Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (30): 4861-4867.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1428
Previous Articles Next Articles
Methods for detecting glycosaminoglycan in the extracellular matrix of animal cells
- 1Guanhao Biotech Co., Ltd., National Engineering Laboratory for Regenerative Medical Implantable Devices, Guangzhou 510530, Guangdong Province, China; 2Guangzhou Keyue Biotech Co., Ltd., Guangzhou 510530, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2019-05-31Online:2019-10-28Published:2019-10-28 -
About author:Zhang Wei, Doctoral candidate, Guanhao Biotech Co., Ltd., National Engineering Laboratory for Regenerative Medical Implantable Devices, Guangzhou 510530, Guangdong Province, China; Guangzhou Keyue Biotech Co., Ltd., Guangzhou 510530, Guangdong Province, China) -
Supported by:National Key R & D Program of China, No. 2016YFC1103200
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Wei, Chen Junlin, Hu Kang. Methods for detecting glycosaminoglycan in the extracellular matrix of animal cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(30): 4861-4867.
share this article
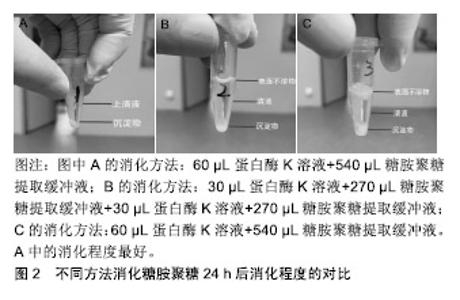
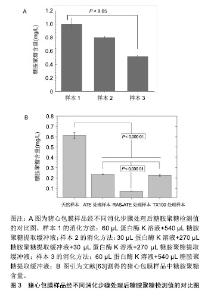
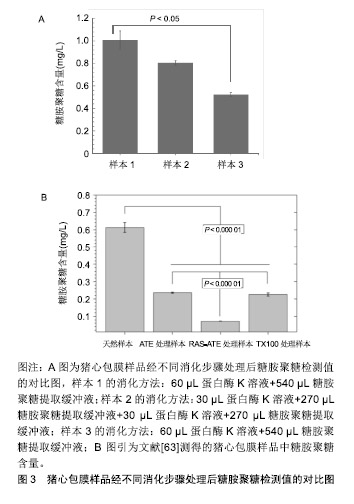
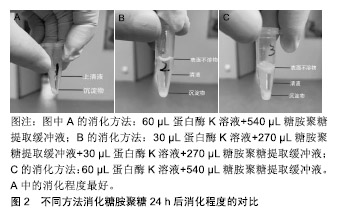
2.1 细胞外基质的特性 在组织修复重建过程中,生物材料的主要作用是对细胞附着和细胞行为提供结构支持和微环境梯度调节[13],而动物源性细胞外基质最为常见。细胞外基质是由组织和器官中细胞分泌出来具有结构和功能分子的复合物[14]。研究表明作为细胞外基质重塑过程的一部分,蛋白质降解带来的形态变化影响了细胞存活、增殖、迁移及分化[15]。细胞外基质一直处于与细胞动态相互作用的状态:产生影响细胞形态和表现的信号及生物物理学的诱因,同时细胞也会因为微环境信号的影响(包括机械刺激、氧气和营养素浓度)修饰其分泌的细胞外基质产物[16]。细胞外基质具有储存和隔离生长因子及细胞因子的能力,在机体内建立浓度梯度,并暂时的对生物利用率进行空间上的调控[17-18]。此外在有限的蛋白水解作用下,细胞外基质可作为水解作用释放出来的生物活性片段的储存库,这些生物活性片段自身具有生物学特性和活性,可以参与调节包括血管生成在内的生理和病理过程[19]。细胞外基质的生化特性允许细胞通过各种信号传导途径感知细胞外环境并与其相互作用,这些化学信号由细胞外基质的组分提供,尤其是黏附蛋白类因子如纤维连接蛋白、整合素和非整合素受体[2-21]。 细胞外基质优异的物理和生物学特性,使其具有广泛的应用领域。目前,包含单个细胞外基质组分或者整个脱细胞组织的细胞外基质基底已被广泛应用于生物材料研究领域[22]。 2.2 细胞外基质的临床应用 虽然细胞外基质广泛存在于多种缺损组织和器官的修复重建,但能被用来作为支架起到治疗作用的原材料相对较少[23],目前应用较多的是动物源的真皮、小肠和膀胱的下层黏膜、心包膜、基底膜、脱细胞肝脏基质及脱细胞跟腱等[24]。在实际应用中细胞外基质以多种形式进行使用,包括片材、颗粒、粉末或根据特定的位点修饰成对应的结构[25]。在生物材料产品开发中,牛或猪的心包膜能够提供良好的结构支撑、细胞附着点位及储存信号因子,以确保组织重塑的有序进行[26]。心包膜组织具有不同组织层次的结构如原纤维、纤维、纤维束等,这些结构特征赋予其非线性和各向异性的力学行为[27-28]。心包膜作为多嵌段复合柔韧补片材料,在使用时为了避免免疫排斥反应,会使用多种方法去除细胞等免疫原性物质,并尽可能的保持细胞外基质的完整性[29]。实验表明,脱细胞处理后的细胞外基质补片不仅能够避免植入材料在机体内引起排异反应发生,同时其支架结构和功能蛋白、糖原蛋白、糖胺聚糖的复杂混合物能够起到优良的结构效应和生化效应[30],在硬脑膜、烧伤整形、口腔黏膜等软组织缺损修复方面有着良好的应用[31]。因此,对细胞外基质中重要生物组分的检测成为了研究者和产业界关注的内容之一。 