Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (30): 4848-4854.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1477
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bone tissue engineering in infectious bone defect: advantages and problems
- 1Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Traumatic Orthopedics and Hand Surgery, Ruikang Hospital, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2019-05-13Online:2019-10-28Published:2019-10-28 -
Contact:Chen Yueping, Doctoral supervisor, Chief physician, Department of Traumatic Orthopedics and Hand Surgery, Ruikang Hospital, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Zhan Huasong, Master candidate, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81760796 (to CYP); the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region of China, No. 2015GXNSFAA139136 (to CYP); the Basic Research Ability of Young and Middle-aged Teachers in Colleges and Universities of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region of China, No. 2019KY0352 (to ZXY); the Training Subject-Osteosurgery Construction Project of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine in 2017, No. 04B2017082 (to CYP)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhan Huasong, Chen Yueping, Zhang Xiaoyun. Bone tissue engineering in infectious bone defect: advantages and problems[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(30): 4848-4854.
share this article
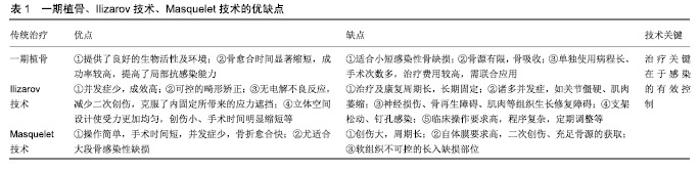
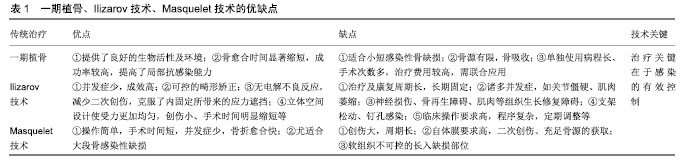
2.1 传统治疗 对于感染性骨缺损的治疗一直以来都是国内外骨科医生面临的一项艰巨的挑战。虽然临床治疗方式在不断丰富和改进,疗效也得到了明显的改善;但主流而传统的治疗手段不外乎一期植骨、骨搬运技术(Ilizarov技术)及诱导膜(Masquelet)技术等,见表1。 2.1.1 一期植骨 一期植骨治疗感染性骨缺损及骨不愈合具有明显疗效,既缩短了骨折愈合时间,提高愈合率,增强骨折断端的自愈能力,也提高局部环境抗感染能力,在临床中得到了充分验证。早期彻底清创、剔除坏死组织配合抗生素药物使用是植骨的基础,反之则可能造成手术的失败,甚至加剧病情的发展。 颗粒状松质骨为一期植骨的常用材料,它有良好的附着及通透性,便于骨诱导因子及抗菌药物分散到松质骨中,构建良好的生物屏障,能够有效的防止微生物附着及繁殖,明显减少感染,它的使用为临床治疗骨缺损感染搭建了良好的平台[2]。同时,颗粒状松质骨的生理结构便于新生血管长入,配合改善血液循环药物的使用,既增强了骨缺损部位的血液供给,又加强了骨组织抗感染能力,有效的加速骨折愈合,修复缺损[3-4]。 一期植骨在小段的骨缺损或骨不连中治愈率可观,其成功的关键在于感染的控制,在必要时可亦可联合高浓度的局部给药。对于抗感染的治疗,局部抗生素给药冲洗亦取得一定成效。有报道指出使用载药磷酸钙骨水泥局部缓释抗生素能在骨感染治疗中取得良好的效果,同样聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯在该病的临床应用中也收到了满意的疗效[5-6];具有抗菌和骨诱导特性的生物材料治疗感染性骨缺损研究也得到显著进步。据不完全病案随访统计示感染复发多在1年内,这也高度提醒医者及患者应当重视,并加强对患者的随访和监测。 2.1.2 Ilizarov技术 Ilizarov骨搬移技术依照张力-应力法则,由俄罗斯Ilizarov医师于20世纪50年代首次提出,通过牵拉反复刺激促进软组织及骨组织再生、修复和重塑,是骨缺损治疗行之有效的手段[7]。 对于大段的感染性骨缺损的治疗,首要亦在于感染问题的解决,而Ilizarov技术为此提供了良好的基础。它不仅便于感染的控制,而且有利于软组织组织与骨的修复,促进骨断端愈合。同时它能够矫正肢体畸形,恢复肢体长度,减少手术频次。