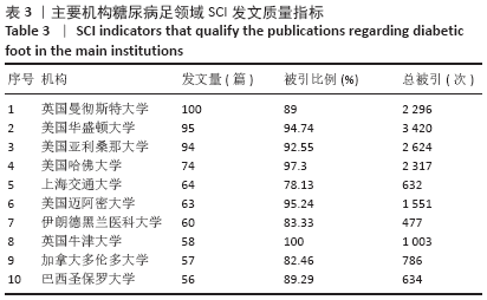
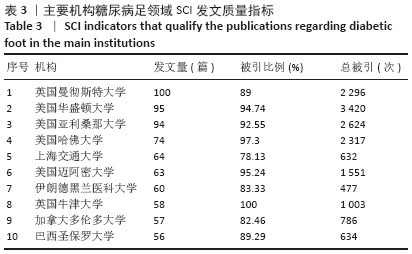
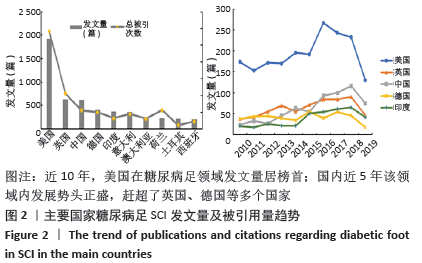
2.3 研究国家来源 糖尿病足领域近10年来发文数量排名前10位的国家为美国、英国、中国、德国、印度、意大利、澳大利亚、荷兰、土耳其和西班牙等,其中美国以1 930篇的发文数量和29 186次被引用次数占据榜首,表明美国在糖尿病足领域的学科领军地位,详见图2。综合文章平均被引用次数及比例,荷兰、英国、美国的文章质量最高,国内发文量虽排第三,但文章被引用率偏低,论文质量仍有提升空间,详见表2。研究国家可视化提示,中心度排名前5分别是英国0.26、美国0.19、新加坡0.18、法国0.13和瑞士0.13,这5个国家均与其他各国建立了良好的研究合作关系,详见图3。国内建立合作关系较多的为美国、新加坡及韩国,中心度0.01,应加大国际合作的广度与深度,详见图4。 "
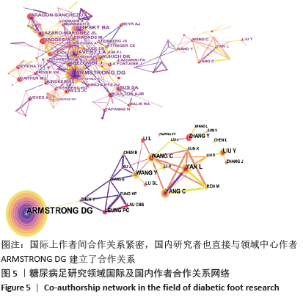
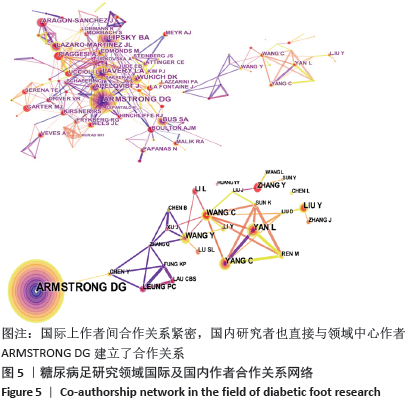
2.5 作者及合作关系图谱 作者关系网络如图5,年轮越大表示出现次数越大,其中标有红色年轮的作者表示被引用频率急速增加。文章作者出现频次前5位的是ARMSTRONG DG 83次、LIPSKY BA 67次、LAVERY LA 50次、LAZARO-MARTINEZ JL 39次和BUS SA 36次。可见Armstrong DG教授以发文量、中心度的绝对优势,占据该领域的领头地位,其研究领域非常广泛,包括糖尿病机制(如体外研究、炎症、温度等)、新型治疗措施(如负压吸引、氧疗、足底电击)、预防保健举措(减压鞋、健康传感器等),综合其近3年文献可知其关注体外研究和新型治疗方案,着眼于预防保健,致力于提高患者生活质量,希望构建完善的区域、国际治疗合作网络。 国内放大关系网络可见,陆军军医大学西南医院、重庆大学附属中心医院等与ARMSTRONG DG建立了直接合作关系,研究领域包括糖尿病足的外科干预或再生医学疗法,如负压创面疗法结合富血小板血浆、脱细胞基质移植术等治疗糖尿病足溃疡[8],骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗糖尿病大疱病[9];另外还有国内生物标志物的研究,如血清胱抑素C与糖尿病足溃疡相关性研究[10]。 "
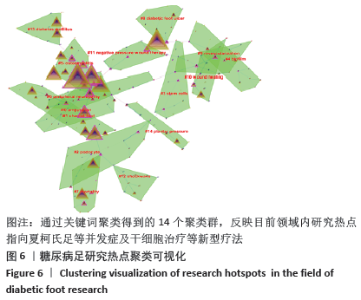
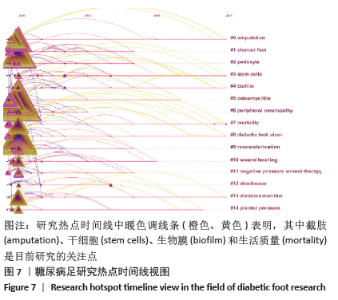
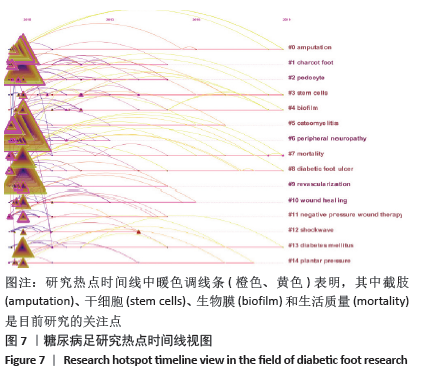
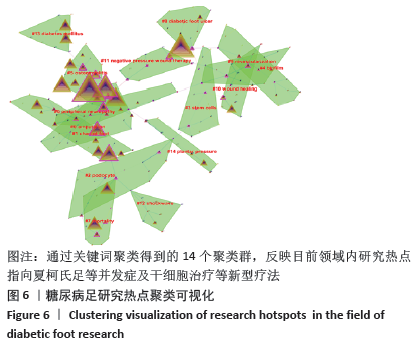
2.6 关键词可视化 利用CiteSpace软件对关键词进行可视化分析,见图6,共得到203个节点,频次前五的是糖尿病足(diabetic foot)1 303次、糖尿病足溃疡(diabetic foot ulcer)1 178次、伤口管理(management)1 003次、溃疡(ulcer)914次、糖尿病(diabete)802次;中心度前五是溃疡(ulceration)0.80、下肢静脉溃疡(venous leg ulcer)0.73、骨髓炎(osteomyelitic) 0.69、危险因素(risk factor)0.65、慢性伤口(chronic wound)0.63。目前糖尿病足的研究主要集中在慢性溃疡的治疗和伤口的综合管理,在再生医学疗法方面取得一定进展。通过关键词聚类,共得到14个聚类群,Mean Silhouette值为0.871 4,同质性较好。0#聚类为截肢(amputation),这是糖尿病足最严重的并发症;1#聚类为夏柯氏足(charcot foot),其特点是活跃期炎症反应后紧随不同程度跟骨结构永久性破坏;糖尿病足患者普遍存在慢性肾脏疾病,2#聚类足细胞(podocype)损伤是糖尿病肾病的关键;国际学界对糖尿病足严重预后的关注,反映对生活质量的极大关注。紧随其后的3#聚类干细胞(stem cells)表明细胞角度的研究和治疗措施已成为目前研究的热点。研究聚类时间线视图见图7,越接近暖色调线条(橙色、黄色)表明研究年份约近,其中截肢(amputation)、干细胞(stem cells)、生物膜(biofilm)和生活质量(mortality)是目前研究的关注点。"

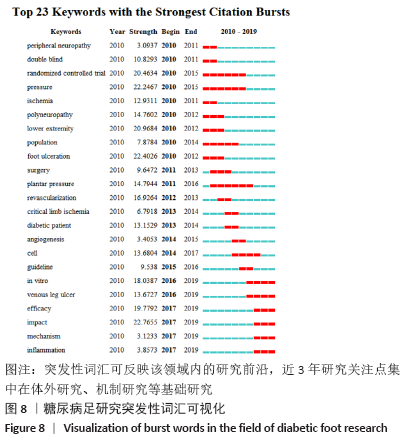
关键词突发性节点检测(Burstness)见图8,能展示其中短时间内频次突然增加或频次明显提高的,突发值越大说明该领域越活跃,能更好地聚焦研究热点。近3年,体外实验、炎症以及对于发病机制的探讨等突变点成为近年的研究前沿。 2.7 高被引文献 被引用次数排名前五的文献分别为LIPSKY BA,2012[11] 541次、PARENTEAU-BAREIL R,2010[12] 399次、KUMAR PTS,2012[13] 301次、LAHIRI BB,2012[14] 299次和MILLS JL,2014[15] 272次,其中第一篇和第五篇分别是美国传染病学会及血管外科学会针对糖尿病足制定的指南性文章,第二、三篇介绍了可促进糖尿病足伤口愈合的新型材料,第四篇的热红外成像技术则涉及到糖尿病足的诊疗。可见,糖尿病足虽然是老命题,不仅有不断更新的指南规范,针对创面愈合的新技术、新材料仍在不断发展进步,学术界仍然充满了活力。"
