Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (12): 1929-1934.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2507
Previous Articles Next Articles
Wounds repaired by flap transfer after total knee arthroplasty
Chen Jianguo1, 2, Qian Wenwei1, Peng Huiming1
- 1Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China; 2Plastic Surgery Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100144, China
-
Received:2019-08-02Revised:2019-08-03Accepted:2019-10-09Online:2020-04-28Published:2020-03-03 -
Contact:Peng Huiming, MD, Associate chief physician, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China -
About author:Chen Jianguo, Master candidate, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China; Plastic Surgery Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100144, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Beijing (General Project), No. 7192173
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Jianguo, Qian Wenwei, Peng Huiming. Wounds repaired by flap transfer after total knee arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(12): 1929-1934.
share this article
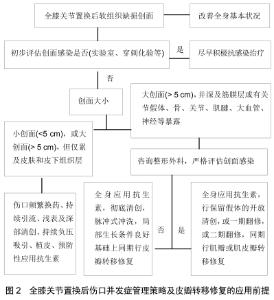
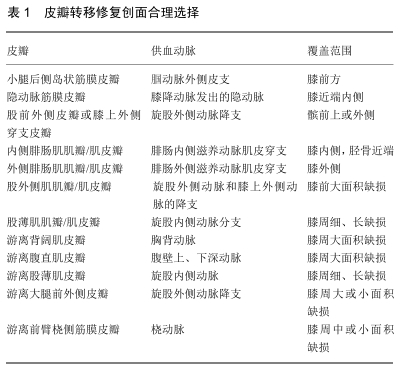
2.1 全膝关节置换后伤口并发症管理策略及皮瓣转移修复的应用前提 早期伤口并发症严重程度可依据短期伤口渗液、持续伤口渗液及全层软组织坏死进行简单区分,而治疗方案的选择取决于有无骨骼、肌腱和(或)假体暴露、有无污染和(或)伴随的感染、伤口的大小及深度等因素[9]。如患者合并糖尿病、类风湿性关节炎、吸烟、肥胖或营养不良等高风险因素,需积极改善全身健康状况。如伤口合并感染需迅速得出初步诊断并行抗感染治疗,避免发生急慢性假体关节感染,并且为后续伤口愈合提供良好环境[10]。如伤口无感染,一些浅表的小伤口可通过早期减少膝关节活动、伤口频繁换药、持续引流、浅表组织清创等创伤较小方法帮助健康肉芽组织生成达到二期愈合。如果伤口较大、较深,或未能通过局部伤口换药改善或患者无法忍受必要的伤口清创时,则应考虑返回手术室进行彻底的清创[6,8,11]。如果深大的伤口新鲜肉芽组织少、皮缘无法重新对合甚至合并感染,可考虑行伤口负压吸引治疗,其可以减少组织水肿、伤口碎片,维持清洁、无感染创面环境,改善局部血液循环,促进新鲜肉芽组织形成,达到二期愈合目的,或利于后续的植皮或皮瓣移植覆盖创面[12-13]。自体皮片或皮瓣移植需由骨科医生与整形外科医生共同评估、完成。对于存在皮肤及脂肪缺损但因张力过大无法行直接缝合的伤口,可选择行皮片移植,但在植皮前须确认假体被完整筋膜覆盖,创面有血供,并控制任何活动性感染。通常在大腿前外侧或后侧通过电动取皮肌选取刃厚或中厚皮片去覆盖创面,而供皮区平均愈合时间为9 d。在植皮早期,膝关节活动需受限,以防外力影响皮片存活;感染的存在亦能影响膝关节周围皮片存活。膝关节周围植皮最大的风险是皮肤挛缩,日后对膝关节的活动度产生负面影响[14-15]。 作者认为,如果膝关节周围创面过大并深及筋膜层或有假体、骨骼、肌腱等暴露,需尽早进行严格、系统的评估。少数情况软组织缺损创面为非感染因素导致或不存在感染,为避免深层组织或假体因暴露而发生感染风险,尽早的软组织覆盖创面尤为关键。经咨询整形外科医生,若患者全身状况良好,在预防性全身应用广谱抗菌药物基础上,彻底清创,脉冲式灌洗,同期直接行皮瓣转移修复(如局部皮瓣、肌瓣或肌皮瓣、游离皮瓣),从而减少假体取出、截肢风险,减少患者痛苦,降低医疗费用。多数情况软组织缺损创面为感染因素导致或存在感染,不能直接行皮瓣转移覆盖,而是骨科医生与整形外科医生协作综合考虑,在全身应用广谱抗菌药物基础上,一方面针对假体周围感染尽快、积极采取外科干预;另一方面,由于依靠表面伤口闭合或皮片转移覆盖暴露的假体或深部组织远期效果欠佳,应在改善创面局部生长环境基础上尽快行皮瓣移植修复,有望减少假体取出、截肢风险,减少患者痛苦,降低医疗费用。肌瓣或肌皮瓣由于血管化良好、体积大的特点,能较好地填充死腔,帮助输送抗菌药物,即使是在慢性感染的创面中也能为组织愈合提供良好生长环境,应作为覆盖全膝关节置换后感染性软组织缺损创面的首选。