Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (19): 3055-3062.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2071
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes and regenerative medicine: outlook for future cell-free therapy in clinical practice
Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Chen Xiaoxu, Yang Kun
- Department of Periodontology, Hospital of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2019-10-09Revised:2019-10-11Accepted:2019-11-15Online:2020-07-08Published:2020-04-09 -
Contact:Yang Kun, MD, Associate professor, Department of Periodontology, Hospital of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Luo Yaxin, Master candidate, Department of Periodontology, Hospital of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81760199; the Science and Technology Foundation of Guizhou Province, No. [2018]1185
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Chen Xiaoxu, Yang Kun. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes and regenerative medicine: outlook for future cell-free therapy in clinical practice[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(19): 3055-3062.
share this article
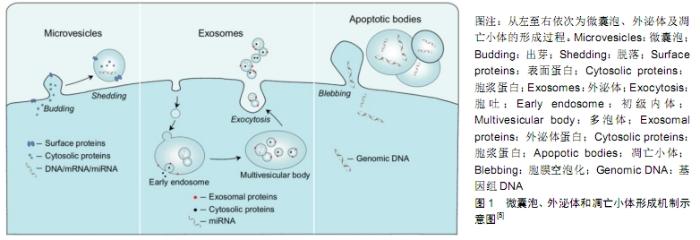
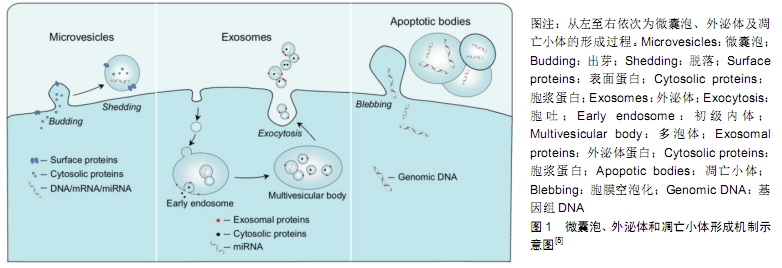
2.1 外泌体的定义 细胞外囊泡(extracellular vesicles,EVs)是内源性产生的膜结合囊泡,具有磷脂双分子层,其内包含各种分子,可根据细胞起源和生物发生而分为微囊泡、外泌体和凋亡小体[5],见图1。过去,细胞外囊泡一直被认为是细胞废弃物,直到近些年才逐渐引起研究者们的兴趣。它们的来源、大小和内容物各有所区 别[6],其中外泌体(Exosome)是一种存在于细胞外的多囊泡体,可通过细胞内吞泡膜向内凹陷形成多泡内涵体,内涵体与细胞膜融合后释放其中的小囊泡。此过程可将腔内囊泡释放到细胞外的环境中[7]。1987年,JOHNSTONE等[8]在网织红细胞的成熟过程中发现它的存在并命名为“外泌体”。它是一种区别于微泡具有特异脂质、蛋白、信使RNA(mRNA)和微小非编码RNA (miRNA)的微小膜性囊泡结构[9],其大小均一,直径为40-100 nm,密度为1.10-1.18 g/mL。外泌体可由血小板、树突状细胞、淋巴细胞、间充质干细胞和肿瘤细胞等多种类型细胞主动分泌释放,在大多数体液以及细胞上清中都能被检测到[10-12]。 "

2.2 外泌体的组成 外泌体内主要含有核酸、蛋白质和脂质等[13-15],这些物质也各自发挥着自己的功能,例如作为疾病诊断标记物[16]、调控靶细胞功能[17]、参与细胞生物学活动等。近年来,大量研究发现蛋白质、mRNAs、miRNAs可参与调控多种原因导致的组织缺损再生修复。文献报道存在于外泌体表面的蛋白质可以与受体细胞上的细胞表面受体结合,从而诱导细胞内信号传导[18]。TAO等[19]研究发现含有miR-140-5p的滑膜间充质干细胞来源外泌体(SMSC-Exo)可影响软骨组织再生,通过对miR-140-5p进行调控以及动物实验验证miR-140-5p的过表达可促进软骨组织的再生。QIN等[20]发现骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体携带的miR-196a在调节成骨细胞分化和成骨基因的表达中起着至关重要的作用,从而促进大鼠颅骨缺损的骨再生。将含外泌体的内皮细胞植入到免疫缺陷小鼠中,可形成血管网状结构,而当核糖核酸酶预处理外泌体后可减弱其成血管能力,分析表明外泌体中包含有与成血管相关的通路和内皮型一氧化氮合酶信号通路mRNA,从而促进血管生成[21]。 2.3 外泌体的提取方法 根据大量文献报道,外泌体的提取方法多样,可根据它的物理及生物特性分为以下几类提取方式,见表1。 "


2.3.1 超速离心法 超速离心法是一种根据外泌体的密度及尺寸进行分离的方法,其主要利用不同物质(如蛋白质、囊泡、细胞及细胞碎片等)在悬浮液中的沉降速度存在差异,通过逐渐增强离心力及离心时间来分离细胞、碎片和细胞器等,从而得到外泌体[22]。该方法包括一系列离心过程:首先300×g离心10 min,2 000×g离心10 min去除死亡细胞,10 000×g离心30 min去除细胞碎片和大分子蛋白质,用0.22 μm滤膜过滤除去凋亡小体和微囊泡,然后100 000×g离心2 h得到外泌体,最后用PBS清洗沉淀以去除可溶的干扰蛋白质,并可于-80 ℃冻存[23]。在该方法中,外泌体的提取效率受离心力、样本黏度、PBS清洗次数等因素的影响。超速离心法是目前外泌体分离的“金标准”且为外泌体提取的最常用方法[24],其优势包括方法成熟、适用于大体积样本。然而,该方法的缺点在于仪器设备昂贵,操作耗时费力,所得的外泌体易受蛋白质聚合体和脂蛋白的干扰,外泌体易聚集成块[25]。 2.3.2 密度梯度离心法 密度梯度离心法相比传统的超速离心法更为严格,能够根据样品密度进一步纯化,以清除由蛋白质等造成的干扰,使得到的外泌体纯度更高[22]。常用的分离介质包括碘克沙醇和蔗糖[26-27]。以蔗糖为例,实际操作时需要预先制备不同浓度梯度(2.0,1.3,1.16,0.8,0.5和0.25 mol/L)的蔗糖/D2O溶液,随后加入待分离物质;在100 000×g条件下离心2.5 h[28],外泌体将在等密度区域(1.13-1.19 g/mL)驻留,收集该组分即可得纯化的外泌体。