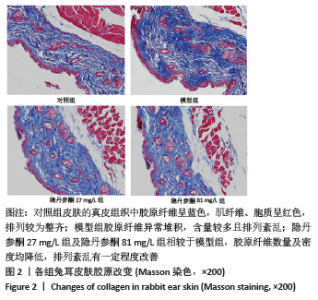
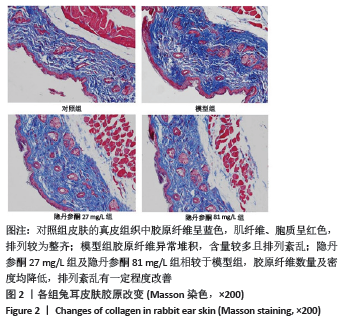
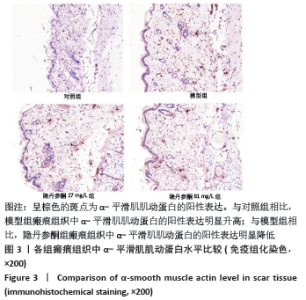
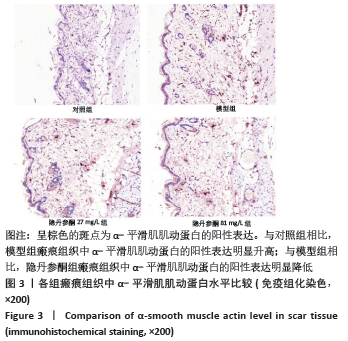
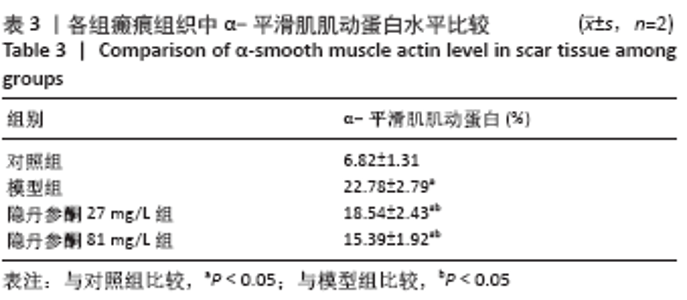
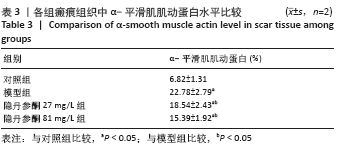
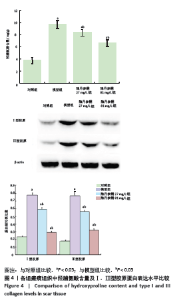
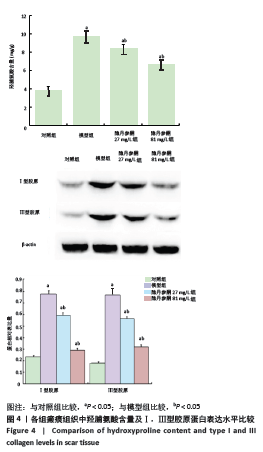
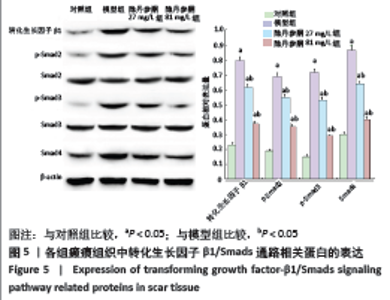
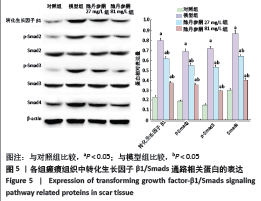
[1] ZHANG J, LI Y, BAI X, et al. Recent advances in hypertrophic scar. Histol Histopathol. 2017;33(1):27-39.
[2] 徐志山, 陶凯, 郭冰玉. miRNA在病理性瘢痕中作用的研究进展[J]. 中国美容整形外科杂志,2018,29(1):63-64,后插1.
[3] ZHAO W, WU C, CHEN X. Cryptotanshinone Inhibits oxidized LDL-Induced Adhesion Molecule Expression via ROS Dependent NF-κB Pathways. Cell Adh Migr. 2016;10(3):248-258.
[4] 陈伟达, 罗成华, 苗成利. 隐丹参酮对人纤维肉瘤HT-1080细胞增殖和凋亡影响[J]. 中华肿瘤防治杂志,2019,26(7):457-462.