如肌瓣或肌皮瓣无法填充创面,也可以考虑选择游离皮瓣,其次是局部筋膜皮瓣或穿支皮瓣。作者认为,全膝关节置换后细菌在假体表面形成假膜一般需两三周,如感染性软组织缺损创面为急性阶段(<3周),并且病原菌数量少、毒性低,尚未出现耐药菌,即可考虑行保留假体的开放清创术,取出聚乙烯垫片,彻底清创,脉冲式冲洗,局部应用抗生素,在创面局部条件改善基础下同期行皮瓣转移修复。如感染性软组织缺损创面为3周至1个月内,未培养出耐药菌,软组织条件相对良好,可考虑行一期全膝关节翻修术。取出聚乙烯垫片和股骨、胫骨假体,彻底清创,脉冲式冲洗,局部应用抗生素,创面局部条件良好状况下同期行皮瓣转移修复。如感染性软组织缺损创面为慢性阶段(>1个月),并培养出耐药菌,软组织条件差,即可考虑行二期翻修术。取出假体,彻底清创,脉冲式冲洗,局部应用抗生素,放置抗生素骨水泥占位器,在创面局部条件改善基础下行肌瓣或肌皮瓣转移覆盖创面,以便为行第二期手术进一步创造良好生长环境。对于感染性软组织缺损创面,无论采取何种修复方式,术前、术后均需长期全身应用广谱抗菌药物治疗,术后可考虑行灌注引流,连续注入抗生素,提高局部抗菌药物浓度。皮瓣依据其组织类型、血供模式、与受区的空间关系、转移机制等进行分类,而选择何种皮瓣修复全膝关节置换后创面由组织缺损区的三维立体形状及位置决定,用于修复全膝关节置换后创面的皮瓣可考虑局部筋膜皮瓣、穿支皮瓣、肌瓣或肌皮瓣以及游离皮瓣等。骨科医生熟悉皮瓣的解剖位置对合理选择皮瓣同样重要。此次综述介绍了几种修复全膝关节置换后创面的皮瓣特点,有助于加深骨科医生对皮瓣的理解,从而减少因伤口并发症,避免进一步的假体暴露、假体周围感染、假体取出、截肢等严重并发症,见图2。 "

2.2.1 局部皮瓣转移修复 局部筋膜皮瓣由皮肤、皮下组织及深筋膜组成,该皮瓣薄、灵活、柔软、容易设计,可用来有效修复有浅表坏死或肉芽组织生成不足的膝关节周围软组织缺损,利于增加美学。局部筋膜皮瓣包含真皮内、皮下、筋膜多个血管网,即便是通过旋转进入创面,也能保证其在筋膜上下及真皮下水平的血供[16-17],可用于修复膝关节周围组织缺损的皮瓣包括小腿后侧岛状筋膜皮瓣、隐动脉筋膜皮瓣等。前者是以小腿外侧腓肠浅动脉及外侧腓肠皮神经为蒂的岛状筋膜皮瓣[18],外侧腓肠浅动脉即腘动脉外侧皮支,据报道出现率为100%。该皮瓣最大面积10 cm×9 cm,血管蒂长8.0-9.0 cm,能提供良好的外形、感觉,可用于修复膝前创面。隐动脉筋膜皮瓣可修复骨膝近端内侧创面[19-20],由膝降动脉发出的隐动脉供血。近10年来出现了应用局部筋膜皮瓣成功修复全膝关节置换后创面的报道。PAPAIOANNOU等[21]应用单侧或双侧V-Y局部筋膜皮瓣修复16例患者全膝关节置换后创面,其中成功覆盖了15例创面,另1例出现部分皮瓣坏死,但最终所有膝关节假体能成功保留并获得良好膝关节功能。陈昌伟等[22]学者报道了应用局部筋膜皮瓣成功修复全膝关节置换后创面。 此外,小腿局部穿支皮瓣转移修复全膝关节置换后创面逐渐受欢迎,但需注意评估血管供血的能力及其覆盖暴露骨块的能力。每一穿支血管提供一穿支体区或三维立体的血管分布范围,对应了该穿支皮瓣所能切取的最大范围。从深部血管发出的穿支能被超声识别,并基于该穿支走行方便设计出旋转推进皮瓣或自由式穿支蒂螺旋桨皮瓣[23]。获取穿支皮瓣对供区创伤小,可获得血供良好的全层健康软组织,避免因使用肌瓣或肌皮瓣带来肌肉损伤。逆行的股前外侧穿支皮瓣或膝上外侧穿支皮瓣由旋股外侧动脉降支供血,可提供皮肤、筋膜或肌肉,常用于各种肢体创面重建,如膝周、小腿中上段组织缺损的修复,修复面积可达20 cm×12 cm,但穿支动脉存在解剖变异。与腓肠肌肌瓣相比,膝外上穿支皮瓣供区能直接缝合,并发症少,但该穿支皮瓣在游离过程中有皮瓣尖端坏死、静脉淤血等风险[24-26]。 2.2.2 肌瓣和肌皮瓣 肌瓣为血供丰富的肌肉皮瓣,肌皮瓣包含血供丰富的肌肉及覆盖其的皮肤、皮下组织,但局部肌瓣或肌皮瓣因损伤肌肉功能。伤口裂开深及筋膜层时可能出现假体和(或)骨骼外露,创面长期不愈合,这时肌瓣或肌皮瓣为首选。然而在感染性伤口中,皮瓣的存活率仅为48%[27],在进行腓肠肌皮瓣转移修复之前应充分抗感染。腓肠肌肌瓣或肌皮瓣具有血供丰富、体积庞大、有效消除死腔、协助抗生素输送、加快慢性感染伤口愈合速度等优点,可用于修复胫骨近端和膝部创面。腓肠内外侧滋养动脉发出肌皮穿支分别供应内、外侧腓肠肌及对应的皮下组织和皮肤,且内侧头比外侧头长。内侧腓肠肌皮瓣可覆盖胫骨近端、膝内侧组织缺损,而外侧腓肠肌皮瓣限于修复膝关节外侧,内外侧腓肠肌皮瓣可以同时使用以修复更大的创面[28-30]。该皮瓣的主要缺点是供体部位不美观,容易损伤腓总神经。最早应用腓肠肌皮瓣修复全膝关节置换后创面历史可追溯到1989年[31],其后近10年来亦有关于腓肠肌皮瓣用于修复全膝关节置换后巨大创面的报道,并有助于避免假体取出、翻修、截肢等风险[32-33]。 此外,股外侧肌肌瓣或肌皮瓣由旋股外侧动脉和膝上外侧动脉的降支供血,腓肠肌皮瓣中腓肠肌伸肌功能受阻则无法提供足够皮瓣覆盖缺损较大的膝前方创面,此时需联合使用股外侧肌肌瓣或肌皮瓣,WHITESIDE[34]报道了该联合使用皮瓣的方法覆盖8例全膝关节置换后患者的巨大创面,尽管肌瓣或肌皮瓣覆盖有助于保住膝关节假体,但其膝关节活动功能受到影响。带蒂股薄肌肌瓣长而薄[35],同样能用于修复膝关节长区域创面,其由旋股内侧动脉分支支配,通常从患肢进行取皮瓣,从而将切口限制在单侧,并能简化皮瓣转移至膝部创面的定位过程,供区并发症少。 