2.3 糖胺聚糖的特性 糖胺聚糖是4类哺乳动物生物高聚物之一,也是结构功能最复杂的。通常情况下,糖胺聚糖以糖脂和蛋白聚糖的形式存在。从结构上看,糖胺聚糖是长链分子,无支链,具有活性阴离子和亲水性,由重复二糖组成的聚合物分子[32]。现在发现至少有5种糖胺聚糖存在,机体内存在量最大的为透明质酸,也是仅有的一种不含硫酸盐基团且不与蛋白质共价结合的糖胺聚糖[33]。其余糖胺聚糖(软骨素和硫酸皮肤素)通常与小连接蛋白结合,通过这种结合方式与核心蛋白连接形成蛋白聚糖[34]。由于糖胺聚糖带有高浓度的负电荷且具有固有的亲水性,因此这些分子能够在机体中吸收大量水分。这些特性使得糖胺聚糖成为了细胞外基质重要的生物活性物质[35]。研究表明糖胺聚糖通常以蛋白聚糖形式进行聚集,这一现象可增加糖胺聚糖与其他生物高聚物之间的亲和力。此外,糖胺聚糖的聚集会产生高阴离子电荷区,导致高渗透压[36]。高度负电荷的糖胺聚糖链使得蛋白聚糖具有隔离水合二价阳离子的能力,赋予其空间充填、润滑的功能[37]。同时,蛋白聚糖的分子多样性为许多生物学功能提供了结构基础[38],如软骨中聚集的蛋白聚糖可产生高弹性和高生物机械性,从而能够抵抗压力[39]。此外,蛋白聚糖也能够与生长因子、受体因子相互作用,在细胞信号的传导和血管生成过程中起到了重要作用[40]。对蛋白聚糖生理活动的模拟实验显示,蛋白聚糖在细胞外基质中起到的诸多功能,包括保护细胞外基质免受蛋白水解酶活性的影响、调节基质的硬度、抑制血小板的黏附、从纳米层面调节胶原纤维的组装等[41-42]。 2.4 糖胺聚糖检测方法 2.4.1 高效液相色谱法 高效液相色谱法是一个比较敏感的糖胺聚糖定量方法,可以用来量化大部分种类的糖胺聚糖,多用于实验室对微量样品的检测[43];同时还能检验葡萄糖胺糖胺聚糖,例如硫酸乙酰肝素、透明质酸和硫酸角质素等是否被半乳糖胺糖胺聚糖如硫酸软骨素、硫酸皮肤素污染,反之亦然[44]。然而,这种检测方法比较耗时,且需要荧光检测器和Pico-tag水解站的高效液相色谱仪,而大多数实验室难以具备上述仪器。 近来,一类由高效液相色谱法延伸出的检测方法已被开发用于一般碳水化合物分析,研究发现糖胺聚糖完全被水解成非硫酸化糖醛酸和糖胺后进行检测,能够有效检测糖胺聚糖的具体含量[45]。这个过程仍然需要一个Pico-tag水解站,因为糖胺聚糖比N-或O-连接的寡糖更难水解。该方法对糖胺聚糖进行了酸水解、氢氧化钠还原,邻苯二甲醛和3-巯基丙酸对材料的柱前衍生化,然后使用反相高效液相色谱法对异吲哚衍生物进行荧光检测[46]。方法为:以含360 pmol去甲亮氨酸为糖胺聚糖为内标,然后用HCl蒸气在N2气体中在100 ℃下水解3 h;将样品在0.56%NaBH4中再水合,葡萄糖胺和半乳糖胺会分别被酸还原水解为氨基葡萄糖醇和氨基半乳糖;室温下过夜孵育后,向每个小瓶中加乙酸终止反应;样品用真空离心蒸发浓缩器干燥,并溶于水中,柱前衍生化,最后在硼酸盐中用NaOH调节到pH=9.3;接着将反应混合物的一半注入4.6×250 mm C-12柱,再加入等体积的磷酸钠,加热到35 ℃;在流速为0.8 mL/min时,加入缓冲液B(甲醇、水和四氢呋喃,体积比为70∶30∶3);注射后,缓冲液浓度B根据时间变化,下柱前衍生化注入序列,在337 nm处激发氨基葡萄糖醇、半乳糖胺醇和糖胺聚糖制剂中所含氨基酸的荧光衍生物,在454 nm处检 测[47]。该方法不适合实验室的日常检测,难以运用于细胞外基质材料生产环节的糖胺聚糖检测[48]。 2.4.2 糖醛酸定量分析法 作为在动物细胞表面和细胞外基质上表达的线性多糖,糖胺聚糖的合成一直处在一个复杂机制的控制下,并且有能力与蛋白质受体结合,所以通过检测糖胺聚糖同其他生物活性相关的反应如糖醛酸化,能够间接定量分析糖胺聚糖的含量[49]。该方法已被证实能够用于猪主动脉瓣膜中糖胺聚糖含量的定量分析[50]。方法为:将目标材料冷冻于液氮中,并用生物粉碎机粉碎成末,接着将材料粉末进行低压冻干处理并记录干质量作为标准化对比;冻干处理后的粉末置入4 ℃的氢氧化钠溶液中进行24 h的组织消化,随后用三氯乙酸在4 ℃环境下沉淀蛋白质24 h;沉淀完成后,样品被置入离心机离心并将上清液透析24 h;透析完全后将溶液用氯化十六烷基吡啶在37 ℃下于玻璃离心管中沉淀24 h,然后离心收集沉淀下来的糖胺聚糖,并溶于乙酸钠中,在-20 ℃的环境下使用无水乙醇对糖胺聚糖溶液进行再沉淀;再次离心,收集沉淀物,在氮气下干燥后得到糖胺聚糖球团;将球团溶解于苯甲酸饱和水中,加入硼砂-硫酸试剂,同时对样品进行持续降温。之后将样品在沸水中水浴加热10 min,并冷却至室温;加入咔唑显色剂,再将样品沸水水浴15 min,冷却至室温,在530 nm处测量光吸收率[51-52]。 2.4.3 乙醣胺定量分析法 糖胺聚糖的单一分子量较大,但是聚合度较低,直接分析完整糖胺聚糖分子具有一定的难度,可以通过蛋白酶解或化学降解方式简化分析目标的分散度,该方法中减小分子量对于糖胺聚糖的检测十分关键[53]。各类糖胺聚糖分子都有对应的降解物,如硫酸软骨素裂解酶、肝素裂解酶等[54]。这类降解方式可以为糖胺聚糖二糖及寡糖等比色分析提供一个良好的预处理手段,能够针对性地检测特定的糖胺聚糖分子。有实验通过运用猪主动脉瓣膜成功验证了酶解后使用乙醣胺定量分析法检测糖胺聚糖含量的可行性[55]。实验将瓣膜样品放入95 ℃的真空干燥器中使材料充分干燥,接着将材料放入2 mol/L盐酸中水解20 h,然后将溶液放入氮气下,热水浴干燥,随后将组织水解物和D(+)-葡萄糖胺标准品溶解在2 mL M溶液中,加入碳酸钠和乙酰丙酮后并在96 ℃下孵育1 h,然后依次加入无水乙醇及Ehrlich试剂(对二甲氨基苯甲醛加入50%乙醇和盐酸)。