| [1] BOULTON AJ. The diabetic foot:a global view.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2000;16(Suppl 1): S2-5. [2] International Diabetes Federation. IDF DIABETES ATLAS, 9th edition 2019. [3] SINGH N, ARMSTRONG DG, LISPSKY BA. Preventing foot ulcers in patients with diabetes. JAMA. 2005;293(2):217-228. [4] 中华医学会糖尿病学分会, 中华医学会感染病学分会, 中华医学会组织修复与再生分会.中国糖尿病足防治指南(2019版)(Ⅰ)[J].中华糖尿病杂志,2019,11(2):92-108. [5] MARGOLIS DJ, MALAY DS, HOFFSTAD OJ, et al. Incidence of diabetic foot ulcer and lower extremity amputation among Medicare beneficiaries, 2006 to 2008: Data Points #2. Rockville (MD):Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality(US), 2011. [6] CATTERALL RC, MARTIN MM, OAKLEY W. Aetiology and management of lesions of the feet in diabetesp. Br Med J. 1956;2:953-957. [7] CHEN C. CiteSpaceⅡ: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J Am Soc Inf Sci Tech. 2006; 57(3):359-377. [8] DENG W, BOEY J, CHEN B,et al. Platelet-rich plasma, bilayered acellular matrix grafting and negative pressure wound therapy in diabetic foot infection.J Wound Care. 2016;25(7):393-397. [9] CHEN Y, MA Y, LI N, et al. Efficacy and long-term longitudinal follow-up of bone marrow mesenchymal cell transplantation therapy in a diabetic patient with recurrent lower limb bullosisdiabeticorum.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):99. [10] ZHAO J, DENG W, ZHANG Y, et al. Association between Serum Cystatin C and Diabetic Foot Ulceration in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study. J Diabetes Res. 2016;2016:8029340. [11] LIPSKY BA, BERENDT AR, CORNIA PB,et al.2012 Infectious Diseases Society of America Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Diabetic Foot Infections. Clin Infect Dis. 2012; 54(12):e132-173. [12] PARENTEAU-BAREIL R , GAUVIN R , BERTHOD F. Collagen-Based Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering Applications.Materials. 2010;3(3): 1863-1887. [13] KUMAR PT, LAKSHMANAN VK, ANILKUMAR TV, et al. Flexible and microporous chitosan hydrogel/nanoZnO composite bandages for wound dressing: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2012;4(5):2618-2629. [14] LAHIRI BB, BAGAVATHIAPPAN S, JAYAKUMAR T, et al. Medical applications of infrared thermography: A review.Infrared Phys Technol. 2012;55(4):221-235. [15] MILLS JL, CONTE MS, ARMSTRONG DG, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery Lower Extremity Threatened Limb Classification System: Risk stratification based on Wound, Ischemia, and foot Infection (WIfI).J Vascular Surg. 2014;59(1):220-234. [16] 中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2017年版)[J].