长期适当的牵张刺激也有利于各组织细胞分裂再生修复。Ilizarov对于传统骨科难以解决的骨缺损问题,如先后天畸形、骨不连等提供了切实可行的方案,且成果可观。王兴义[8]应用Ilizarov技术修复骨缺损,并得到良好的远期疗效,恢复了患者的正常生活。 在治疗感染性骨缺损问题中,Ilizarov技术具有一定优势[9-10]:①并发症少,成效高,配合抗生素使用能有效控制感染复发;②可控的畸形矫正,为后期康复提供的基础;③无电解不良反应,不需要内固定切开取出,减少了二次创伤,克服了内固定所带来的应力遮挡;④立体空间设计使受力更加均匀,创伤小、手术时间明显缩短,减少患者痛苦等。但由于术式后续治疗及康复周期长,需长期的固定,常导致患者在治疗康复过程中出现诸多并发症,如长期固定会引起的关节僵硬及肌肉萎缩,关节功能障碍;操作不当又会导致的神经损伤、骨再生障碍、肌肉等组织生长修复障碍;支架松动、钉孔护理不当更将会诱发感染[11]。该技术对于医生临床操作能力要求高,且程序复杂,需定期调整等,这严重限制了其推广使用。 2.1.3 Masquelet技术 该项技术又名“诱导膜”技术,由法国Masquelet于1986年提出,并逐渐应用于治疗骨缺损,特别是对于长骨感染性骨缺损,其疗效可观。Masquelet认为自体膜是骨缺损取得快速愈合的关键性因素。“诱导膜”技术是在体内诱导形成自体膜后,将自体松质骨移植在骨缺损处治疗较大骨缺损的技术,对于大段骨缺损或(和)骨感染治疗采用该有明显疗效。喻胜鹏等[12]利用Masquelet和万古霉素治疗慢性骨髓炎骨缺损观察25例患者,认为Masquelet在治疗慢性骨髓炎及感染性骨缺损等效果确切。Akgun等[13]通过将Masquelet与Ilizarov对比分析,前者固定时间更短,远期效果更好,通过进一步统计分析认为,在膜或自体骨单独存在时骨折愈合时间明显延迟,只有同时存在时,骨折才能得到快速愈合。 诱导膜为后期植骨提供了生物性及物理环境,这是该项技术的关键,有利于诱导骨再生修复缺损。诱导膜可以分泌诸多因子(转化生长因子、血管内皮生长因子、骨形成蛋白2等[14-15])和祖细胞加速诱导骨再生,它类似一层保护膜,具有通透性,能够选择性允许促进骨细胞再生修复的营养液成分通过[16],为骨缺损区修复提供优质的环境。这明显缩短了骨愈合时间,提高了其在临床的实用价值。该项技术配合抗生素骨水泥的使用,能够防止异常增生组织长入骨缺损处,控制感染,加强后期治疗效果[17]。但是事物都具有两面性,同样Masquelet 技术也存在许多需要攻克的难题:①创伤大,周期长;②自体膜要求高,充足骨源的获取,二次创伤;③软组织不可控的长入缺损部位,如出现创面软组织缺损则需要肌皮瓣移植覆盖创面,增加了手术的难度和创伤;④控制感染亦是手术成功的关键。 2.2 抗菌药物及缓释系统的使用 对于骨感染的药物治疗方法仍在不断的尝试与实践,但不外乎局部给药和全身性给药;感染的发生往往不是在受伤后的早期就显现,在微生物潜伏期生化检查、影像学及临床症状等指标难以检测诊断。受伤部位骨及软组织异常增生纤维化,改变局部环境,影响血供,药物不能到达,抗生素全身性给药难以通过微循环将药物送达及药物浓度低,难以达到杀死细菌抗感染作用,严重影响骨的自我修复,长期使用甚至会造成耐药,不利于后期治疗。相比于全身性用药,局部抗生素使用克服了全身性用药的诸多困难,局部用药优点[18-20]:直达病灶,降低了药物毒副作用,减少了药物使用剂量;能达到有效杀菌药物浓度,且效果更直接。局部给药方式在日新月异,如微泵复合介入疗法、直接创口敷药、药物冲洗法及抗生素缓释系统等。 在过去数十年的国内外对骨感染治疗的基础研究和临床研究中,抗生素缓释系统治疗骨感染的效果确切且安全性得到保障,得到临床广泛使用。当前已研发出多种抗生素局部缓释系统用于治疗和预防骨感染,根据使用材料的生物降解性能,缓释系统在临床中分为不可生物降解和可生物降解2类,常见的为医用硫酸钙及基甲基丙烯酸甲酯载药系统。基甲基丙烯酸甲酯载药系统为不可生物降解材料的代表作,也是传统载药系统的金标准。据研究,它在临床治疗骨感染中取得一定疗效被推广使用,且能承载多种抗生素,如万古霉素、头孢类及妥布霉素等。但随着基甲基丙烯酸甲酯临床使用和实验研究深入,不足之处也逐渐显现[21-22],当负载抗生素基甲基丙烯酸甲酯释放药物浓度下降难以起到杀菌作用时,这为耐药菌株提供了附着的根基,从而会导致感染复发,该系统的使用需二次手术取除,这也增加手术及感染风险,因为基甲基丙烯酸甲酯的不可降解性,药物释放浓度常难以保障,抗生素释放并不彻底。这使得人们更需要一种可降解材料来处理者一系列问题。医用硫酸钙抗生素缓释系统则有效的规避了基甲基丙烯酸甲酯的缺点,为治疗感染性骨感染开辟了新的治疗方式,但不足的是其在降解过程中并不能对骨组织起到足够的支撑作用,极有可能导致治疗的失败。 2.3 骨组织工程 骨组织工程的概念涉及到各种相关成分的整合。干细胞由一个三维生物材料框架连接在一起,提供形状和初始机械强度,以及分子信号诱导祖细胞分化成成骨细胞表型。由此产生的结构可以在体外进行机械预适应,使生长结构适应体内条件,从而改善与宿主骨的功能耦合。骨组织工程技术关键在于筛选最合适的种子细胞,这也成为近年来国内外学者研究的热点,通过不断的探索和研究,优良种子细胞必需具备:①无排斥反应和致瘤伤害;②能快速增殖和分化,助于成骨细胞增殖和分化,加速骨再生,体外培养条件可控;③取材简单,满足社会需求,资源广,损伤小。2.3.1 成骨细胞 顾名思义,它是能直接成骨的细胞,且增殖能力强,而增殖的过程中,多种信号通路在细胞增殖过程中发挥了关键性作用。Wnt通路是调控成骨分化及细胞增殖的重要细胞内信号转导通路。Wnt系列中的通过经典途径进行信息转输(如Wnt1和Wnt3a)[23-24],通过与关键受体、蛋白结合引起机体连锁反应,最终引起成骨标志基因Runx2增多;Wnt 系列中的 Wnt5a则是通过非经典途径进行信号转输,进而激活细胞内 JNK分子、改变细胞内钙离子浓度来促进成骨细胞分裂增殖。