[5] 邹伟, 钱程, 张婷婷, 等. 隐丹参酮对小鼠下肢缺血的保护作用研究[J]. 中药药理与临床,2019,35(2):40-45.
[6] LI Y, SHI S, GAO J, et al. Cryptotanshinone downregulates the profibrotic activities of hypertrophic scar fibroblasts and accelerates wound healing: A potential therapy for the reduction of skin scarring. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;80:80-86.
[7] 宋雅娟, 余州, 王彤, 等. 中草药单体松萝酸抑制兔耳增生性瘢痕的作用研究[J]. 中国美容整形外科杂志,2019,30(7):401-403,后插2.
[8] 王斐, 赖林英, 梁黎明. 脂肪组织移植抑制体表瘢痕形成的临床研究进展[J]. 中国美容医学,2018,27(10):170-173.
[9] BERMAN B, MADERAL A, RAPHAEL B. Keloids and Hypertrophic Scars: Pathophysiology, Classification, and Treatment. Dermatol Surg. 2017;43(Suppl 1):S3-S18.
[10] LI H, YANG L, ZHANG Y, et al. Kaempferol inhibits fibroblast collagen synthesis, proliferation and activation in hypertrophic scar via targeting TGF-β receptor type I. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;83:967-974.
[11] HE T, BAI X, YANG L, et al. Loureirin B Inhibits Hypertrophic Scar Formation via Inhibition of the TGF-beta 1-ERK/JNK Pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;37(2):666-676.
[12] SHAN S, ZHANG Y, WU M, et al. Naringenin attenuates fibroblast activation and inflammatory response in a mechanical stretch-induced hypertrophic scar mouse model. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(4):4643-4649.
[13] MA S, YANG D, WANG K,et al. Cryptotanshinone attenuates isoprenaline-induced cardiac fibrosis in mice associated with upregulation and activation of matrix metalloproteinase-2. Mol Med Rep. 2012;6(1):145-150.
[14] LO SH, HSU CT, NIU HS, et al. Cryptotanshinone Inhibits STAT3 Signaling to Alleviate Cardiac Fibrosis in Type 1-like Diabetic Rats. Phytother Res. 2017;31(4):638-646.
[15] 张文夺,邓呈亮, 郭常敏, 等. 人真皮间充质干细胞对增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞α-SMA和DCN表达的影响[J]. 中华整形外科杂志, 2016,32(4):285-292.
[16] 孙玉娇, 王俊卿, 焦卉朵, 等. 超声对兔耳瘢痕组织形态学及α-平滑肌肌动蛋白表达的影响[J]. 中华物理医学与康复杂志,2014, 36(1):63-65.
[17] 孙桂芳, 张晓芬, 李红昌,等. 生肌玉红膏对增生性瘢痕的抑制作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2016,20(33):4890-4898.
[18] 刘国菊, 李丛丛, 李睿坤, 等. 转化生长因子β1在纤维化疾病发病中作用的研究进展[J]. 山东医药,2018,58(30):106-109.
[19] HATA A, CHEN YG. TGF-β Signaling from Receptors to Smads. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Biol. 2016;8(9):a022061.
[20] LOBODA A , SOBCZAK M , JOZKOWICZ A , et al. TGF-β 1/Smads and miR-21 in Renal Fibrosis and Inflammation. Mediator Inflamm. 2016; 2016(7):1-12.
[21] WEN S, WEI Y, ZHANG X, et al. Methyl helicterilate ameliorates alcohol-induced hepatic fibrosis by modulating TGF-β1/Smads pathway and mitochondria-dependent pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;75: 105759.
[22] CHEN H, XU Y, YANG G,et al. Mast cell chymase promotes hypertrophic scar fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis by activating TGF-β1/Smads signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(5):4438-4442.
[23] 王重阳, 姜京植,李俊峰, 等. 隐丹参酮通过TWEAK/Fn14和TGF-β1/Smads信号通路缓解OVA诱导哮喘小鼠气道炎症[J]. 中国药理学通报,2019,35(8):1149-1154.
[24] WANG W, ZHOU PH, HU W, et al. Cryptotanshinone hinders renal fibrosis and epithelial transdifferentiation in obstructive nephropathy by inhibiting TGF-β1/Smad3/integrin β1 signal. Oncotarget. 2018; 9(42):26625-26637.
[25] HONARDOUST D , VARKEY M , MARCOUX Y , et al. Reduced decorin, fibromodulin, and transforming growth factor-β3 in deep dermis leads to hypertrophic scarring. J Burn Care Res. 2012;33(2):218-227. |