22 ℃下等待45 min,使彩色产物显影,记录540 nm的光吸收率,通过与标准曲线的对比成功得出来样品中糖胺聚糖的实际含量[56-57]。 2.4.4 二甲基亚甲基蓝检测法 染料1,9-二甲基亚甲基是噻嗪变体试剂,该试剂与硫酸化糖胺聚糖结合时诱导变态变化而呈现吸收光谱的变化,能够快速检测溶液中的糖胺聚糖,适合检测各种动物组织样品中的糖胺聚糖总量[58]。关于1,9-二甲基亚甲基与糖胺聚糖特殊结合已有大量的研究报道,包括使用质谱法对糖胺聚糖进行质谱分析。染料在任何贮存条件下都是不稳定的,无机分析表明不同来源染料的纯度存在多样性,所以使用不纯的染料会导致结果呈假阴性,影响最终结果[59]。在该检测方法中,1,9-二甲基亚甲基与糖胺聚糖结合后形成的络合物最大吸收波长为525 nm,且该络合物的吸光度与糖胺聚糖浓度呈线性关系,最高质量浓度可达 150 mg/L[60]。通过计算可得出糖胺聚糖分子的比摩尔消光系数与糖胺聚糖-染料络合物的摩尔吸光度,以及与糖胺聚糖中碳氮含量之间的关系[61]。研究表明染料会与糖胺聚糖分子上的离子化硫酸盐及羧基发生结合,动物组织样品实验证实了1,9-二甲基亚甲基可以用来分析样品中糖胺聚糖的含量[58]。简单的步骤如下:将样品冷冻干燥至恒质量,然后将样品置入木瓜蛋白酶缓冲液(125 g/L木瓜蛋白酶,5 mmol/L半胱氨酸-盐酸, 5 mmol/L二钠EDTA,PBS)中60 ℃环境下消化24 h,然后将50 mL样品与1,9-二甲基亚甲基蓝250 mL在96孔中混合,在530 nm处测定微量滴定板和吸光度。通过参考使用不同浓度来自鲨鱼软骨的硫酸软骨素钠盐制备的标准曲线,计算糖胺聚糖含量[62]。 2.5 基于二甲基亚甲基蓝检测法的改进 通过对二甲基亚甲基染料检测方法的研究发现,此方法的灵敏度与样品消化及糖胺聚糖提取步骤有着紧密联系。在该原理的基础上[58],通过对比实验比较了普通水浴酶解和磁力搅拌器辅助水浴酶解后的糖胺聚糖提取量,进一步优化样品的消化提取步骤。 该方法使用了Blyscan™ Sulfated Glycosaminoglycan Assays试剂盒(B1000 Std. Kit,110 assays)。针对样品中糖胺聚糖的提取过程,设计了水浴加热和磁力搅拌器辅助2个实验条件。具体的提取方法如下:①配置50 mL糖胺聚糖提取缓冲液:50 mL纯化水,0.06 g Tris, 0.29 g NaCl,1 g NaOH,EDTA 0.46 g;②实验组1消化过程:将50 mg猪心包膜样品加入到60 μL蛋白酶K溶液(20 g/L)中消化,取540 μL糖胺聚糖提取缓冲液,56 ℃条件下水浴酶解,同时采用磁力搅拌器持续搅拌消化24 h;③实验组2消化过程:将50 mg猪心包膜样品加入到30 μL蛋白酶K溶液(20 g/L)中消化,取270 μL糖胺聚糖提取缓冲液,56 ℃条件下水浴酶解,同时采用磁力搅拌器持续搅拌消化12 h,然后12 000 r/min离心10 min,提取上层清液,再次加入30 μL蛋白酶K溶液 (20 g/L)消化,再次取270 μL糖胺聚糖提取缓冲液,磁力搅拌器持续搅拌,56 ℃水浴酶解消化12 h,再次 12 000 r/min离心10 min,提取上层清液,混合2次提取的清液,作为实验组2的酶解液进行检测;④实验组3消化过程: 将50 mg猪心包膜样品加入到60 μL蛋白酶K溶液(20 g/L)中消化,取540 μL糖胺聚糖提取缓冲液,56 ℃水浴锅中水浴酶解24 h。3组样品最终消化结果见图2所示,实验组1中样品的消化程度最好。相比于实验组2与实验组3,实验组1离心管中上清液上方没有表面不溶物的存在,说明实验组1的样品消化程度相对较高,上清液中不含杂质,而实验组2与实验组3的离心管中上清液上方均存在有表面不溶物,且实验组3中不溶物更多。该现象说明实验组2与实验组3中样品的消化程度均不够高,且实验组3消化程度最低。"
| [1]Sonbol HS.Extracellular Matrix Remodeling in Human Disease.J Microsc Ultrastruct.2018;6(3):123-128. [2]Mouw JK,Ou G,Weaver VM.Extracellular matrix assembly: a multiscale deconstruction. Nature Reviews.Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15(12):771-785. [3]Hinderer S,Layland SL,Schenke-Layland K.ECM and ECM-like materials- biomaterials for applications in regenerative medicine and cancer therapy.Adv Drug Deliv Rev.2016;97:260-269. [4]姜龙,刘昶,薛松,等. 生物补片的临床应用进展[J].现代生物医学进展,2015,15(8):1577-1581. [5]Dziki JL,Huleihel L,Scarritt ME,et al.Extracellular Matrix Bioscaffolds as Immunomodulatory Biomaterials.Tissue Eng Part A.2017;23(19-20):1152-1159. [6]Tracy LE,Minasian RA,Caterson EJ.Extracellular matrix and dermal fibroblast function in the healing wound.Adv Wound Care.2016;5(3):119-136. [7]聂玉胜,申英末.