密度梯度离心法相较于传统差速离心法提取的外泌体更纯,但是操作较为繁琐。 2.3.3 超滤法 超滤法是利用不同截留相对分子质量(MWCO)的超滤膜离心分离外泌体。截留相对分子质量是指能自由通过某种有孔材料的分子中最大分子的相对分子质量。外泌体是一个囊状小体,相对分子质量大于一般蛋白质,因此选择不同大小的截留相对分子质量超滤膜可使外泌体与其他大分子物质分离。该方法通常选用截留分子质量为100 kD的超滤管,能够在提取外泌体的同时浓缩样本量[29]。这种操作简单、省时,可在低转速下提取到外泌体,不影响外泌体的生物活性,但滤膜吸附的囊泡和蛋白质不仅严重影响外泌体的提取效率,还可能堵塞滤孔,降低滤膜的寿命[30]。 2.3.4 沉淀法 沉淀法是商业化外泌体提取试剂盒通常采用的策略,其中聚乙二醇是目前最常用的沉淀试剂。它具有极强的亲水性,可与疏水性的脂质双分子层结合,改变外泌体的溶解度或分散性使其沉淀[23]。该方法通过常规离心即可实现分离,若配合0.22 μm滤膜可提高外泌体的纯度。基于沉淀原理的试剂盒均加入了 聚乙二醇,其主要是先在低速离心条件下去除细胞碎片和蛋白质等,然后再加入试剂均匀混合,根据说明书要求静置一段时间后离心得到外泌体。而不同品牌的外泌体提取试剂盒的用法和用量可能会存在差异,具体提取方法应根据说明书进行操作。有研究分别用Total Exosome Isolation试剂盒、Exo Quick试剂盒及差速超速离心法3种方法提取人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体并进行比较[31],发现超速离心法提取的外泌体中的蛋白浓度及纯度最高,Exo Quick试剂盒法其次,Total Exosome Isolation试剂盒法得到的蛋白浓度最低;但差速超速离心法和Total Exosome Isolation试剂盒法耗时长。沉淀法操作简便、快速,外泌体回收率也较高[32],然而提取产物中混杂大量的蛋白质和RNA,纯度较差,而且其中的聚合物较难去除,对下游分析会产生一定不良影响[33]。 2.3.5 免疫磁珠法 免疫磁珠是包被有单克隆抗体的球型磁性微粒,它可特异性地与靶物质结合[34]。在超速离心的基础上,预先使磁珠包被含有外泌体相关抗原的抗体(如CD9、CD63、Alix),并与外泌体共同孵育,再用蒸馏水洗涤,重悬于PBS中[35]。这种方法可以保证外泌体形态的完整,特异性高、操作简单、无需特殊及昂贵的仪器设备,但是对pH值和生理性盐浓度要求较高,否则会影响外泌体生物活性,不利于后续实验的开展。 2.4 外泌体的功能 外泌体具有多种生物学功能,主要可分为以下几点。 2.4.1 清除废弃物质 在过去,外泌体一直被认为是细胞代谢的废弃物。后来,研究发现外泌体可将网织红细胞成熟过程中多余的转铁蛋白受体清除[36]。红细胞成熟过程中会释放外泌体,外泌体中富含大量转铁蛋白受体,而转铁蛋白受体可通过与热休克同源70 kD蛋白相互作用而从红细胞表面消失。 2.4.2 介导细胞间信息传递 细胞之间存在信息交流,它是多细胞生物中的关键过程,通常通过直接的细胞接触或分泌旁分泌因子转移来实现。外泌体作为间充质干细胞旁分泌的重要产物之一,是细胞交流过程中传递信息的一种关键物质,同样也被越来越多的研究证实在此活动中的重要性。细胞内传递蛋白质以取代功能失调蛋白并调节细胞信号通路已被认为是调控细胞功能和治疗疾病的最直接和有效的途径。利用生物素键合外泌体可有效传递蛋白质和生物素结合物,突出了含叠氮外泌体胞内传递的优势和多功能性,该策略应易于适应各种亲和素融合或生物素结合药物的传递[37]。 2.4.3 产生免疫耐受 外泌体的体积微小,因此不易被机体免疫细胞识别和清除而表现出低免疫状态。树突状细胞是免疫系统中的重要细胞,研究发现由未成熟的树突状细胞释放的外泌体是介导自身免疫耐受的重要中介之一。由外泌体呈递的供体MHC抗原可以调节同种异体移植排斥,并以供体特异性方式延长同种异体移植的存活时间,说明外泌体可以刺激或调节抗原特异性免疫反应[38]。 2.4.4 作为肿瘤治疗疫苗 癌症治疗需要具有低免疫原性和毒性的靶向药物递送载体,利用抗癌药物治疗肿瘤是抑制肿瘤的重要方法之一。外泌体是治疗肿瘤疾病的一种新兴潜在手段。通过研究外泌体在紫杉醇(PTX)释放机制中的作用[39],发现用紫杉醇处理间充质干细胞后,间充质干细胞可以通过吸收和释放紫杉醇从而获得强大的抗肿瘤活性,进一步研究发现该药物被内化在间充质干细胞来源外泌体中并产生一定积累。装载有紫杉醇的SR4987细胞(SR4987PTX)可分泌大量的紫杉醇,SR4987PTX来源外泌体对人胰腺癌细胞(CFPAC-1)具有很强的抗增殖活性,证明间充质干细胞能够通过外泌体包装和递送紫杉醇,成功为外泌体运载抗癌药物进行体内肿瘤治疗奠定了基础。研究发现通过化学转染使小鼠未成熟树突状细胞来源外泌体表面含有Lamp2b[40],并与av整合蛋白特异性iRGD肽结合,从而可促进肿瘤的靶向性。静脉注射含阿霉素的iRGD-外泌体可将阿霉素传递到BALB/c裸鼠的肿瘤组织中,其能够抑制肿瘤生长而无明显毒性。通过靶向配体修饰的外泌体可治疗性地将阿霉素递送至肿瘤,因此在临床应用中具有巨大的潜在价值。 随着对外泌体越来越深入的研究,人们发现它发挥的作用可涉及多个领域,如免疫调控、肿瘤相关治疗、肝脏炎症及中枢系统感染性疾病等。近年来,间充质干细胞来源外泌体已被鉴定为细胞间信息交流的潜在载体,外泌体相关的科学研究正在再生医学领域中大放光彩,关于外泌体的研究也有了突飞猛进的发展,外泌体在间充质干细胞修复损伤组织和组织再生中起到的关键作用而得到越来越多的重视。 2.5 外泌体与再生医学 研究表明,间充质干细胞来源外泌体与间充质干细胞有着相似的功能[41],包括修复与再生组织、抑制炎症反应及调节机体免疫,但外泌体相对于间充质干细胞又有许多优势。首先,间充质干细胞来源外泌体更稳定,更好保存,易于管理和控制,可以人为改变其内容物的种类和数量,可根据需要调节用量;其次,它们没有活细胞,不会像间充质干细胞那样可能会过多增殖而放大疗效或者癌变导致疾病加重[42];另外,它有可能避免某些针对间充质干细胞的调控问 题[43],间充质干细胞来源外泌体有代替间充质干细胞的趋势,从依赖间充质干细胞的细胞替代疗法向依赖间充质干细胞来源外泌体的生物疗法转变。外泌体作为间充质干细胞旁分泌活动的重要方式,在组织再生中发挥重要作用[44]。 2.5.1 皮肤损伤修复 皮肤伤口通常需要精细组织修复,愈合不良会产生瘢痕,若发生坏死,不仅会破坏皮肤的屏障功能,而且对疼痛、温度和触感的感知也会发生变化。因此,寻找一种替代方法来加速伤口愈合至关重要。FANG等[45]研究发现,脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体(uMSC-Exos)的miR-21、miR-23a、miR-125b和miR-145抑制TGF-β2、TGF-bR2和SMAD2,从而抑制靶基因α-SMA的表达和减少胶原蛋白Ⅰ沉积。