该细胞通过合成分泌骨基质,并矿化形成骨组织,且本身含有纤维粘连蛋白、骨钙素等多种细胞生长因子,具有强大的成骨潜能[25-26]。经过临床实验验证在移入生物支架材料中仍然保持着的分裂增殖和分化活性。尽管成果细胞具备很多优点,但却有着不可规避的缺点[27]:取材途径和资源有限,体外增殖能力有限,尚无标准的培养基培养,这明显限制了其广泛使用。 2.3.2 间充质干细胞 是一种多功能的成体干细胞,其分化潜力巨大,可分化为多种不同类型的组织谱系,包括骨(成骨细胞)、软骨(软骨细胞)、肌肉(肌细胞)和脂肪(脂肪细胞)[28-29]。因间充质干细胞具有强大的自我复制和多方向分化能力,被作为较为理想的种子细胞用于组织工程研究。有实验证明成人骨髓间充质干细胞较胎儿骨髓间充质干细胞的分化及增殖能力都要明显弱,但成人骨髓具有更强的造血功能和恢复能力[30];He等[31]及Sheikh等[32]学者将骨形态发生蛋白2基因成人间充质干细胞作为损伤后组织再生的诱导后备力量,因此其在骨折愈合和骨再生方面的治疗潜力被广泛研究。间充质干细胞可从许多不同的组织中分离出来,包括骨髓、骨骼肌、滑膜、脐血和脂肪等组织。因此,对于从不同组织部位获得的间充质干细胞的成骨潜力进行了大量研究。 骨髓源性干细胞由于其相对容易获得、增殖能力高、再生潜能等特性,是目前最常用和研究的成人间充质干细胞来源。各种动物模型骨缺损治疗实验表明,基于细胞的同种异体骨髓基质干细胞移植治疗对骨再生有效,为自体骨移植的可行替代方案提供了证据[33-34]。与脂肪来源的间充质干细胞相比,骨髓源性干细胞在分化成成骨细胞方面更有效。诸多学者利用骨髓间充质干细胞复合生物材料用于治疗骨缺损,且取得显著疗效[35];近年来有许多学者在做各个方面的深入研究及尝试,加速了各项技术进程,为未来更好的利用间充质干细胞治疗骨缺损的临床应用提供坚实而可靠依据。 2.3.3 胚胎干细胞 多能性人类胚胎干细胞于1998年Thomsonetal首次从人类囊胚中分离出来,即使在体外增殖数月后仍能保持所有3个胚胎胚层的发育潜力,从而证明了组织工程治疗的潜在来源;它身兼无限增殖性、分化全能性和高度未分化等多种要职;甚有“万能细胞”之称,因其几乎可以被诱导形成全部细胞类型可能[36-37]。然而需要其定向分化形成骨细胞,则需要在特定环境条件和相关诱导物的作用[38]。这些多能性人类胚胎干细胞在形态和表型上都与骨髓源性干细胞相似,提供了一种替代的、丰富的、可复制的、更像胚胎的间充质干细胞的来源。事实上,在成骨诱导后,多能性人类胚胎干细胞通过体外矿化骨结节的形成具有类似于骨组织的分子和结构特征[39]。尽管有巨大的增殖和分化潜力带来的兴奋,但多能性人类胚胎干细胞也有一些局限性,需要进一步深入研究。挑战关于文化为其所需的复杂条件,包括使用的可行性,形成畸胎瘤的危险和免疫反应,以及周围的道德、宗教和道德辩论,所有构成挑战性。 2.3.4 诱导多能干细胞 是一种具备多向分化能力、完整的基因组和自我更新的干细胞,可以从成人体细胞(如皮肤成纤维细胞)中获得并重新编程,它具有产生体内各种类型细胞并无限繁殖的能力[40-41]。诱导多能干细胞最早由日本京都大学Yamanaka研究团队于2006年利用反转录病毒,将一组确定的转录因子OSMK系列(c-Myc、Oct3/4、Sox2和Klf4)转入成熟体细胞中,重编码形成的一种可与多能性人类胚胎干细胞相媲美的多能状态的干细胞。诱导多能干细胞在整个再生医学领域具有巨大的潜力,因为它们具有与多能性人类胚胎干细胞类似的多能性和分化潜力,由于它们来自于患者自身的细胞,如此细胞来源充足,同时避免了潜在的免疫排斥。此外,由于诱导多能干细胞的产生绕过了人类胚胎的使用,这为围绕多能性人类胚胎干细胞的伦理困境提供了一个潜在的答案。通过胚状体生成的诱导多能干细胞在体外已经被证明能够生成具有进一步分化成成骨细胞潜力的间充质干细胞样细胞[42-43]。此外,有研究者通过动物实验研究,由诱导多能干细胞培养的间充质干细胞样细胞具有形成与骨组织学相似的成熟矿化物质的能力[44]。除了在诱导多能干细胞产生过程中效率低下外,畸胎瘤的潜在形成也是临床关注的问题。合适的生物材料如羟基磷灰石、3D生物材料等对于诱导多能干细胞成骨分化亦有重要作用;Tang等[45]和Jin等[46]将诱导多能干细胞分别移植到磷酸钙骨水泥及聚乙内酯合成的3D材料等生物材料上,展示了在体内诱导多能干细胞分化和新生骨形成。尽管诱导多能干细胞研究及技术在十多年的发展得到快速进步和完善,但是在诱导成骨分化过程仍然存在着致癌性隐患等缺陷,正因为这些潜在不足,同时也加速了它的成长。综合来看,这些发现表明了诱导多能干细胞对于骨组织工程的未来有着令人兴奋的前景。然而,在接受诱导多能干细胞作为可行的治疗方案之前,进一步的临床研究不仅关注疗效(如成骨潜力),而且关注稳定性、安全性(如畸胎瘤形成)和高效性变得至关重要。 2.4 生物支架材料 随着近年来组织细胞培养技术、生物材料及各项医疗技术水平的不断提高,明显推进了支架材料在骨组织工程修复骨缺损治疗的应用及研究,生物支架材料是骨组织工程技术重要要素之一,支架材料提供种子细胞吸附、增殖分化和移植的根基,关系到骨组织修复的成败。国内外学者已对支架材料做了大量研究,并取得了一定成果,目前应用最多的支架材料包括生物陶瓷、复合材料、金属材料及聚合物材料(人工/天然聚合物)等。 传统支架材料包括生物陶瓷、高分子材料及金属材料等,这些材料尽管在临床治疗中取得一定疗效,但仍然不能满足快速发展的社会需求。生物陶瓷主要包括羟基磷灰石和磷酸钙。羟基磷灰石可以通过运用化学方法和从天然材料中分离制备,其无毒性、无排斥反应、无致畸及优良的生物相容性深得广大学者青睐,但由于降解速度慢,影响骨修复及理化性能等缺陷,难以满足骨缺损修复需求[47],尽管学者们在不断尝试将其他离子加入羟基磷灰石中以改变性能,如锶、镁及硅等掺入[48-49],虽然能够改善部分性能,但还是存在不同程度的缺点。