化学性医用胶固定生物补片在腹腔镜经腹腹膜前疝修补术中的应用[J].中华疝和腹壁外科杂志, 2017,11(3): 168-170. [8]Mao AS,Mooney DJ.Regenerative medicine: Current therapies and future directions.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(47):14452-14459. [9]Svystonyuk DA,Mewhort HEM,Fedak PWM.Using Acellular Bioactive Extracellular Matrix Scaffolds to Enhance Endogenous Cardiac Repair.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2018; 5:35. [10]Ghatak S, Maytin EV, Mack JA, et al. Roles of proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans in wound healing and fibrosis. Int J Cell Biol. 2015; 1-20. [11]王亮,刘梅包,陈双.猪小肠黏膜下层脱细胞组织基质材料的制备与体内相容性的检验[J].中华疝和腹壁外科杂志(电子版), 2016, 10(2):89-93. [12]Aquino RS, Park PW. Glycosaminoglycans and infection.Front Biosci(Landmark Edition) 2016;21:1260-1277. [13]Hussey GS,Cramer MC,Badylak SF.Extracellular matrix bioscaffolds for building gastrointestinal tissue.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol.2018;5(1):1-13. [14]Yue B. Biology of the extracellular matrix: an overview.J Glaucoma.2014;23(8):S20-S23. [15]Bonnans C, Chou J, Werb Z.Remodelling the extracellular matrix in development and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15(12):786-801. [16]Poltavets V, Kochetkova M, Pitson SM,et al.The role of the extracellular matrix and its molecular and cellular regulators in cancer cell plasticity.Front Oncol.2018;8:431.[17]Sawicka KM,Seeliger M,Musaev T,et alFibronectin Interaction and Enhancement of Growth Factors: Importance for Wound Healing.Adv Wound Care.2015;4(8):469. [18]Matsuo I,Kimura-Yoshida C.Extracellular distribution of diffusible growth factors controlled by heparan sulfate proteoglycans during mammalian embryogenesis.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci.2017;369:1-9. [19]Rohrs JA,Sulistio CD,Finley SD.Predictive model of thrombospondin-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor in breast tumor tissue.NPJ Syst Biol Appl.2016;2:16030.[20]Sergé A.The Molecular Architecture of Cell Adhesion: Dynamic Remodeling Revealed by Videonanoscopy.Front Cell Dev Biol.2016;4:36. [21]Maas SLN,Breakefield XO,Weaver AM.Extracellular Vesicles: Unique Intercellular Delivery Vehicles.Trends Cell Biol. 2017; 27(3):172-188.