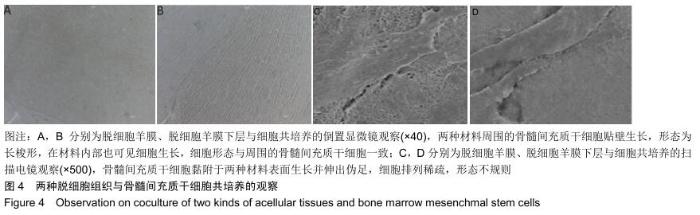
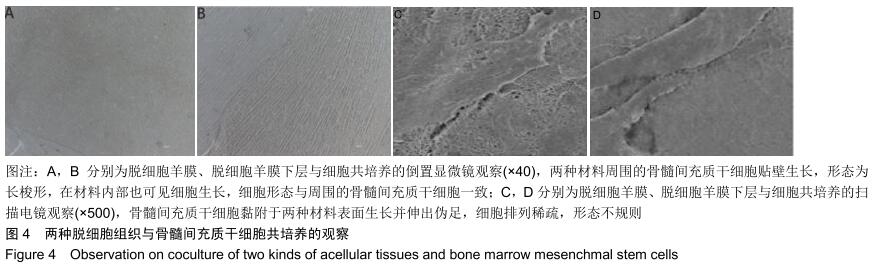
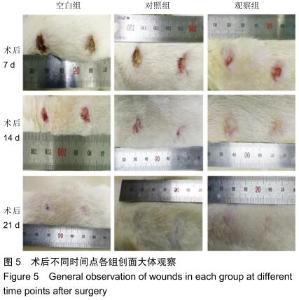
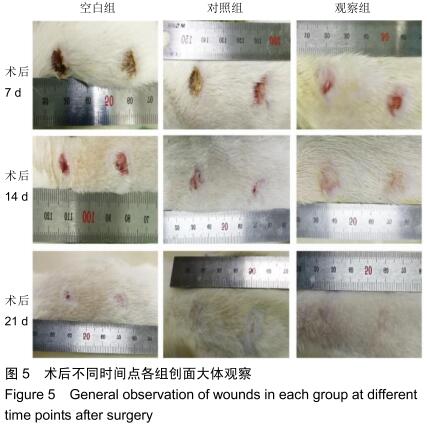
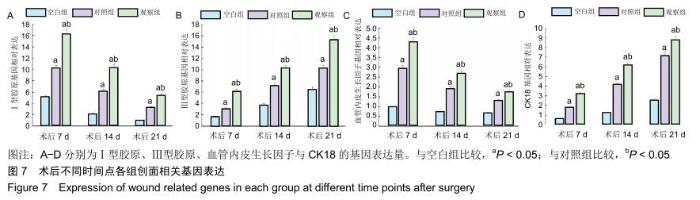
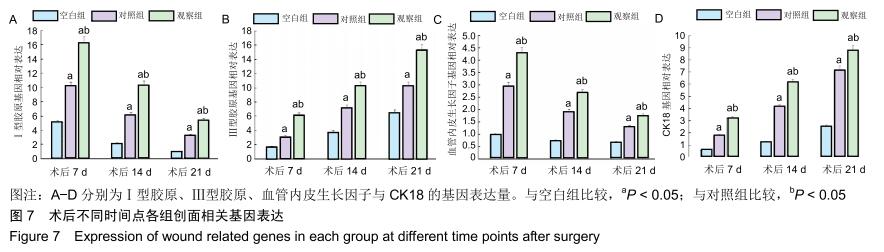
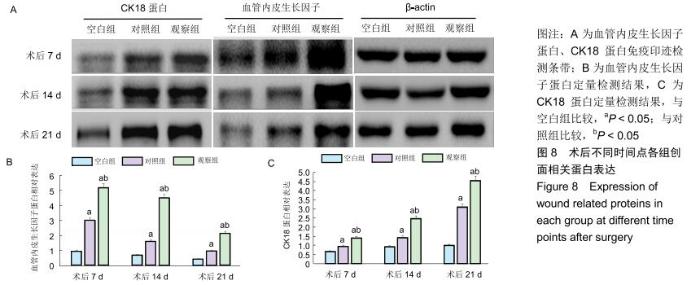
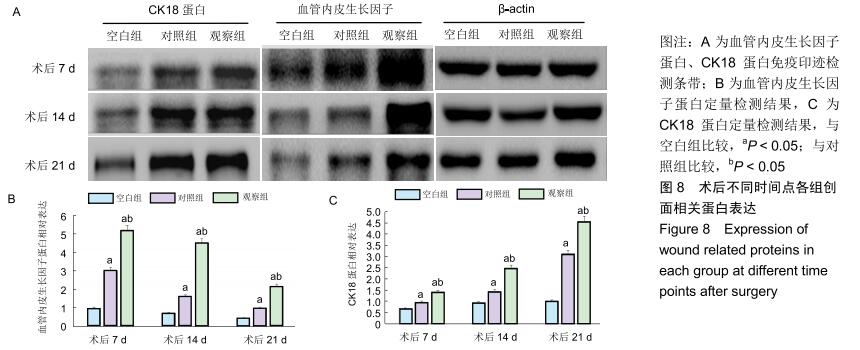
|
[1] BUNNELL AM. The Facial Skin Defect: A Reconstructive Opportunity.Atlas Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2020;28(1):ix. doi:10.1016/j.cxom.2019.12.001.No abstract available.
[2] XIAO Y, MO W, JIA H, et al. Ionizing radiation induces cutaneous lipid remolding and skin adipocytes confer protection against radiation-induced skin injury.J Dermatol Sci. 2020;97(2):152-160.
[3] LI S, YANG X, LIU L, et al. A case of skin autograft for skin ulcers in ichthyosis. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban.2017;42(10):1239-1240.