2.2.3 游离皮瓣移植 对于有广泛坏死及骨骼或假体外露的较大创面,肌肉或筋膜皮瓣不足且不存在其他局部皮瓣的情况下,游离皮瓣转移修复可能是最佳选择。游离皮瓣旋转完全自由,利于皮瓣设计和植入创面[36-37]。LOUER等[36]回顾性分析了34例修复膝关节创面的游离皮瓣,发现其成活率为97%。游离皮瓣修复膝部创面需要考虑的因素较多,如设计适当长的血管蒂与受区进行吻合、可预测的供体血管供应、适应膝关节表面的相对薄的皮瓣和合理设计符合缺损区大小和形状的皮瓣。覆盖膝关节周围的游离皮瓣供区包括背阔肌、股薄肌和腹直肌皮瓣,以及大腿前外侧或前臂桡侧筋膜皮瓣等。 游离背阔肌皮瓣具有宽阔和血供丰富的优点,能覆盖膝关节大面积的创面。血管蒂解剖稳定,供吻合的胸背动脉较粗,可长达12 cm,通常与旋股外侧动静脉降支吻合,需取供区刃厚皮片植皮修复。张明华等[38]采用游离背阔肌肌皮瓣成功修复25例膝关节周围大面积 (10 cm×8 cm至43 cm×23 cm)皮肤软组织缺损,术后患者均能站立及行走。游离腹直肌皮瓣除用于膝关节大面积缺损修复外,还可用于身体的多个区域。血管蒂中包含腹壁上、下深动脉。供区并发症包括腹部无力、腹胀或疝气,并且需要对腹直肌鞘进行加强修补。腹直肌游离皮瓣可依据组织缺损情况设计成纵行或横行的皮瓣,如缺损区呈纵行、缺损范围过大可设计成以健侧腹壁上动脉为蒂的岛状转移[39],也可以尝试用来修复膝关节周围组织缺损。PERRAULT等[40]报道了1例因膝关节假体周围感染经历多次大清创手术最终导致膝关节周围巨大组织缺损形成的患者,并发现合用内外侧腓肠肌皮瓣无法覆盖该创面,最终由纵行的腹直肌游离皮瓣覆盖,避免了截肢。游离股薄肌皮瓣可用于覆盖长而薄的创面,旋股内侧动脉为其蒂,皮瓣容易定位、获得,供体部位结构不会变弱,并且不影响美观[41]。大腿前外侧游离皮瓣面积大,可覆盖膝关节周围大或小的组织缺损[42],其血管蒂包含旋股外侧动脉降支,血管吻合容易,并且容易设计合适形状、厚度的皮瓣,更重要的是供体部位结构不会减弱,而且大腿部瘢痕容易被隐藏。JUNG等[43]报道了1例行腓肠肌肌皮瓣移植失败再次行逆行股薄肌皮瓣移植治疗的患者,最终能获得良好的扩大创面覆盖范围。同样,MITSALA等[44]报道了9例无法行游离皮瓣和带蒂腓肠肌皮瓣转移的患者,最终接受带蒂股薄肌皮瓣治疗,发现89%的患者能够保住膝关节假体。最后,前臂桡侧筋膜皮瓣是前臂掌侧一种薄的、可弯曲的肌间隔皮瓣[45],由桡动脉供血,其容易获得较长血管蒂,以便在膝关节近端进行吻合,但供体部位需要植皮,该种皮瓣可用于中或小的缺损创面。游离皮瓣转移修复极具挑战,同其他皮瓣转移一样影响膝关节活动度,但能覆盖巨大的膝关节周围创面。 "

| [1] GALAT DD, MCGOVERN SC, LARSON DR, et al. Surgical treatment of early wound com-plications following primary total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(1): 48-54. [2] ROCHE M, LAW TY, KUROWICKI J, et al. Albumin, realbumin, and transferrin may be pre-dictive of wound complications following total knee arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2018;31(10):946-951. [3] CARTER J, SPRINGER B, CURTIN BM. Early complications of revision total knee arthroplasty in morbidly obese patients. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2019;29(5):1101-1104. [4] BEDARD NA, DOWDLE SB, WILKINSON BG, et al. What Is the Impact of Smoking on Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty? J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(7): 172-176. [5] RAO AJ, KEMPTON SJ, ERICKSON BJ, et al. Soft Tissue Reconstruction and Flap Coverage for Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(7):1529-1538. [6] SIMONS MJ, AMIN NH, SCUDERI GR. Acute Wound Complications After Total Knee Ar-throplasty: Prevention and Management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2017;25(8):547-555. [7] GOTTFRIEDSEN TB, SCHRØDER HM, ODGAARD A. Knee Arthrodesis After Failure of Knee Arthroplasty: A Nationwide Register-Based Study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016;98(16): 1370-1377. [8] IORIO R, OSMANI FA. Strategies to prevent periprosthetic joint infection after total knee arthroplasty and lessen the risk of readmission for the patient. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2017; 25(1):13-16. [9] SCUDERI GR. Avoiding postoperative wound complications in total joint arthroplasty. J Ar-throplasty. 2018;33(10): 3109-3112. [10] ALRASHIDI Y, GALHOUM AE, WIEWIORSKI M, et al. How to Diagnose and Treat Infec-tion in Total Ankle Arthroplasty. Foot Ankle Clin. 2017;22(2):405-423. [11] SOUSA R, ABREU MA. Treatment of prosthetic joint infection with debridement, antibiotics and irrigation with implant retention - a narrative review. J Bone Jt Infect. 2018;3(3): 108-117. [12] HELITO CP, BUENO DK, GIGLIO PN, et al. Negative-pressure wound therapy in the treat-ment of complex injuries after total knee arthroplasty. Acta Ortop Bras.2017; 25(2),85-88. [13] KEENEY JA, COOK JL, CLAWSON SW, et al. Incisional negative pressure wound therapy devices improve short-term wound complications, but not long-term infection rate following hip and knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(4): 723-728. [14] LIU HH, CHANG CK, HUANG CH, et al. Use of split-thickness plantar skin grafts in the management of leg and foot skin defects. Int Wound J. 2018;15(5):783-788. [15] 俞泽浩,肖亮,邹崎葩,等.人工真皮复合自体刃厚皮片修复关节处皮肤缺损创面的临床研究[J].重庆医学,2014,(28):3727-3729. [16] MISRA A, NIRANJAN NS. Fasciocutaneous flaps based on fascial feeder and perforator ves-sels for defects in the patellar and peripatellar regions. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005; 115(6):1625-1632. [17] 汪洪源,王明刚,赵李平,等.小腿筋膜皮瓣修复局部软组织缺损的临床应用[J].解剖与临床,2011,16(3):221-224. [18] 章一新,张余光,杨军,等.小腿后侧岛状筋膜皮瓣血供的解剖观察及临床应用[J].中华整形外科杂志,2008,24(3):192-5. [19] KRISHNAMOORTHY VP, INJA DB, ROY AC. Knee extensor loss and proximal tibial soft tissue defect managed successfully with simultaneous medial gastrocnemius flap, saphenous fasciocutaneous flap and medial hemisoleus flap: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2013,18(7):76. [20] LU S, WANG C, WEN G, et al. Versatility of the greater saphenous fasciocutaneous perforator flap in coverage of the lower leg. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2014;30(3):179-186. [21] PAPAIOANNOU K, LALLOS S, MAVROGENIS A, et al. Unilateral or bilateral V-Y fasciocutaneous flaps for the coverage of soft tissue defects following total knee arthroplasty. J Orthopaedic Surg Res. 2010;5:82. [22] 陈昌伟,钱齐荣,吴海山,等.全膝关节置换术后感染的伤口处理[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2008,2(6):701-705. [23] KIM JT, KIM SW. Perforator Flap versus Conventional Flap. J Korean Med Sci. 2015;30(5):514-522. [24] LU D, CHAN P, FERRIS S, et al. Anatomic symmetry of anterolateral thigh flap perforators: a computed tomography angiographic study. ANZ J Surg. 2019;89(5):584-588. [25] 王海峰,李小河,李世元,等.旋股外侧动脉降支-膝上外侧动脉穿支逆行股前外侧皮瓣的临床应用[J].中华解剖与临床杂志,2017, 22(6):515-518. [26] NGUYEN AT, WONG C, MOJALLAL A. Lateral supragenicular pedicle perforator flap: clinical results and vascular anatomy. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011;64(3):381-385. [27] TETREAULT MW, DELLA VALLE CJ, BOHL DD, et al. What factors influence the success of medial gastrocnemius flaps in the treatment of infected TKAs? Clin Orthop Relat Res 2016; 474(3):752-763. [28] MAYOLY A, MATTEI JC, MOULLOT P, et al. Gastrocnemius myocutaneous flaps for knee joint coverage. Ann Plast Surg. 2018;81(2):208-214. [29] MANJUNATH KN, VENKATESH MS, SHIVAPRASAD A. Distal major pedicle of sartorius muscle flap: Anatomical study and its clinical implications. Indian J Plast Surg. 2018;51(1): 40-45. [30] LAMARIS GA, CARLISLE MP, DURAND P, et al. Maximizing the reach of the pedicled gastrocnemius muscleflap: a comparison of 2 surgical approaches. Ann Plast Surg. 2017; 78(3):342-346. [31] LIAN G, CRACCHIOLO A, LESAVOY M. Treatment of major wound necrosis following total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1989;4 Suppl: S23-32. [32] HOUDEK MT, WAGNER ER, WYLES CC, et al. Long-term outcomes of pedicled gas-trocnemius flaps in total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018;100(10):850-856. [33] TETREAULT MW, DELLA VALLE C, HELLMAN MD, et al. Medial Gastrocnemius Flap in the Course of Treatment for an Infection at the Site of a Total Knee Arthroplasty. JBJS Essent Surg Tech. 2017;10;7(2): e14. [34] WHITESIDE LA. Surgical technique: vastus medialis and vastus lateralis as flap transfer for knee extensor mechanism deficiency. Clin Orthopaedics Relat Res. 2013;471(1): 221-230. [35] MITSALA G, VAREY AH, O’NEILL JK, et al. The distally pedicled gracilis flap for salvage of complex knee wounds. Injury. 