这些脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体衍生的miRNAs可能是TGF-β/SMAD信号的重要调节因子,可抑制皮肤伤口愈合过程中肌成纤维细胞的分化从而减少瘢痕形成促进皮肤伤口的愈合。ZHANG等[46]研究结果显示脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体可通过传递Wnt4激活皮肤细胞中的Wnt/β-连环蛋白来促进伤口愈合,并通过激活AKT途径抑制急性热应激诱导的皮肤细胞凋亡,表明脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体可以促进皮肤烧伤修复,而Wnt4是皮肤伤口愈合过程分子机制中的关键介质。Hu等[47]发现经脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体(ASCs-Exos)处理的小鼠皮肤伤口愈合比对照小鼠更快,表明脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体可以加速皮肤伤口愈合。组织学分析显示在伤口愈合早期脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体可增加胶原蛋白Ⅰ和Ⅲ的表达,而在伤口愈合晚期,脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体可能抑制胶原蛋白表达以减少瘢痕形成。研究结果表明,脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体可以通过优化成纤维细胞的特性(如促进成纤维细胞的迁移、增殖和胶原合成)从而促进软组织的伤口愈合。ZHANG等[48]研究发现脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体被成纤维细胞摄取,其细胞增殖和迁移的剂量依赖性也显著增加;更重要的是,成纤维细胞中Ⅰ型胶原、Ⅲ型胶原、基质金属蛋白酶1、碱性成纤维细胞生长因子、转化生长因子β1的mRNA和蛋白水平均增加;此外,脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体显著加速体内伤口愈合并在体外增加PI3K/Akt水平。后期实验也证实脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体可通过PI3K/Akt信号传导途径促进成纤维细胞增殖和迁移并优化胶原沉积,以进一步加速伤口愈合。DING等[49]通过对人骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体进行去铁胺预处理(DFO-Exos),并建立链脲佐菌素诱导的糖尿病大鼠模型,然后进行组织学分析来测量伤口愈合效果,并且评估新血管形成情况。结果发现,DFO-Exos通过miR-126介导的PTEN下调激活PI3K/AKT信号通路,从而在体外刺激血管生成,表明DFO-Exos有助于增强体内链脲佐菌素诱导的糖尿病大鼠的伤口愈合和血管生成。 2.5.2 骨损伤修复 骨损伤的愈合是一个涉及一系列生理活动的复杂过程,骨折部位的各种干细胞增殖和分化在愈合中起着至关重要的作用。随着干细胞技术的兴起,越来越多的研究将干细胞用于治疗多种疾病。近年来,研究人员将干细胞衍生的外泌体应用于骨损伤修复。ZHANG等[50]将间充质干细胞来源外泌体与软骨细胞共培养后,间充质干细胞来源外泌体中CD73介导的AKT和ERK信号传导的腺苷活化促进软骨修复过程中细胞迁移、增殖和基质合成;将其植入动物缺损模型后,可显著增加软骨细胞的数量,使软骨缺损得以愈合。ZHOU等[51]分别对大鼠骨折部位采用人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体、空白对照和PBS注射处理,结果显示人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体组β-catenin、Wnt3a的蛋白表达水平及COL-1、OPN和RUNX2的表达水平均高于其余两组;Micro-CT扫描结果也发现人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体组大鼠骨折部位的愈合情况优于空白对照组和PBS注射组,进一步研究发现人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体可能通过Wnt信号传导途径参与大鼠骨折的修复。LI等[52]建立类固醇激素引起的股骨头坏死大鼠模型,并将人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体注射到部分股骨头坏死大鼠模型的坏死骨髓腔中,以观察其对坏死骨组织的修复作用。结果显示:与对照组相比,人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体组骨组织坏死明显改善,其主要表现为骨细胞凋亡减少,骨小梁重建水平增加,坏死骨组织中血管生成增加,同时血管内皮生长因子、骨形态发生蛋白2的mRNA和蛋白水平上调。CHEN等[53]发现富含miR-375的人脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体可以将miRNA载体递送至人骨髓间充质干细胞,从而抑制IGFBP3的表达以发挥成骨作用。LI等[54]研究表明人脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体在体外具有促进人骨髓间充质干细胞迁移、增殖和成骨分化的能力。将人脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体与聚乳酸-乙醇酸共聚物/聚多巴胺支架结合植入小鼠颅骨缺损部位可增强其缺损部位的骨再生,从而证实人脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体可为骨组织工程提供一种新的治疗方法。FURUTA等[55]发现注射人骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体可挽救CD92/2小鼠骨折愈合的延迟,而无外泌体组未能加速骨折修复。 2.5.3 心血管损伤修复 尽管目前医疗水平已有了飞速发展,但心血管疾病的发病率和死亡率仍然很高,且预后不佳。干细胞治疗策略的出现可能代表心血管疾病的治疗前景,尤其是间充质干细胞来源外泌体。BIAN课题组[56]发现间充质干细胞来源外泌体能通过促进血管形成保护心脏组织,推断间充质干细胞来源外泌体的促血管生成活性在保护缺血性心脏损伤中发挥至关重要的作用。间充质干细胞来源外泌体可通过协调多种细胞过程(如迁移、增殖、基质合成、细胞浸润和细胞因子的产生等)从而实现最佳的组织缺损再生修复。