[22]Kim Y,Ko H,Kwon IK,et al.Extracellular matrix revisited: roles in tissue engineering.Int Neurourol J.2016;20(Suppl 1): S23-29. [23]Lee EJ,Kasper FK,Mikos AG. Biomaterials for tissue engineering.Ann Biomed Eng.2014;42(2):323-337. [24]Porzionato A,Stocco E,Barbon S,et al.Tissue-engineered grafts from human decellularized extracellular Matrices: a systematic review and future perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19:1-79.[25]Bonnans C,Chou J,Werb Z.Remodelling the extracellular matrix in development and disease. Nature Reviews.Mol Cell Biol.2014;15(12):786-801. [26]Shaheen NL,Kataria E,Antony J,et al.Extracellular matrix composition modulates angiosarcoma cell attachment and proliferation.Oncoscience.2017;4(11-12):178-188.[27]Boroumand S,Asadpour S,Akbarzadeh A,et al.Heart valve tissue engineering: an overview of heart valve decellularization processes.Regen Med.2018;13(1):41-54.[28]Murdock K,Martin C,Sun W.Characterization of mechanical properties of pericardium tissue using planar biaxial tension and flexural deformation.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2018; 77:148-156. [29]Chen FM,Liu X.Advancing biomaterials of human origin for tissue engineering.Prog Polym Sci.2016;53:86-168. [30]Gilpin A,Yang Y.Decellularization strategies for regenerative medicine: from processing techniques to applications.Biomed Res Int.2017;2017:9831534. [31]杨凯,刘昶.生物补片的临床应用及研究进展[J].医学综述, 2015, 21(11):1951-1953. [32]Prydz K.Determinants of Glycosaminoglycan (GAG) Structure. Biomolecules, 2015;5(3):2003-2022. [33]Liu G,Ding Z,Yuan Q,et al.Multi-layered hydrogels for biomedical applications.Front Chem.2018;6:439.[34]Pauly HM,Place LW,Haut Donahue TL,et al.Mechanical properties and cell compatibility of agarose hydrogels containing proteoglycan mimetic graft copolymers. Biomacromolecules.2017;18(7):2220-2229.[35]Humphrey JD,Dufresne ER,Schwartz MA.Mechanotransduction and extracellular matrix homeostasis. Nature Reviews.Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15(12):802-812. [36]Sattelle BM, Shakeri J,Cliff MJ,et al.Proteoglycans and their heterogeneous glycosaminoglycans at the atomic scale. Biomacromolecules.2015;16(3):951-961. [37]Köwitsch A,Zhou G,Groth T. Medical application of glycosaminoglycans: a review.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(1):e23-e41.[38]Pillet F,Gibot L,Madi M,et al.Importance of endogenous extracellular matrix in biomechanical properties of human skin model.Biofabrication.2017;9(2):025017.[39]Acevedo-Jake AM,Ngo DH,Hartgerink JD.Control of collagen triple helix stability by phosphorylation. Biomacromolecules. 