中国实用内科杂志,2018, 38(4):292-344. [17] MIYAJIMA S, SHIRAI A, YAMAMOTO S, et al. Risk factors for major limb amputations in diabetic foot gangrene patients.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2006;71(3):272-279. [18] MARMOLEJO VS, ARNOLD JF, PONTICELLO M, et al. Charcot foot:clinical clues, diagnostic strategies,and treatment principles.Am Fam Physician. 2018;97(9):594-599. [19] MORBACH S, FURCHERT H, GROBLINGHOFF U, et al. Long-term prognosis of diabetic foot patients and their limbs:amputation and death over the course of a decade. Diabetes Care. 2012;35(10): 2021-2027. [20] GURJALA AN, GERINGER MR, SETH AK, et al. Development of a novel,highly quantitative in vivo model for the study of biofilm-impaired cutaneous wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2011;19(3):400-410. [21] HURLOW J, BOWLER PG. Potential implications of biofilm in chronic wounds:a case series. J Wound Care. 2012;21(3):109-110. [22] WOLCOTT RD, COX S. More effective cell-based therapy through biofilm suppression. J Wound Care. 2013;22(1):26-31. [23] HEYBOER M. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy side effects-where do we stand? J Am Coll Clin Wound Spec. 2016;8(1-3):2-3. [24] 徐进,殷嫦嫦,宋伟,等.间充质干细胞治疗糖尿病足溃疡的Meta分析[J].中国糖尿病杂志,2019,27(6):417-423. [25] ALBEHAIRY A, ABDELGHAFFAR H, ABDELHAFEZ H, et al. Autologous mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of recalcitrant neuropathic diabetic foot ulcer: randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia. 2016; 59(1):S19. [26] GONZALES KAU, FUCHS E. Skin and Its Regenerative Powers:An Alliance between Stem Cells and Their Niche.Dev Cell. 2017;43(4):387-401. [27] YANG Z, HE C, HE J, et al. Curcumin-mediated bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell sheets create a favorable immune microenvironment for adult full-thickness cutaneous wound healing.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):21. [28] SHINGYOCHI Y, ORBAY H, MIZUNO H. Adipose-derived stem cells for wound repair and regeneration.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2015; 15(9):1285-1292. [29] WU YY, JIAO YP, XIAO LL, et al. Experimental Study on Effects of Adipose-Derived Stem Cell-Seeded Silk Fibroin Chitosan Film on Wound Healing of a Diabetic Rat Model.Ann Plast Surg. 2018;80(5):572-580. [30] 刘瑾,袁晓勇,袁戈恒,等. 