MA等[57]将Akt转染到人脐带间充质干细胞中,然后再分离出外泌体(Akt-Exo),发现其在体外可促进内皮细胞增殖、迁移以及形成管状结构,同时血小板来源生长因子D(PDGF-D)的表达显著上调;然后从PDGF-D-siRNA转染的人脐带间充质干细胞中提取外泌体(siRNA-Akt-Exo)并作用于内皮细胞,发现由Akt-Exo诱导的促进作用明显减弱,表明PDGF-D在Akt-Exo介导的血管生成中起着重要作用。然后他们创建大鼠急性心肌梗死模型,通过尾静脉注射Akt-Exo后发现大鼠心脏功能得到明显改善,从而说明Akt-Exo通过促进血管生成在心肌梗死治疗中发挥作用,PDGF-D是Akt-Exo介导血管生成中的关键因素。张静等[58]通过建立脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体与人脐静脉血管内皮细胞共培养体系,发现脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体可以进入人脐静脉血管内皮细胞胞质,并促进人脐静脉血管内皮细胞增殖、迁移及管样分化;将脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体注入裸鼠皮下,观察到血管数量显著高于对照组。由此可见,脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体可促进人脐静脉血管内皮细胞增殖、迁移及管样结构形成,并可在体内促进血管新生,可用于组织工程血管的构建。 2.5.4 肌肉损伤修复 肌组织的再生受到一系列因素的精细调控,包括细胞内在转录因子、信号通路和外界的微环境。随着细胞治疗技术的发展,应用干细胞衍生物治疗肌肉损伤是今后的发展趋势。WANG等[59]建立巨大肩袖撕裂大鼠模型,并立即向模型大鼠的棘上肌局部注射脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体,术后观察发现脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体对肩袖撕裂可表现出抗炎、抗凋亡和促增殖作用,因此脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体可以防止肌肉萎缩并提供一种新的无细胞治疗方法来防止与肩袖撕裂相关的肌肉变性。NAKAMURA等[60]发现骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体通过促进C2C12细胞的增殖和分化使肌肉形成和血管生成增加,体外实验结果显示,骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体可在小鼠肌肉损伤模型中加速组织学肌肉再生,增强血管生成并减少纤维化,从而在骨骼肌修复再生中起到一定的重要作用。 2.6 外泌体与口腔医学 近年来,口腔组织缺损的再生修复也越来越得到人们的重视,其中牙周组织缺损再生修复尤为重要。牙周组织是由牙周膜、牙槽骨、牙骨质和牙龈组成的复杂结构,如果管理不善或得不到治疗,该病通常会导致牙周支持组织缺损并最终发生牙齿脱落。而目前的临床治疗虽能在一定程度上控制及恢复牙周组织缺损,但仍不能达到理想效果。朱斌等[61]研究发现经人骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体处理后的人牙周膜干细胞增殖速率、克隆形成能力、碱性磷酸酶染色及茜素红染色定量表达显著高于对照组,同样其成骨基因Runx2、OCN、ALP、BSP和Col-Ⅰ的表达也显著高于对照组,说明人骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体可促进牙周膜干细胞的体外增殖和成骨分化,从而促进牙周组织缺损的再生修复。CHEW等[62]研究表明来自人间充质干细胞的外泌体通过激活AKT和ERK信号通路,促进牙周膜细胞的活性作用(如迁移和增殖),从而提高牙周缺损模型大鼠牙周组织的再生能力。MOHAMMED等[63]通过研究脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体在非手术牙周治疗中的作用,对大鼠下切牙进行结扎制造实验性牙周炎,14 d后对其进行龈下刮治和根面平整处理,再将脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体注入牙周袋内,经过一段时间后发现脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体组炎症浸润最少,并且牙周组织的新生也最明显。因此脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体可作为龈下刮治和根面平整的辅助治疗,从而提高非手术性牙周治疗的效果。 "

| [1] 许怡薇,冯凯,石炳毅.干细胞在再生医学领域的临床应用现状及其前景[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(36): 7163-7166. [2] LAI RC, YEO RW, LIM SK. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015;40:82-88. [3] 邓蓉蓉,谢伊旻,谢林.间充质干细胞归巢的研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(19):2879-2888. [4] HAN C, SUN X, LIU L, et al. Exosomes and Their Therapeutic Potentials of Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:7653489. [5] LAWSON C, VICENCIO JM, YELLON DM, et al. Microvesicles and exosomes: new players in metabolic and cardiovascular disease. J Endocrinol. 2016;228(2):R57-71. [6] ZHANG W, ZHOU X, ZHANG H, et al. Extracellular vesicles in diagnosis and therapy of kidney diseases. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016;311(5):F844-F851. [7] EDGAR JR. Q&A: What are exosomes, exactly? BMC Biol. 2016;14:46. [8] JOHNSTONE RM, ADAM M, HAMMOND JR, et al. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J Biol Chem. 1987;262(19):9412-9420. [9] YU S, CAO H, SHEN B, et al. Tumor-derived exosomes in cancer progression and treatment failure. Oncotarget. 2015; 6(35):37151-37168. [10] ALENQUER M, AMORIM MJ. Exosome Biogenesis, Regulation, and Function in Viral Infection. Viruses. 2015; 7(9):5066-5083. [11] LI XB, ZHANG ZR, SCHLUESENER HJ, et al. Role of exosomes in immune regulation. J Cell Mol Med. 2006;10(2): 364-375. [12] THÉRY C, AMIGORENA S, RAPOSO G, et al. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 2006;Chapter 3:Unit 3.22. [13] LÄSSER C, ELDH M, LÖTVALL J. Isolation and characterization of RNA-containing exosomes. J Vis Exp. 2012;(59):e3037. [14] SUBRA C, GRAND D, LAULAGNIER K, et al. Exosomes account for vesicle-mediated transcellular transport of activatable phospholipases and prostaglandins. J Lipid Res. 2010;51(8):2105-2120. [15] MORELLI AE, LARREGINA AT, SHUFESKY WJ, et al. Endocytosis, intracellular sorting, and processing of exosomes by dendritic cells. Blood. 2004;104(10):3257-3266. [16] BOON RA, VICKERS KC. Intercellular transport of microRNAs. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013;33(2):186-192. [17] 孙晓燕,陈宁,谢臻蔚.外泌体在软组织损伤后修复中的研究进展[J].中国医药指南,2018,16(28):32-34. [18] COLOMBO M, RAPOSO G, THÉRY C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2014;30: 255-289. [19] TAO SC, YUAN T, ZHANG YL, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-140-5p-overexpressing human synovial mesenchymal stem cells enhance cartilage tissue regeneration and prevent osteoarthritis of the knee in a rat model. Theranostics. 2017; 7(1):180-195. [20] QIN Y, WANG L, GAO Z, et al. Bone marrow stromal/stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles regulate osteoblast activity and differentiation in vitro and promote bone regeneration in vivo. Sci Rep. 2016;6:21961. [21] KALLURI R. The biology and function of exosomes in cancer. J Clin Invest. 2016;126(4):1208-1215. [22] GUPTA S, RAWAT S, ARORA V, et al. An improvised one-step sucrose cushion ultracentrifugation method for exosome isolation from culture supernatants of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):180. [23] 缪着,卢福琼,马波,等.人间充质干细胞外泌体研究进展[J].中国医药生物技术,2019,14(4):361-365. [24] LOBB RJ, BECKER M, WEN SW, et al. Optimized exosome isolation protocol for cell culture supernatant and human plasma. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:27031. [25] 高方园,焦丰龙,张养军,等.外泌体分离技术及其临床应用研究进展[J].色谱,2019,37(10):1071-1083. [26] KALRA H, ADDA CG, LIEM M, et al. Comparative proteomics evaluation of plasma exosome isolation techniques and assessment of the stability of exosomes in normal human blood plasma. Proteomics. 2013;13(22): 3354-3364. [27] KELLER S, RIDINGER J, RUPP AK, et al. Body fluid derived exosomes as a novel template for clinical diagnostics. J Transl Med. 2011;9:86. [28] RUNZ S, KELLER S, RUPP C, et al. Malignant ascites-derived exosomes of ovarian carcinoma patients contain CD24 and EpCAM. Gynecol Oncol. 