[1] PERILLO L, ESPOSITO M, CAPRIOGLIO A, et al. Orthodontic treatment need for adolescents in the Campania region: the malocclusion impact on self-concept. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2014;8:353-359.
[2] ORSINI MG, HUANG GJ, KIYAK HA, et al. Methods to evaluate profile preferences for the anteroposterior position of the mandible. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2006;130(3):283-291.
[3] ANDREWS LF. The 6-elements orthodontic philosophy: Treatment goals, classification, and rules for treating. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2015;148(6):883-887.
[4] MENDELSON B, WONG CH. Changes in the facial skeleton with aging: implications and clinical applications in facial rejuvenation. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2012;36(4):753-760.
[5] 颜彦. 美貌女性唇、鼻及颏部软组织侧貌美观评价[D].天津:天津医科大学,2016.
[6] HOENIG JF. Sliding osteotomy genioplasty for facial aesthetic balance: 10 years of experience. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2007;31(4):384-391.
[7] LAHAYE MB, BUSCHANG PH, ALEXANDER RG, et al. Orthodontic treatment changes of chin position in Class II Division 1 patients. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2006;130(6):732-741.
[8] LUDLOW JB, GUBLER M, CEVIDANES L, et al. Precision of cephalometric landmark identification: cone-beam computed tomography vs conventional cephalometric views. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2009;136(3):312.e1-313.
[9] LAGRAVÈRE MO, CAREY J, TOOGOOD RW, et al. Three-dimensional accuracy of measurements made with software on cone-beam computed tomography images. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2008;134(1):112-116.
[10] CHEN D, CHEN CH, TANG L, et al. Three-dimensional reconstructions in spine and screw trajectory simulation on 3D digital images: a step by step approach by using Mimics software. J Spine Surg. 2017;3(4): 650-656.
[11] MIHALIK CA, PROFFIT WR, PHILLIPS C. Long-term follow-up of Class II adults treated with orthodontic camouflage: a comparison with orthognathic surgery outcomes. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2003;123(3):266-278.
[12] SINGH AK, GANESHKAR SV, MEHROTRA P, et al. Comparison of different parameters for recording sagittal maxillo mandibular relation using natural head posture: A cephalometric study. J Orthod Sci. 2013; 2(1):16-22.
