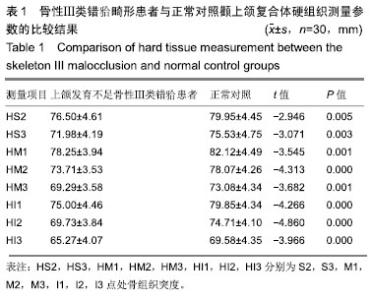
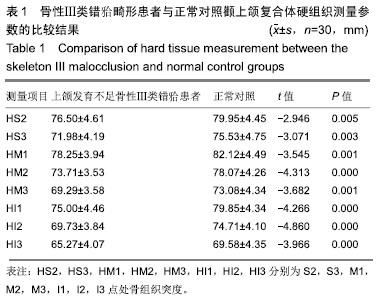
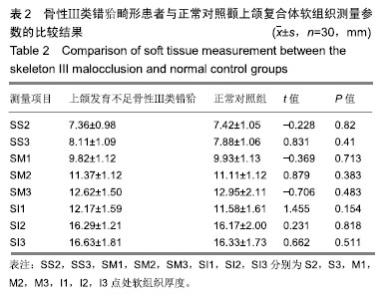
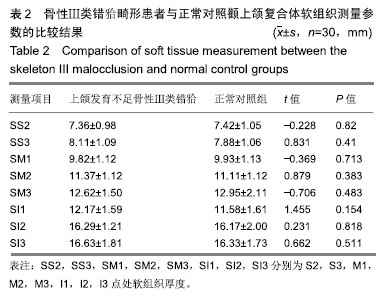
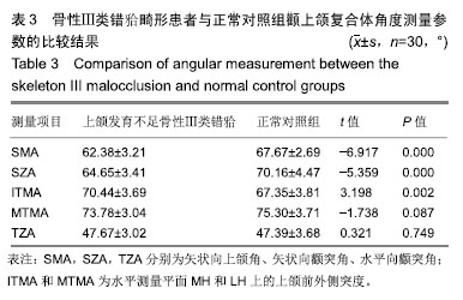
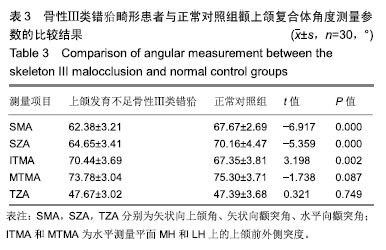
| [1]Gazzani F, Pavoni C, Cozza P, et al. Stress on facial skin of class III subjects during maxillary protraction: a finite element analysis. BMC Oral Health. 2019;19(1):31.[2]Ren CC, Bai YX. Effectiveness and long-term stability of maxillary protraction. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2018;53(10): 649-652. [3]Sendyk M, de Paiva JB, Abrão J, et al. Correlation between buccolingual tooth inclination and alveolar bone thickness in subjects with Class III dentofacial deformities. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2017;152(1):66-79.[4]Shi Y, Shang H, Tian L, et al. Three-dimensional study of facial soft tissue changes in patients with skeletal Class Ⅲ malocclusion before and after orthognathic surgery. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018;32(5):612-616. [5]De Clerck H, Cevidanes L, Baccetti T. Dentofacial effects of bone-anchored maxillary protraction: a controlled study of consecutively treated Class III patients. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2010;138(5):577-581.[6]Frey ST. New diagnostic tenet of the esthetic midface for clinical assessment of anterior malar projection. Angle Orthod. 2013; 83(5):790-794. [7]Bao T, Yu D, Luo Q, et al. Quantitative assessment of symmetry recovery in navigation-assisted surgical reduction of zygomaticomaxillary complex fractures. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2019;47(2):311-319. [8]Hayashi T, Arai Y, Chikui T, et al. Clinical guidelines for dental cone-beam computed tomography. Oral Radiol. 2018;34(2):89-104. [9]De Vos W, Casselman J, Swennen GR. Cone-beam computerized tomography (CBCT) imaging of the oral and maxillofacial region: a systematic review of the literature. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009; 38(6):609-625.[10]傅民魁.口腔正畸学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2012.[11]Johnston L,许天民,腾起民.Johnston头影测量技术图解手册[M].北京:北京大学医学出版社,2011.[12]Chen D, Chen CH, Tang L, et al. Three-dimensional reconstructions in spine and screw trajectory simulation on 3D digital images: a step by step approach by using Mimics software. J Spine Surg. 2017; 3(4):650-656. [13]Almeida GA. Class III malocclusion with maxillary deficiency, mandibular prognathism and facial asymmetry. Dental Press J Orthod. 2016;21(5):103-113. [14]Chien PC, Parks ET, Eraso F, et al. Comparison of reliability in anatomical landmark identification using two-dimensional digital cephalometrics and three-dimensional cone beam computed tomography in vivo. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2009;38(5):262-273.[15]Nocini PF, Boccieri A, Bertossi D. Gridplan midfacial analysis for alloplastic implants at the time of jaw surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;123(2):670-679.[16]崔娅铭.现代各主要人群中面部3D几何形态的对比[J].人类学学报, 2016,35(1):89-100.[17]Park HC, Lee JW. Study of horizontal skeletal pattern and dental arch in skeletal Class III malocclusion patients. Korean J Orthod. 2008;38(5):358-370.[18]Kamburo?lu K, Kir?an Büyükkoçak B, Acar B, et al. Assessment of zygomatic bone using cone beam computed tomography in a Turkish population. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2017;123(2):257-264. [19]Enlow DH, McNamara JA Jr. The neurocranial basis for facial form and pattern. Angle Orthod. 1973;43(3):256-270.[20]Choi JY, Lee SH, Baek SH. Effects of facial hard tissue surgery on facial aesthetics: changes in facial content and frames. J Craniofac Surg. 2012;23(6):1683-1686.[21]Precious D, Delaire J. Balanced facial growth: a schematic interpretation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1987;63(6):637-644.[22]Enlow DH, Hans MG. Essentials of Facial Growth. W.B. Saunders Company, 1996.[23]Nguyen T, Cevidanes L, Cornelis MA, et al. Three-dimensional assessment of maxillary changes associated with bone anchored maxillary protraction. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2011;140(6): 790-798. [24]胡骁颖.上颌牵引应力分布三维有限元分析及Angle'sⅢ错上颌前牵引临床矫治研究[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2012.[25]刘艳丽,赵薇,张碧莹,等.生长发育期骨性III类错畸形骨支抗上颌前牵引的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志, 2019,46(1):112-117.[26]Morris DE, Moaveni Z, Lo LJ. Aesthetic facial skeletal contouring in the Asian patient. Clin Plast Surg. 2007;34(3):547-556.[27]李海涛,李鸣,董刚,等.不同垂直颅面结构年轻女性嚼肌超声厚度及肌电活动的相关性研究[J].中国美容医学, 2011,20(5):131-132.[28]Kim MG, Lee JW, Cha KS, et al. Three-dimensional symmetry and parallelism of the skeletal and soft-tissue poria in patients with facial asymmetry. Korean J Orthod. 2014;44(2):62-68. [29]刘艳丽,赵薇,张碧莹,安晓莉.生长发育期骨性Ⅲ类错畸形骨支抗上颌前牵引的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志, 2019,46(1):112-118.[30]Jung JH, Kim SS, Son WS, et al. Soft tissue change of the midface in skeletal class III orthognathic surgery patients. Korean J Orthod. 2008;38(2):83-94. |