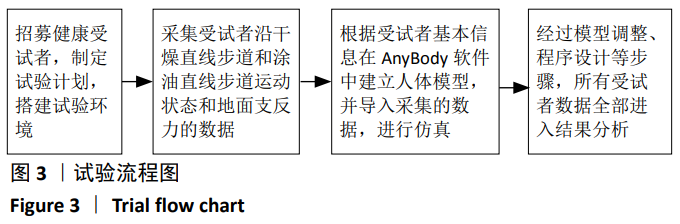
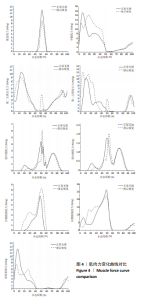
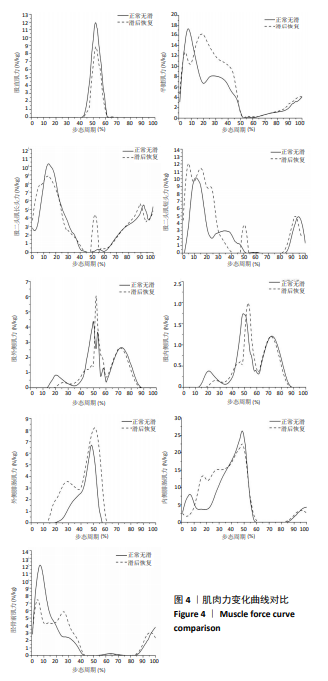
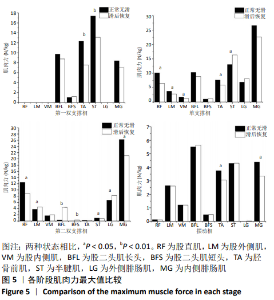
[1] Nonfatal occupational injuries and illnesses requiring days away from work, 2013.U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics: Washington D.C, 2014.
[2] Fatal occupational injuries by event or exposure, 2013-2014. U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics: Washington D.C, 2015.
[3] CHAM R, REDFERN MS. Lower extremity corrective reactions to slip events. J Biomech. 2001;34:1439-1445.
[4] Center for Disease Control, CDC Facts Book 2000/2001; 2000.
[5] LIU J, LOCKHART TE. Age-related joint moment characteristics during normal gait and successful reactive-recovery from unexpected slip perturbations. Gait Posture. 2009;30:276-281.
[6] DEBBIA EM, WOLFA A, HAIMA A. Detecting and quantifying global instability during a dynamictask using kinetic and kinematic gait parameters. J Biomech. 2012;45:1366-1371.
[7] DAMSGAARD M, RASMUSSEN J, CHRISTENSEN ST. Analysis of musculoskeletal systems in the AnyBody Modeling System. Simul Mod Pract Theor.2006;14:1100-1111
[8] STAMBOLIAN D, ELTOUKHY M, ASFOUR S. Development and validation of a three dimensional dynamic biomechanical lifting model for lower back evaluation for careful box placement. Int J Industr Ergon.2016;54: 10-18.
[9] 刘述芝,胡志刚,张健.冲击载荷下运动员下肢动态响应的逆动力学仿真[J].医用生物力学,2015, 30(1):30-37.
[10] TRINLER U, SCHWAMEDER H, BAKER R. Muscle force estimation in clinical gait analysis using anybody and opensim. J Biomech. 2019;86: 55-63.
[11] YANG BS, HU HY. Effect of floor material change on gait stability. ICBME. 2009:1797-1800.
[12] CHANG WR, LESCH MF, CHANG CC, et al. Contribution of gait parameters and available coefficient of friction to perceptions of slipperiness. Gait Posture. 2015;41:288-290.
[13] LAWRENCE D, DOMONE S. Gait adaptations to awareness and experience of slip when walking on a cross-slope. Gait Posture. 2015; 15:575-579.
[14] SOUZA SILVA W, MCFADYEN BJ, FUNG J, et al. Reading text messages at different stages of pedestrian circumvention affects strategies for collision avoidance in young and older adults. Gait Posture. 2020;76: 290-297.
[15] DAMSGAARD M, RASMUSSEN J, CHRISTENSEN ST,et al. Analysis of musculoskeletal systems in AnyBody Modeling System. Sim Mod Practi Theor. 2006;4(8):1100-1111.
[16] 茆军兵,贾晓红,王人成,等.头部前屈运动过程中颈肌特性的研究[J].医用生物力学,2012,27(5):577-579.
[17] 徐欢欢,何育民,孙朝阳等. AnyBody环境下人体步态的逆向动力学研究[J].机械科学与技术,2019,38(12):1819-1824.
[18] LEW FL, QU X. Effects of multi-joint muscular fatigue on biomechanics of slips. J Biomech.2014;47:59-64.
[19] QU X, HU X, LEW FL. Differences in lower extremity muscular responses between successful and failed balance recovery after slips. Int J Industr Ergon. 2012;42:499-504.
[20] HORLINGS CG, VAN ENGELEN BG, ALLUM JH, et al. A weak balance: The contribution of muscle weakness to postural instability and falls. Nat Clin Pract Neurol. 2014;4(9):505-515.
[21] 王静,吴效明.基于表面肌电的步态分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(26):4834-4840.
[22] 纪仲秋,赵盼超,蒋桂萍等.人体在向后滑倒时平衡调节能力的生物力学研究[J].北京师范大学学报(自然科学版),2018,54(2): 269-276.
[23] RAJACHANDRAKUMAR R, MANN J, SCHINKEL-IVY A, et al. Exploring the relationship between stability and variability of the centre of mass and centre of pressure. Gait Posture. 2018;63:254-259.
[24] WILSON SJ, DONAHUE PT, WILLIAMS CC, et al. Differences in falls and recovery from a slip based on an individual’s lower extremity corrective response. Int J Kinesiol Sports Sci. 2019;7(3):34-40.
[25] YOO D, SEO KH, LEE BC. The effect of the most common gait perturbations on the compensatory limb’s ankle, knee, and hip moments during the first stepping response. Gait Posture.2019; 71: 98-104.
[26] HUNTLEY AH, RAJACHANDRAKUMAR R, SCHINKEL-IVY A, et al. Characterizing slip-like responses during gait using an entire support surface perturbation: Comparisons to previously established slip methods. Gait Posture. 2019;69:130-135.
[27] OKUBO Y, BRODIE MA, STURNIEKS DL, et al. Exposure to trips and slips with increasing unpredictability while walking can improve balance recovery responses with minimum predictive gait alterations.PLOS ONE. 2019;13: e0202913.
[28] YANG J, JIN D, JI L,et al. The reaction strategy of lower extremity muscles when slips occur to individuals with trans-femoral amputation. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2007;17:228-240.
[29] CHAMBERS AJ, CHAM R. Slip-related muscle activation patterns in the stance leg during walking. Gait Posture. 2007;25:565-572.
[30] YANG F, WANG TY, PAI YC. Reduced intensity in gait-slip training can still improve stability. JBiomech. 2014;47:2330-2338.
[31] LEE A, BHATT T, PAI YC. Generalization of treadmill perturbation to overground slip during gait: effect of 31 different perturbation distances on slip recovery. J Biomech. 2016;49(2):149-154.
[32] 胡建平.太极拳运动对老年步态稳定性的功用[J].体育科技,2018, 39(3):94-95.
[33] OCONNELL C, CHAMBER A, MAHBOOBIN A, et al. Effect of slip severity on muscle activity of the trailing leg during an unexpected slip. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2016;28:61-66. |