2007;107(3): 563-571. [29] LAI RC, ARSLAN F, LEE MM, et al. Exosome secreted by MSC reduces myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury.Stem Cell Res. 2010;4(3):214-222. [30] ABRAMOWICZ A, WIDLAK P, PIETROWSKA M. Proteomic analysis of exosomal cargo: the challenge of high purity vesicle isolation. Mol Biosyst. 2016;12(5):1407-1419. [31] 郭莹,王秀伟,牛玉虎,等.人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体提取方法的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(9):1382-1388. [32] KIM J, SHIN H, KIM J, et al. Isolation of High-Purity Extracellular Vesicles by Extracting Proteins Using Aqueous Two-Phase System. PLoS One. 2015;10(6):e0129760. [33] ZAROVNI N, CORRADO A, GUAZZI P, et al. Integrated isolation and quantitative analysis of exosome shuttled proteins and nucleic acids using immunocapture approaches. Methods. 2015;87:46-58. [34] 卢婉,杨人强,王伶.外泌体的研究进展[J].生命的化学, 2013, 33(4):438-442. [35] JANSEN FH, KRIJGSVELD J, VAN RIJSWIJK A, et al. Exosomal secretion of cytoplasmic prostate cancer xenograft-derived proteins. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2009;8(6): 1192-1205. [36] GÉMINARD C, DE GASSART A, BLANC L, et al. Degradation of AP2 during reticulocyte maturation enhances binding of hsc70 and Alix to a common site on TFR for sorting into exosomes. Traffic. 2004;5(3):181-193. [37] WANG M, ALTINOGLU S, TAKEDA YS, et al. Integrating Protein Engineering and Bioorthogonal Click Conjugation for Extracellular Vesicle Modulation and Intracellular Delivery. PLoS One. 2015;10(11):e0141860. [38] PÊCHE H, HESLAN M, USAL C, et al. Presentation of donor major histocompatibility complex antigens by bone marrow dendritic cell-derived exosomes modulates allograft rejection. Transplantation. 2003;76(10):1503-1510. [39] PASCUCCI L, COCCÈ V, BONOMI A, et al. Paclitaxel is incorporated by mesenchymal stromal cells and released in exosomes that inhibit in vitro tumor growth: a new approach for drug delivery. J Control Release. 2014;192:262-270. [40] TIAN Y, LI S, SONG J, et al. A doxorubicin delivery platform using engineered natural membrane vesicle exosomes for targeted tumor therapy. Biomaterials. 2014;35(7):2383-2390. [41] YU B, ZHANG X, LI X. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(3):4142-4157. [42] LOU G, CHEN Z, ZHENG M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as a new therapeutic strategy for liver diseases. Exp Mol Med. 2017;49(6):e346. [43] KATSUDA T, KOSAKA N, TAKESHITA F, et al. The therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Proteomics. 2013;13(10-11): 1637-1653. [44] MERINO-GONZÁLEZ C, ZUÑIGA FA, ESCUDERO C, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Promote Angiogenesis: Potencial Clinical Application. Front Physiol. 2016;7:24. [45] FANG S, XU C, ZHANG Y, et al. Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomal MicroRNAs Suppress Myofibroblast Differentiation by Inhibiting the Transforming Growth Factor-β/SMAD2 Pathway During Wound Healing. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(10): 1425-1439. [46] ZHANG B, WANG M, GONG A, et al. HucMSC-Exosome Mediated-Wnt4 Signaling Is Required for Cutaneous Wound Healing. Stem Cells. 