2017;18(4):1157-1161.[40]Griffith AR, Rogers CJ, Miller GM,et al.Predicting glycosaminoglycan surface protein interactions and implications for studying axonal growth.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2017;114(52):13697-13702.[41]Ricard-Blum S.Protein–glycosaminoglycan interaction networks: Focus on heparan sulfate. Perspect Sci.2017;11:62-69. [42]Huang G,Huang H.Application of hyaluronic acid as carriers in drug delivery.Drug Deliv. 2018;25(1):766-772. [43]Shrikanth CB,Sanjana J,Chilkunda ND.One-pot analysis of sulfated glycosaminoglycans. Glycoconj J. 2018;35(1): 129-137.[44]Wimmer T,Schroeter E,Lorenz B,et al.Detection of the vascular endothelial growth factor with a novel bioluminescence resonance energy transfer pair using a two-component system.Sensors.2017;17(145):1-10. [45]Köwitsch A, Zhou G, Groth T. Medical application of glycosaminoglycans: a review.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(1):e23-e41.[46]Westergren-Thorsson G,Hedström U,Nybom A,et al.Increased deposition of glycosaminoglycans and altered structure of heparan sulfate in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.2017;83:27-38.[47]Osago H,Shibata T,Hara N,et al.Quantitative analysis of glycosaminoglycans, chondroitin/dermatan sulfate, hyaluronic acid, heparan sulfate, and keratan sulfate by liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization–tandem mass spectrometry.Anal Biochem.2014;467:62-74.[48]Nagy G,Peng T,Pohl NLB.Recent liquid chromatographic approaches and developments for the separation and purification of carbohydrates.Anal Methods. 2017;9(24): 3579-3593. [49]Staples GO, Zaia J.Analysis of glycosaminoglycans using mass spectrometry.Curr Proteomics.2011; 8(4):325-336. [50]VeDepo MC,Detamore MS,Hopkins RA,et al.Recellularization of decellularized heart valves: Progress toward the tissue-engineered heart valve.J Tissue Eng.2017;8:1-21 [51]Li L,Ly M,Linhardt RJ.Proteoglycan sequence.Mol Biosyst. 2012;8(6):1613-1625. [52]Kubaski F,Osago H,Mason RW,et al.Glycosaminoglycans detection methods: Applications of mass spectrometry.Mol Genet Metab.2017;120(1-2):67-77. [53]Stassen OMJA, Muylaert DEP, Bouten CVC, et al. Current challenges in translating tissue-engineered heart valves.Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med.2017;19(9):1-13.[54]Lane RS,St Ange K,Zolghadr B,et al.Expanding glycosaminoglycan chemical space: towards the creation of sulfated analogs, novel polymers and chimeric constructs. Glycobiology.2017; 27(7):646-656.