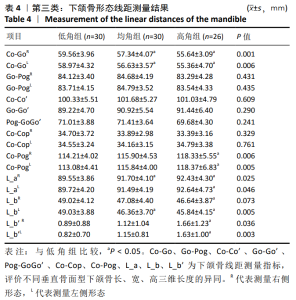
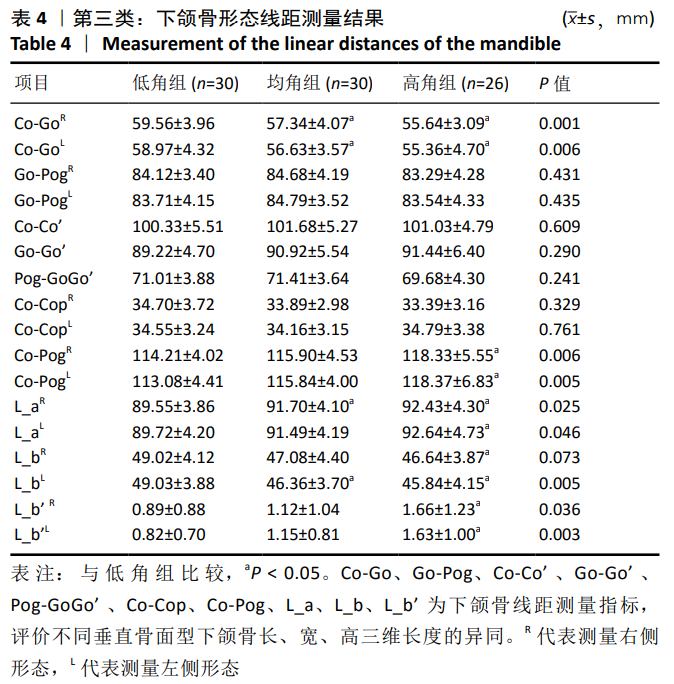
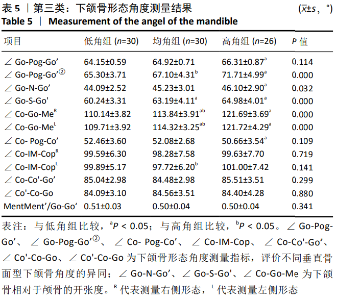
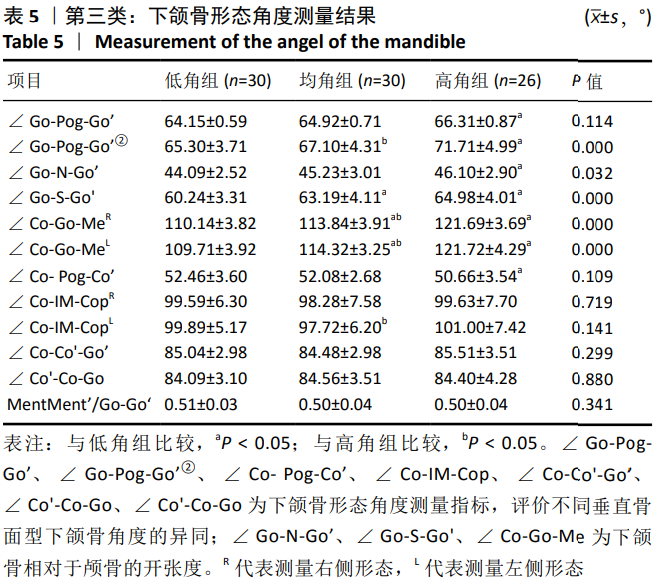
[13] 邹冰爽,曾祥龙,傅民魁. 高角和低角病例的诊断、临床特征及正畸治疗特点[J].口腔正畸学,1999,6(1):39-42.
[14] BURSTONE CJ. Lip posture and its significance in treatment planning. Am J Orthod. 1967;53(4):262-284.
[15] RICKETTS RM. Cephalometric Analysis And Synthesis. Angle Orthod. 1961;31(3):141-156.
[16] STEINER CC. Cephalometrics for you and me. Am J Orthod. 1953; 39(10):729-755.
[17] MERRIFIELD LL, KLONTZ HA, VADEN JL. Differential diagnostic analysis system. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1994;106(6):641-648.
[18] HOLDAWAY RA. A soft-tissue cephalometric analysis and its use in orthodontic treatment planning. Part I. Am J Orthod. 1983;84(1):1-28.
[19] 周晗.成人骨性Ⅱ类不同垂直骨面型下颌骨及颏部形态三维研究[D].大连:大连医科大学,2016.
[20] 管默.成年男性骨性Ⅲ类不同垂直骨面型软组织侧貌及颏部形态的研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2019.
[21] 韩保迪.安氏Ⅰ类错(牙合)不同垂直骨面型下颌骨和颅底形态的比较研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2008.
[22] 贾培增,吴威.不同垂直骨面型者的颏部形态[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2007,25(2):142-145.
[23] 舒艳,刘珺,陈杰,等.成人骨性Ⅲ类错不同垂直骨面型下颌骨及颏部的比较[J].上海口腔医学,2011,20(2):191-195.
[24] 李婧,樊永杰.女性青少年不同垂直骨面型颏部形态的研究[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2016,43(4):387-390.
[25] 孙毅.成人骨性Ⅱ类不同垂直骨面型患者切牙区和颏部形态的三维研究[D].福州:福建医科大学,2015.
[26] SIRIWAT PP, JARABAK JR. Malocclusion and facial morphology is there a relationship? An epidemiologic study. Angle Orthod. 1985;55(2): 127-138.
[27] KARLSEN AT. Craniofacial growth differences between low and high MP-SN angle males: a longitudinal study. Angle Orthod. 1995;65(5): 341-350.
[28] BJORK A.Variations in the growth pattern of the human mandible: longitudinal radiographic study by the implant method. J Dent Res. 1963;42(1)Pt 2:400-411.
[29] ENLOW DH. The Human Face: An Account of the Postnatal Growth and Development of the Craniofacial Skeleton. New York: Hoeber Medical Division, Harper and Row Publishers, 1968.
[30] FERRARIO VF, SFORZA C, DE FRANCO DJ. Mandibular shape and skeletal divergency. Eur J Orthod. 1999;21(2):145-153.
[31] NAKAWAKI T, YAMAGUCHI T, TOMITA D, et al. Evaluation of mandibular volume classified by vertical skeletal dimensions with cone-beam computed tomography. Angle Orthod. 2016;86(6):949-954. |