2015;33(7):2158-2168. [47] HU L, WANG J, ZHOU X, et al. Exosomes derived from human adipose mensenchymal stem cells accelerates cutaneous wound healing via optimizing the characteristics of fibroblasts. Sci Rep. 2016;6:32993. [48] ZHANG W, BAI X, ZHAO B, et al. Cell-free therapy based on adipose tissue stem cell-derived exosomes promotes wound healing via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Exp Cell Res. 2018;370(2):333-342. [49] DING J, WANG X, CHEN B, et al. Exosomes Derived from Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Stimulated by Deferoxamine Accelerate Cutaneous Wound Healing by Promoting Angiogenesis. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019: 9742765. [50] ZHANG S, CHUAH SJ, LAI RC, et al. MSC exosomes mediate cartilage repair by enhancing proliferation, attenuating apoptosis and modulating immune reactivity. Biomaterials. 2018;156:16-27. [51] ZHOU J, LIU HX, LI SH, et al. Effects of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on fracture healing in rats through the Wnt signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(11):4954-4960. [52] LI R, CHEN C, ZHENG RQ, et al. Influences of hucMSC-exosomes on VEGF and BMP-2 expression in SNFH rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(7): 2935-2943. [53] CHEN S, TANG Y, LIU Y, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-375-overexpressing human adipose mesenchymal stem cells promote bone regeneration. Cell Prolif. 2019;52(5): e12669. [54] LI W, LIU Y, ZHANG P, et al. Tissue-Engineered Bone Immobilized with Human Adipose Stem Cells-Derived Exosomes Promotes Bone Regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(6):5240-5254. [55] FURUTA T, MIYAKI S, ISHITOBI H, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Promote Fracture Healing in a Mouse Model. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(12):1620-1630. [56] BIAN S, ZHANG L, DUAN L, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote angiogenesis in a rat myocardial infarction model. J Mol Med (Berl). 2014;92(4):387-397. [57] MA J, ZHAO Y, SUN L, et al. Exosomes Derived from Akt-Modified Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improve Cardiac Regeneration and Promote Angiogenesis via Activating Platelet-Derived Growth Factor D. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(1):51-59. [58] 张静,易阳艳,阳水发,等.脂肪干细胞来源外泌体对人脐静脉血管内皮细胞增殖、迁移及管样分化的影响[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2018, 32(10):1352-1357. [59] WANG C, SONG W, CHEN B, et al. Exosomes Isolated From Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: A New Cell-Free Approach to Prevent the Muscle Degeneration Associated With Torn Rotator Cuffs. Am J Sports Med. 2019;47(13):3247-3255. [60] NAKAMURA Y, MIYAKI S, ISHITOBI H, et al. Mesenchymal-stem-cell-derived exosomes accelerate skeletal muscle regeneration. FEBS Lett. 2015;589(11): 1257-1265. [61] 朱斌,李楠,田自锋,等.