2014;45(11):1776-1781. [36] LOUER CR, GARCIA RM, EARLE SA, et al. Free flap reconstruction of the knee: an outcome study of 34 cases. Ann Plast Surg. 2015;74(1):57-63. [37] BIGDELI AK, THOMAS B, SCHMIDT VJ, et al. The conjoined parascapular and latissimus dorsi free flap for reconstruction of extensive knee defects. Microsurgery. 2018;38(8):867-875. [38] 张明华,崔旭,曾纪章,等. 游离背阔肌肌皮瓣修复膝关节周围大范围皮肤软组织深度缺损[J].中华烧伤杂志,2015,31(5): 337-339. [39] 梁尊鸿,潘云川,毛汉儒, 等.腹直肌肌皮瓣修复胸部慢性放射性溃疡的应用.中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2016,11(5):354-356. [40] PERRAULT D, MANRIQUE OJ, LEE G, et al. Complex reconstruction of the knee with a free vertical rectus abdominis flap after periprosthetic soft tissue necrosis. Cureus. 2019;11(1): e3969. [41] BESSET M, PENAUD A, QUIGNON R, et al. Donor site morbidity after free gracilis muscle flap. Report of 32 cases. Ann Chir Plast Esthet. 2014;59(1):53-60. [42] KANG CS, LEE JH, CHUNG KJ, et al. Vastus intermedius-anterolateral thigh chimeric free flap for lower extremity reconstruction. Arch Plast Surg. 2018;45(6): 604-605. [43] JUNG JA, KIM YW, CHEON YW, et al. Reverse gracilis muscle flap: an alternative means of skin coverage for recurrent infection after TKA. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013; 21(12):2779-2783. [44] MITSALA G, VAREY AH, O'NEILL JK, et al. The distally pedicled gracilis flap for salvage of complex knee wounds. Injury. 2014;45(11):1776-1781. [45] KHAN MA, JOSE RM, TAYLOR C, et al. Free radial forearm fasciocutaneous flap in the treatment of distal third tibial osteomyelitis. Ann Plast Surg. 2012;68(1):58-61. |
| [1] | Jiang Hongying, Zhu Liang, Yu Xi, Huang Jing, Xiang Xiaona, Lan Zhengyan, He Hongchen. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on pressure ulcers after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1149-1153. |
| [2] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [3] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [4] | Gan Lili, Xiong Na, Liu Yanfei. Hydrogel as drug scaffold in skin wound repair: challenges of clinical application possibilities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3578-3583. |
| [5] | Liu Fang, Shan Zhengming, Tang Yulei, Wu Xiaomin, Tian Weiqun. Effects of hemostasis and promoting wound healing of ozone sustained-release hydrogel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3445-3449. |