糖尿病患者高危足筛查及分级、干预规范流程的构建[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志,2017,9(5):281-285. [31] AHMAD A, ABUJBARA M, JADDOU H, et al. Anxiety and depression among adult patients with diabetic foot: prevalence and associated factors. J Clin Med Res. 2018;10(5):411-418. [32] UDOVICHENKO OV, MAXIMOVA NV, AMOSOVA MV, et al.Prevalence and prognostic value of depression and anxiety in patients with diabetic foot ulcers and possibilities of their treatment. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2017; 13(1):97-106. [33] IVERSEN MM, TELL GS, ESPEHAUG B, et al. Is depression a risk factor for diabetic foot ulcers? 11-years follow-up of the Nord-Trøndelag Health Study (HUNT). J Diabetes Complications. 2015;29(1):20-25. [34] O’NEILL SM, KABIR Z, MCNAMARA G, et al. Comorbid depression and risk of lower extremity amputation in people with diabetes:systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2017;5(1): e000366. [35] MONAMI M, LONGO R, DESIDERI CM, et al. The diabetic person beyond a foot ulcer: healing, recurrence, and depressive symptoms. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2008;98(2):130-136. [36] FEINGOLD D, BRILL S, GOOR-ARYEH I, et al. The association between severity of depression and prescription opioid misuse among chronic pain patients with and without anxiety: a Cross-sectional study. J Affect Disord. 2018;235:293-302. |
| [1] | Wang Mengting, Gu Yanping, Ren Wenbo, Qin Qian, Bai Bingyi, Liao Yuanpeng. Research hotspots of blood flow restriction training for dyskinesia based on visualization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1264-1269. |
| [2] | Fan Yinuo, Guan Zhiying, Li Weifeng, Chen Lixin, Wei Qiushi, He Wei, Chen Zhenqiu. Research status and development trend of bibliometrics and visualization analysis in the assessment of femoroacetabular impingement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 414-419. |
| [3] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [4] | Fan Jin, Zeng Luyao, Zhong Dongling, Li Yuxi, Tian Yanping, Huang Yijie, Jin Rongjiang. Development of functional near-infrared spectroscopy in recent 10 years: a visual analysis using CiteSpace [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3711-3717. |
| [5] | Gan Lili, Xiong Na, Liu Yanfei. Hydrogel as drug scaffold in skin wound repair: challenges of clinical application possibilities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3578-3583. |
| [6] | Ren Wenbo, Liao Yuanpeng. Visualization analysis of traumatic osteoarthritis research hotspots and content based on CiteSpace [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3374-3381. |