这也促使了研究工作者不断的探索寻找具备更理想的生物支架材料,希望能够更好的联合骨组织工程技术用于治疗骨缺损。金属材料是骨科应用最多的支架材料,需要有足够的强的耐腐蚀性、机械强度、无毒性和良好的生物相容性等,钛及钛合金材料也是目前运用较为成熟的,虽然钛金属有优质的生物相容性和力学特性,但不耐腐蚀,故需要结合其他技术(如表面涂层等)弥补不足[50-51],目前还没找到理想的金属材料联合骨组织工程技术应用于治疗骨缺损,需进一步探索研究。 复合材料是指2种及2种以上材料结合形成的支架材料,同时具备多种材料的优良特性,取长补短,克服单一材料性能上的不足[52],有优良的骨修复能力、生物相容性和力学特性等,可以是是同类或者不同类材料的复合(生物陶瓷、金属材料及聚合物等)。Bose等[53]通过在支架材料中添加镁、锶等微量元素发现可有效促进骨再生修复;Lei等[54]学者将锶与羟基磷灰石和壳聚糖通过冷冻干燥法进行混合制备的复合材料,发现其可显著改善骨再生能力。 生物材料领域是生物材料和细胞之间的典型结合。具体来说,生物材料在骨组织工程中的作用是作为种子细胞附着、生长和分化的三维框架。生物材料的成功整合和功能需要几个组成部分,包括:①生物相容性:在融入宿主组织过程中而不引起免疫排斥反应;②生物降解性:生物材料在降解过程中提供支撑性的机械性能,承受载荷力,均匀分布应力;③适当的表面性质和孔隙度:影响细胞增殖分化;④骨诱导和骨传导特性:向缺陷区域招募骨祖细胞,并提供分化线索的受控释放。 2.5 3D打印技术 近年来3D打印技术的不断成熟和技术水平的不断提高,该技术应用领域也在不断扩大。这大大促进了3D打印技术在临床中的只治疗和研究,同时也被逐渐应用骨缺损治疗。3D打印技术起源于20世纪70,80年代,它通过连续的物理层叠加,逐层增加材料,由点、线、面、体的层层堆积来生成三维实体的技术,又称作添加制造。它综合了数字建模技术、机电控制技术、信息技术、材料科学与化学等诸多方面的前沿技术知识,技术含量高。3D打印技术在骨组织工程中的研究和应用极大推动了骨缺损再生修复的研究和发展[55]。利用3D打印技术结合生物材料应用可实现个体化治疗,满足患者及临床需求,并能精准控制[56-57]。Zhang等[58]采用3D打印磷酸三钙支架,并将中孔结构的生物活性玻璃在磷酸三钙支架表面做涂层处理,与单纯磷酸三钙支架相比,获得更好的成骨效果。Adel-Khattab等[59]采用含二氧化硅的碱性磷酸钙为原料3D打印支架,在体外实验观察到明显的新生骨矿化过程。Cavo等[60]利用3D打印技术构建聚乳酸支架并将胶原蛋白涂布与支架表面,成功获得构建组织工程骨相关理论模型。随着3D打印结合生物材料的在骨缺损治疗中的不断研究和技术成熟,未来可能成为骨缺损治疗的主流方法之一。 "
| [1]Bakhshalian N, Jalayer T, Shahoon H, et al. Osteopromotive property of allogenic demineralized dentin matrix: a pilot study. J West Soc Periodontol Periodontal Abstr. 2013;61(2):35-38.[2]缪志锐,陈进昌,陈陆平.万古霉素与自体微小颗粒骨植骨疗法对患者感染性骨缺损的临床疗效评价[J].抗感染药学,2018,15(5):781-783.[3]田青,刘勇,李国庆,等.自体骨复合抗生素一期植骨治疗感染性骨折不愈合[J].临床骨科杂志,2014,17(1):35-37.[4]张超,李文波,孙英杰,等.感染性骨缺损的手术治疗现状[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2017,32(10):1116-1118.[5]祝芳芳,张杰,迟艳侠,等.复合载药CNTs磷酸钙骨水泥的制备及性能研究[J].黑龙江医药科学,2017,40(1):3-5.. [6]李刚,杨皓然,杨炎彬.万古霉素复合型骨水泥治疗感染性骨缺损的临床疗效[J].实用中西医结合临床,2018,18(6):84-85.[7]Napora JK, Weinberg DS, Eagle BA, et al. Hexapod frame stacked transport for tibial infected nonunions with bone loss:, analysis of use of adjunctive stability. J Orthop Trauma. 2017;31(7):393. [8]王兴义.Ilizarov技术一期短缩延长术治疗感染性大段骨缺损[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2015,23(3):229-234.[9]Bisaccia M, Rinonapoli G, Meccariello L, et al. The challenges of monoaxial bone transport in orthopedics and traumatology. Ortopedia Traumatologia Rehabilitacja. 2017;19(4):373-378.[10]杨礼丹,邹刚,何文斌,等.Masquelet技术与Ilizarov技术治疗成人下肢长骨感染性骨缺损临床疗效分析[J].河北医学, 2018,24(6):918-922.[11]许永秋,王文权,卢庆弘,等.Ilizarov骨搬移技术治疗胫骨感染性骨不连的临床疗效[J].广西医学,2018,40(14):1614-1615.