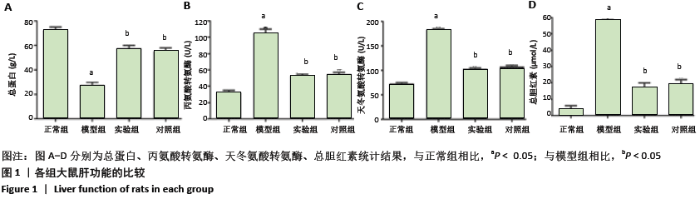
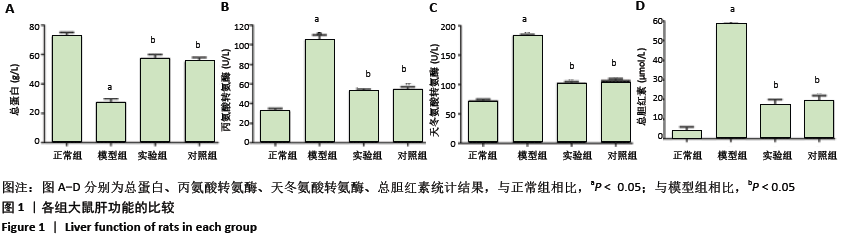
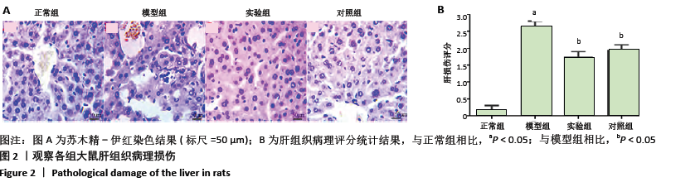
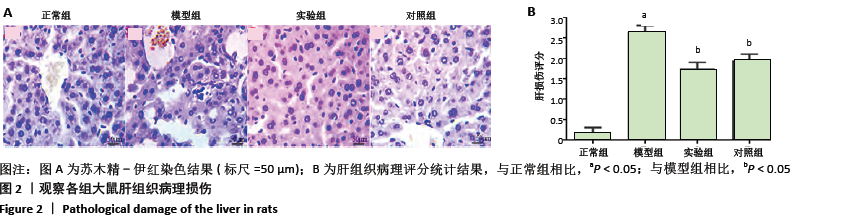
[1] ARMSTRONG F, MCCURDY MT, HEAVNER MS. Synthetic Cannabinoid-Associated Multiple Organ Failure: Case Series and Literature Review. Pharmacotherapy. 2019;39(4):508-513.
[2] 扈红蕾, 高健, 郭文君,等. 富氢水在黄曲霉毒素B1致大鼠肝损伤模型中的抗损伤作用[J].生理学报,2019,71(5):725-731.
[3] 吴月, 杨云梅. 微RNA-155激动剂对脓毒症小鼠肝损伤时炎症应答的影响[J]. 中华危重症医学杂志(电子版),2019,12(4):235-239.
[4] RIZZO MR, FASANO R, PAOLISSO G. Adiponectin and Cognitive Decline. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(6):2010-2023.
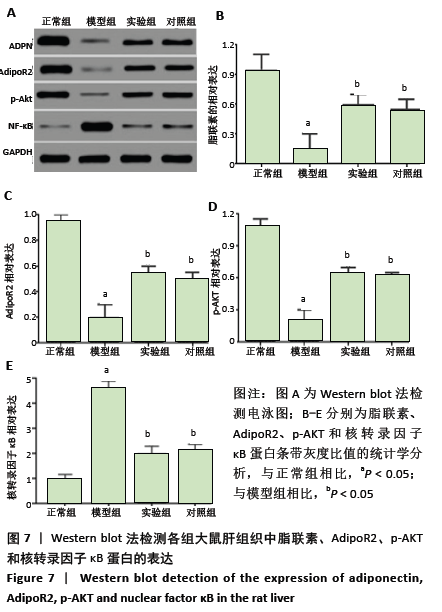
[5] 赵文霞, 张丽慧, 崔健娇,等.化痰祛湿活血方干预非酒精性脂肪性肝炎大鼠ADPN/AKT/NF-κB通路的研究[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志, 2017,37(8):961-967.
[6] 杨雪亮,张凯,孔颖,等.胸腺素α1对急性肝衰竭大鼠血浆TNF-α与IL-10的影响[J]. 西安交通大学学报(医学版),2017,38(5):665-668.
[7] SAHAN FIRAT S, TEMIZ RESITOGLU M, GUDEN DS, et al. NF-κB activation mediates LPS‐or zymosan‐induced hy potension and inflammation reversed by BAY 61-3606, a selective Syk inhibitor, in rat models of septic and non‐septic shock. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2019;46(2): 173-182.
[8] 朱平生,孟玉,付双楠,等. CCl4致大鼠肝损伤24h生物标志物水平的变化规律[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2019,25(2):124-128.
[9] WATANABE M, SUGAWARA A, NOGUCHI Y, et al. Jietacins, azoxy natural products, as novel NF-κB inhibitors: Discovery, synthesis, biological activity, and mode of action.Eur J Med Chem. 2019;178(6):636-647.
[10] HUANG GB, HU P, GAO JM, et al.Analysis of early treatment of multiple injuries combined with severe pelvic fracture. Chin J Traumatol. 2019; 22(3):129-133.
[11] CHUN S, KWON YB. The CCL2 elevation in primary afferent fibers produces zymosan-induced hyperalgesia through microglia-mediated neuronal activation in the spinal dorsal horn.Brain Res Bull. 2019; 149(7):53-59.
[12] YANG X, CHEN Y, ZHANG J, et al. Thymosin α1 treatment reduces hepatic inflammation and inhibits hepatocyte apoptosis in rats with acute liver failure. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(4):3231-3238.
[13] ZHOU L, PAN LC, ZHENG YG, et al. Reduction of FoxP3+ Tregs by an immunosuppressive protocol of rapamycin plus Thymalfasin and Huaier extract predicts positive survival benefits in a rat model of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Transl Med. 2020;8(7):472-487.
[14] WANG YD, WU LL, MA LY, et al.Chronic active EBV infection associated with NK cell lymphoma and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in a 27-year-old woman: A case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(2):1-7.
[15] 金凡,朱盼虎,李家明,等. 吡啶查尔酮类化合物对小鼠肝纤维化的作用[J].中国药理学通报,2019,35(8):1183-1184.
[16] Arab HH, Salama SA, Eid AH, et al. Targeting MAPKs, NF-κB, and PI3K/AKT pathways by methyl palmitate ameliorates ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury in rats. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(12):22424-22438.
[17] Mahmoud AM, Desouky EM, Hozayen WG, et al. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Trigger Liver and Kidney Injury and Fibrosis Via Altering TLR4/NF-κB, JAK2/STAT3 and Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling in Rats. Biomolecules. 2019;9(10):528-549.
[18] Zhao C, Liu L, Liu Q, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 21 is required for the therapeutic effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG against fructose-induced fatty liver in mice. Mol Metab. 2019;29(11):145-157. |