| [7] | Pan Xuan, Zhao Meng, Zhang Xiumei, Zhao Jie, Zhai Yunkai. Research and application of biological three-dimensional printing technology in the field of precision medicine: analysis of Chinese and English literature [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3382-3389. |
| [8] | Wei Jinqiang, Huang Dengcheng, Cao Xuewei, Zhou Jianwei, Sun He, Li Zehui. Analysis of researches on TCM treatments for cartilage diseases in recent 20 years by mapping knowledge domains [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3202-3209. |
| [9] | Tian Lin, Shi Xiaoqing, Duan Zhenglan, Wang Kuan, Zhang Li, Wang Peimin. Efficacy and safety of transverse tibial bone transport technique in the treatment of diabetic foot:a meta-analysis#br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3275-3280. |
| [10] | Xia Wenshen, He Renjiao, Ai Jinwei, Wang Jun, Li Desheng, Pei Bin. Stem cell transplantation for diabetic patients with lower-extremity arterial disease: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3110-3116. |
| [11] | Zhang Kai, Zhang Xiaobo, Shi Jintao, Wang Keping, Zhou Haiyu. Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration: a bibliometric and visualization analysis based on Web of Science database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3031-3038. |
| [12] | Huang Na, Liu Jiayue, Huang Yingjie, Wen Junmao, Wang Haibin, Zhang Qingwen, Zhou Chi . Bibliometric and visualized analysis of research on osteonecrosis of the femoral head from the Web of Science in the last 5 years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2711-2718. |
| [13] | Wen Shuaibo, Han Jie, Wu Yukun. Bibliometric and visual analysis of literature on cartilage repair in the Web of Science in recent 15 years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2657-2663. |
| [14] | Tian Yanping, Li Juan, Liu Xiaobo, Zhang Huiling, Shi Lihong, Jin Rongjiang. Knowledge network mapping of literature regarding platelet-rich plasma in recent 5 years: a visual analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1745-1752. |
| [15] | Xiong Guobing, Liu Aibo, Wang Shize, Wang Yu, Qiu Mingxing. Urine turbulent shear stress system of bionic human bladder based on bacterial biofilm reactor: in vitro construction#br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1560-1565. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||