[4] RODE H, ROGERS AD, MARTINEZ R. Another possible solution of overgranulation following skin autograft procedure. Burns.2020;46(1):240-241.
[5] LUCK J, RODI T, GEIERLEHNER A, et al. Allogeneic Skin Substitutes Versus Human Placental Membrane Products in the Management of Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Narrative Comparative Evaluation of the Literature.Int J Low Extrem Wounds.2019;18(1):10-22.
[6] SHEN ZA. Application of allogeneic skin in burn surgery. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2019;35(4):243-247.
[7] MASTROIANNI M, NG ZY, GOYAL R, et al. Topical Delivery of Immunosuppression to Prolong Xenogeneic and Allogeneic Split-Thickness Skin Graft Survival.Burn Care Res. 2018; 39(3):363-373.
[8] ZHAO X,ZHANG K,DANIEL P,et al.Delayed allogeneic skin graft rejection in CD26-deficient mice.Cell Mol Immunol. 2019; 16(6):557-567.
[9] 祁永军,王晓,焦亚,等.富含小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的生物活性小鼠烧伤变性脱细胞真皮基质的制备[J].中华烧伤杂志,2018, 34(12):895-900.
[10] 王洋,伍津津.组织工程皮肤及其生物反应器的研究进展[J].山东医药,2018,58(39):85-88.
[11] 刘煜凡,黄沙,姚斌,等.3D生物打印的微结构促进小鼠表皮干细胞的增殖和活性[J].南方医科大学学报,2017,37(6):761-766.
[12] BHARDWAJ N, CHOUHAN D, MANDAL BB. Tissue Engineered Skin and Wound Healing: Current Strategies and Future Directions.Curr Pharm Des.2017;23(24):3455-3482.
[13] HALDAR S, SHARMA A, GUPTA S, et al. Bioengineered smart trilayer skin tissue substitute for efficient deep wound healing.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2019;105:110140.
[14] 谢雪锋,陈刚,吴复跃,等.兔包皮来源的上皮细胞与人来源脱细胞羊膜基质(HAAM)组织工程共同培养细胞层片的体外研究[J].复旦学报(医学版),2019,46(3):399-403.
[15] 杨继滨,朱喜忠,熊华章,等.人羊膜间充质干细胞与人脱细胞羊膜支架的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(5):42-747.
[16] 梁远锋,文章,刘尚敏,等.CHAPS联合十二烷基硫酸钠的除垢剂动脉脱细胞支架材料制备[J].岭南心血管病杂志,2018,24(4): 450-455.
[17] 徐子昂,刘晨,肖良,等.髓核组织工程支架的构建及其生物相容性[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(13):1211-1216.
[18] 谷城威,马奎,高冬蕴,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植在糖尿病小鼠创面血管生成及愈合中的作用[J].山东医药,2014(21):22-25.
[19] BHAWAL UK, LI X, SUZUKI M, et al. Treatment with low-level sodium fluoride on wound healing and the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.Dent Traumatol. 2020;36(3):278-284.
[20] DING J, WANG X, CHEN B, et al. Exosomes Derived from Human Bone MarrowMesenchymal Stem Cells Stimulated by Deferoxamine Accelerate Cutaneous Wound Healing by Promoting Angiogenesis.Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019: 9742765.
[21] 叶涛,李永忠,付爱华,等.外泌体与Wnt3a联合诱导间充质干细胞归巢及定向分化[J].华中科技大学学报(医学版),2019,48(6): 637-643.
[22] 胡文捷,章涛.间充质干细胞促进创面愈合研究进展[J].中华实验外科杂志,2019,36(2):377-381.
[23] SAMADIKUCHAKSARAEI A, MEHDIPOUR A, HABIBI ROUDKENAR M, et al. A Dermal Equivalent Engineered with TGF-β3 Expressing Bone Marrow Stromal Cells and Amniotic Membrane: Cosmetic Healing of Full-Thickness Skin Wounds in Rats.Artif Organs.2016;40(12):E266-E279.
[24] 王志敏.过表达hTβ4的hADSCs复合羊皮脱细胞真皮基质对创面愈合影响的研究[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古大学,2018.
[25] 陈端凯,唐乾利.细胞角蛋白在慢性难愈合创面修复中的作用研究进展[J].中国烧伤创疡杂志,2018,30(4):229-232.
[26] 郭鑫,涂晔,安晓强,等.负极性驻极体5氟尿嘧啶贴剂抑制兔耳增生性瘢痕的生长[J].解剖学杂志, 2019,42(6):539-542.
[27] 杨晓双,胡鹏,王达利,等.兔自体真皮成纤维细胞对增生性瘢痕作用的实验研究[J].中华整形外科杂志,2018,34(9):758-768.
[28] 赵奕暄,张国佑,李青峰.病理性瘢痕实验模型[J].中华整形外科杂志,2017,33(2):150-153.
[29] KOK MK, CHAMBERS JK, ONG SM, et al. Hierarchical Cluster Analysis of Cytokeratins and Stem Cell Expression Profiles of Canine Cutaneous Epithelial Tumors.Vet Pathol. 2018;55(6):821-837.
[30] 赵娜,刘登群,汪国建,等.自噬在小鼠皮肤创面修复中作用的初步研究[J].第三军医大学学报,2019,41(1): 25-32.
[31] 奚箐,郑捷新,王西樵.增生性瘢痕中血管内皮功能障碍对成纤维细胞功能的影响[J].上海交通大学学报(医学版),2019,39(10): 1122-1126.
[32] 方颖,曹东升,谢娟,等.富血小板凝胶在兔糖尿病溃疡模型中的研究[J].安徽医科大学学报, 2019,54(11):1831-1834.
|