骨髓间充质干细胞来源的外泌体促进牙周再生的体外研究[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2016,9(12):709-713. [62] CHEW JRJ, CHUAH SJ, TEO KYW, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes enhance periodontal ligament cell functions and promote periodontal regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2019; 89:252-264. [63] MOHAMMED E, KHALIL E, SABRY D. Effect of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells and Their Exo as Adjunctive Therapy to Nonsurgical Periodontal Treatment: A Histologic and Histomorphometric Study in Rats. Biomolecules. 2018; 8(4):E167. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Wu Xun, Meng Juanhong, Zhang Jianyun, Wang Liang. Concentrated growth factors in the repair of a full-thickness condylar cartilage defect in a rabbit [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1166-1171. |
| [3] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [4] | Zhao Min, Feng Liuxiang, Chen Yao, Gu Xia, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Exosomes as a disease marker under hypoxic conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1104-1108. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Liu, Zhou Qingzhu, Gong Zhuo, Liu Boyan, Yang Bin, Zhao Xian. Characteristics and manufacturing techniques of collagen/inorganic materials for constructing tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 607-613. |
| [7] | Ye Haimin, Ding Linghua, Kong Weihao, Huang Zutai, Xiong Long. Role and mechanism of hierarchical microchanneled bone scaffolds in promoting osteogenesis and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 621-625. |
| [8] | Song Kaikai, Zhang Kai, Jia Long. Microenvironment and repair methods of peripheral nervous system injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 651-656. |
| [9] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [10] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [11] | Gao Kun, Chen Dayu, Zhang Yong, Liu Weidong, Sun Shufen, Lai Wenqiang, Ma Dujun, Wu Yihong, Lin Zhanpeng, Jiang Yinglu, Yu Weiji. Achyranthes bidentata alcohol extract inhibits extracellular matrix degradation of the cartilage by regulating synovial fibroblast exosomes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3636-3640. |
| [12] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [13] | Zhou Anqi, Tang Yufei, Wu Bingfeng, Xiang Lin. Designing of periosteum tissue engineering: combination of generality and individuality [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3551-3557. |
| [14] | Gan Lili, Xiong Na, Liu Yanfei. Hydrogel as drug scaffold in skin wound repair: challenges of clinical application possibilities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3578-3583. |
| [15] | Pan Xuan, Zhao Meng, Zhang Xiumei, Zhao Jie, Zhai Yunkai. Research and application of biological three-dimensional printing technology in the field of precision medicine: analysis of Chinese and English literature [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3382-3389. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||