[12]喻胜鹏,傅景曙,李伟,等.Masquelet技术治疗长骨骨髓炎骨缺损的临床分析[J].第三军医大学学报,2014,36(15):1630-1634.[13]Akgun U, Canbek U, Aydogan NH. Masquelet technique versus Ilizarov bone transport for reconstruction of lower extremity bone defects following posttraumatic osteomyelitis. Injury. 2017;48(7): 1616-1622.[14]Saxer F , Eckardt H. Reconstruction of osseous defects using the Masquelet technique. Der Orthopäde. 2017;46(8):1-8.[15]Li L, Zhou G, Wang Y, et al. Controlled dual delivery of BMP-2 and dexamethasone by nanoparticle-embedded electrospun nanofibers for the efficient repair of critical-sized rat calvarial defect. Biomaterials. 2015;37:218-229.[16]Wang X, Wei F, Luo F, et al. Induction of granulation tissue for the secretion of growth factors and the promotion of bone defect repair. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10(1):147.[17]袁冰,韦卓.骨缺损修复的研究进展[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2014, 11(3):38-41.[18]王步祥,杨铁翼,赵振群,等.组织工程技术在感染性骨缺损治疗中的应用及优势[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(28):4543-4549.[19]Celik H, Schibler M, Suvà D, et al. Where are we in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis? Revue Médicale Suisse. 2013; 9(383):885-889. [20]徐永清, 朱跃良, 范新宇, 等. 万古霉素硫酸钙或万古霉素骨水泥治疗胫骨开放性骨折术后并发骨髓炎[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2014, 16(11):925-929.[21]赵宝成, 袁天祥, 马宝通, 等. 局部应用抗生素缓释系统治疗创伤后及内固定相关骨感染临床疗效观察[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2015,23(10):877-881.[22]Lalidou F, Kolios G, Drosos GI. Bone infections and bone graft substitutes for local antibiotic therapy. Surg Tech Int. 2014; 24(XXIV):353-362.[23]陈明, 董启榕. Wnt与转化生长因子-β信号在成骨细胞分化中的相互作用[J]. 中华实验外科杂志, 2016, 33(3):864-868.[24]李俊峰,郭庆山,傅捷辉. Wnt/β-catenin信号通路在调控骨量的作用[J]. 重庆医学, 2017, 46(3):401-403.[25]徐伟丽, 牛玲玲, 王文侠,等. 经典Wnt信号通路对骨代谢的调节作用[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2016, 22(3):376-380.[26]Henkel J, Woodruff MA, Epari DR , et al. Bone regeneration based on tissue engineering conceptions -a 21st century perspective. Bone Res. 2013;1(3):216-248.[27]王桐月,李武伟,马国武. 骨髓间充质干细胞在颌骨缺损修复组织工程中的应用[J]. 口腔医学研究, 2015,31(2):198-200.[28]Oryan A, Alidadi S, Moshiri A, et al. Bone regenerative medicine: classic options, novel strategies, and future directions. J Orthop Surg Res. 2014;9(1):18.[29]Perez JR, Kouroupis D, Li DJ, et al. Tissue engineering and cell-based therapies for fractures and bone defects. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2018;6:105.[30]刘相杰,宋科官.生物支架材料及间充质干细胞在骨组织工程中的研究与应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(10):1618-1624.