| [6] | Li Jie, Xu Jianzhen, Hu Ping, Lei Qiqi, Zhang Wenning, Ao Ningjian . Preparation and performance evaluation of carboxymethyl chitosan/oxidized glucomannan/Panax notoginseng compound sponge dressing for chronic wound [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2528-2534. |
| [7] | Chen Zhenyu, Zhang Xiaoning, Luo Yuxin, Liang Jianwei, Yan Chi. Evaluation of silk fibroin/curcumin composite film for promoting wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2554-2561. |
| [8] | Hu Yigao, Li Gaofeng. Hyperbaric oxygen alleviates scar adhesion at the base and shortens the time of revascularization of delayed skin flap in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1658-1663. |
| [9] | Xiu Yiping, Zhang Liyan, Qian Xueyi, Li Yan, Li Wantong. The clinical application of platelet-rich plasma to repair chronic refractory wounds: a retrospective study and literature retrieval evidence analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1231-1237. |
| [10] | Han Yanfu, Tao Ran, Sun Tianjun. Autophagy has an early protective effect against fibroblast injury induced by advanced glycation end products [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(35): 5619-5624. |
| [11] | Wang Dan, Yin Jing, Wang Yuying, Du Yong, Li Jingling, Yu Shun. Human acellular amniotic membrane and acellular subamniotic membrane in repairing skin defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5570-5576. |
| [12] | Zhao Xin, Shi Xin, Chen Bei, Cao Yanpeng, Chen Yaowu, Liu Xiaoren, He Yusheng, He Liyun, Li Xiying, Liu Jun. Vacuum sealing drainage enhances wound healing by up-regulating collagen type I/III ratio in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(32): 5122-5127. |
| [13] | Li Wenbo, Shi Jie, Shi Peisheng, Xue Yun, Huang Qiang, Li Chuangbing, Gao Qiuming. L-arginine promotes the survival of extended dorsal perforator skin flap through activating L-arginine-nitric oxide pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(29): 4632-4637. |
| [14] | Liu Yanhua, Zhu Zhou, Wan Qianbing. A drug-loading system for electrospinning wound repair: component selection and construction strategy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(28): 4465-4473. |
| [15] |
Geng Kang, Ding Xiaobin, Tian Xinli, Wang Xue, Yang Yuting, Yan Hong.
Electrical stimulation promotes wound healing and angiogenesis in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4152-4156. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||