[31]He X, Dziak R, Yuan X, et al. BMP2 genetically engineered mscs and epcs promote vascularized bone regeneration in rat critical-sized calvarial bone defects. Plos One. 2013;8(4):e60473.[32]Sheikh Z, Javaid MA, Hamdan N, et al. Bone regeneration using bone morphogenetic proteins and various biomaterial carriers. Materials. 2015;8(4):1778.[33]Kowalczewski CJ, Saul JM. Biomaterials for the delivery of growth factors and other therapeutic agents in tissue engineering approaches to bone regeneration. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:513.[34]Dzobo K, Thomford NE, Senthebane DA, et al. Advances in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering: innovation and transformation of medicine. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:2495848.[35]王俊钢,李聪聪,毛广显,等. 骨生物材料复合骨髓间充质干细胞异位成骨修复肋骨大段缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2017, 21(2):182-186.[36]Lorzadeh N, Kazemirad N. Embryonic stem cells and infertility. Am J Perinatol. 2018; 35(10):925-930.[37]Mizuno H. Ethical issues for clinical studies that use human embryonic stem cells: the 2014 revisions to the japanese guidelines. Stem Cell Rev. 2015; 11(5):676-680.[38]夏荃,鲍倩,蒋德菊,等.BMP-Smad信号通路在小鼠胚胎干细胞诱导分化成骨细胞方案优化中的应用[J].广东医学, 2018,39(6):822-827.[39]Chen X, Han T, Fisher JE , et al. Transcriptomics analysis of early embryonic stem cell differentiation under osteoblast culture conditions: Applications for detection of developmental toxicity. Reprod Toxicol. 2017;69:75-83.[40]杨超.诱导多能干细胞治疗颈节段脊髓损伤的研究进展[J].安徽医科大学学报,2018,53(2):323-326.[41]张萍,马月辉,焦淑清,等. 诱导性多能干细胞研究及临床应用[J]. 动物医学进展, 2015,36(8):101-105.[42]Liu Y , Fox V , Lei Y , et al. Synthetic niches for differentiation of human embryonic stem cells bypassing embryoid body formation. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2014;102(5):1101-1112.[43]杨孟恺,易诚青. 诱导多能干细胞在骨再生中的应用[J]. 中国医刊, 2017, 52(6):20-23.[44]Ardeshirylajimi A, Dinarvand P, Seyedjafari E, et al. Enhanced reconstruction of rat calvarial defects achieved by plasma-treated electrospun scaffolds and induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell Tissue Res. 2013;354(3):849-860.[45]Tang M, Chen W, Liu J, et al. Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cell seeding on calcium phosphate scaffold for bone regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A. 2014;20(7-8): 1295-1305.[46]Jin GZ, Kim TH, Kim JH, et al. Bone tissue engineering of induced pluripotent stem cells cultured with macrochanneled polymer scaffold. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013; 101A(5):1283-1291.[47]Goncalves EM, Oliveira FJ, Silva RF, et al. Three-dimensional printed PCL-hydroxyapatite scaffolds filled with CNTs for bone cell growth stimulation. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(6):1210-1219.[48]Dalgic AD, Alshemary AZ, Tezcaner A, et al. Silicate-doped nano- hydroxyapatite/graphene oxide composite reinforced fibrous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J Biomater Appl. 2018;32(10):1392-1405.[49]Andrés NC, Sieben JM, Baldini M , et al. Electroactive Mg2+- hydroxyapatite nanostructured networks against drug - resistance bone infection strains. ACS Appl Mat Interfaces. 2018:acsami.8b06055.[50]Li L, Zhou G, Wang Y, et al. Controlled dual delivery of BMP-2 and dexamethasone by nanoparticle-embedded electrospun nanofibers for the efficient repair of critical-sized rat calvarial defect. Biomaterials. 2015; 37:218-229.[51]Fernandez de Grado G, Keller L, Idoux-Gillet Y, et al. Bone substitutes: a review of their characteristics, clinical use, and perspectives for large bone defects management. J Tissue Eng. 2018;9:2041731418776819.[52]Jahan K , Tabrizian M . Composite biopolymers for bone regeneration enhancement in bony defects. Biomater Sci. 2015;4(1):10.1039. C5BM00163C.[53]Bose S, Fielding G, Tarafder S, et al. Understanding of dopant-induced osteogenesis and angiogenesis in calcium phosphate ceramics. Trends Biotechnol. 2013; 31(10):594-605.[54]Lei Y, Xu Z , Ke Q , et al. Strontium hydroxyapatite/chitosan nanohybrid scaffolds with enhanced osteoinductivity for bone tissue engineering. Mat Sci Eng. 2017;72:134-142.[55]Studart AR. Additive manufacturing of biologically-inspired materials. Chem Soc Rev. 2016;45(2):359-376.[56]Luo Y, Zhai D, Huan Z, et al. Three-dimensional printing of hollow- struts-packedbioceramic scaffolds for bone regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(43):24377-2483.[57]Kao CT, Lin CC, Chen YW, et al. Poly(dopamine) coating of 3D printed poly(lactic acid) scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Mat Sci Eng. 2015;56:165-173.[58]Zhang Y, Xia L, Zhai D, et al. Mesoporous bioactive glass nanolayer-f unctionalized 3D-printed scaffolds for accelerating osteogenesis and angiogenesis. Nanoscale. 2015; 7(45):10.1039.C5NR05421D.[59]Adel-Khattab D, Giacomini F, Gildenhaar R, et al. Development of a synthetic tissue engineered 3D printed bioceramic-based bone graft with homogenously distributed osteoblasts and mineralizing bone matrix in vitro. Key Eng Mat. 2016;720:82-89.[60]Cavo M, Scaglione S. Scaffold microstructure effects on functional and mechanical performance: Integration of theoretical and experimental approaches for bone tissue engineering applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;68:872-879. |
| [1] | Lu Dezhi, Mei Zhao, Li Xianglei, Wang Caiping, Sun Xin, Wang Xiaowen, Wang Jinwu. Digital design and effect evaluation of three-dimensional printing scoliosis orthosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1329-1334. |
| [2] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [3] | Liu Zhengpeng, Wang Yahui, Zhang Yilong, Ming Ying, Sun Zhijie, Sun He. Application of 3D printed interbody fusion cage for cervical spondylosis of spinal cord type: half-year follow-up of recovery of cervical curvature and intervertebral height [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 849-853. |
| [4] | Xu Junma, Yu Yuechao, Liu Zhi, Liu Yu, Wang Feitong. Application of 3D-printed coplanar template combined with fixed needle technique in percutaneous accurate biopsy of small pulmonary nodules [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 761-764. |
| [5] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [6] | Li Li, Ma Li. Immobilization of lactase on magnetic chitosan microspheres and its effect on enzymatic properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 576-581. |
| [7] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [8] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [9] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [10] | Ma Rui, Wang Jialin, Wu Mengjun, Ge Ying, Wang Wei, Wang Kunzheng. Relationship of pathogenic bacteria distribution with drug resistance and treatment cycle for periprosthetic joint infection after total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 380-385. |
| [11] | Huang Youyi, Yuan Wei. Application of 3D printing technology in fracture and deformity of foot and ankle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 438-442. |
| [12] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [13] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [14] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [15] | Zhou Anqi, Tang Yufei, Wu Bingfeng, Xiang Lin. Designing of periosteum tissue engineering: combination of generality and individuality [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3551-3557. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||