[55]Yu Y,Chen Y,Mikael P,et al.Surprising absence of heparin in the intestinal mucosa of baby pigs. Glycobiology. 2017;27(1): 57-63. [56]Mattson JM,Turcotte R,Zhang Y.Glycosaminoglycans contribute to extracellular matrix fiber recruitment and arterial wall mechanics.Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2017;16(1): 213-225.[57]Osago H,Shibata T,Hara N,et al.Quantitative analysis of glycosaminoglycans, chondroitin/dermatan sulfate, hyaluronic acid, heparan sulfate, and keratan sulfate by liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization–tandem mass spectrometry.Anal Biochem.2014;467:62-74.[58]Sakai D,Nakai T,Hiraishi S,et al.Upregulation of glycosaminoglycan synthesis by Neurotropin in nucleus pulposus cells via stimulation of chondroitin sulfate N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 1: A new approach to attenuation of intervertebral disc degeneration.PloS One. 2018;13(8):e0202640. [59]Kubaski F,Osago H,Mason RW,et al.Glycosaminoglycans detection methods: applications of mass spectrometry.Mol Genet Metab.2017;120(1-2):67-77. [60]Miller D.Regulation of sperm function by oviduct fluid and the epithelium: insight into the role of glycans.Reprod Domest Anim.2015;50 Suppl 2:31-39. [61]Sobolev VE,Jenkins RO,Goncharov NV.Sulfated glycosaminoglycans in bladder tissue and urine of rats after acute exposure to paraoxon and cyclophosphamide.Exp Toxicol Pathol.2017;69(6):339-347.[62]Xu H,Xu B,Yang Q,et al.Comparison of decellularization protocols for preparing a decellularized porcine annulus fibrosus scaffold. PloS One.2014;9(1):1-13.[63]Mendoza-Novelo B,Avila EE,Cauich-Rodríguez JV,et al.Decellularization of pericardial tissue and its impact on tensile viscoelasticity and glycosaminoglycan content.Acta Biomaterialia.2011; 7(3):1241-1248. |
| [1] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [2] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [3] | Dai Min, Wang Shuai, Zhang Nini, Huang Guilin, Yu Limei, Hu Xiaohua, Yi Jie, Yao Li, Zhang Ligang. Biological characteristics of hypoxic preconditioned human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3004-3008. |
| [4] | Liu Zhigang, Guo Qinggong, Chen Jingtao. Effect of Capparis spinosa total alkaloid on proliferation and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells in an intervertebral disc degeneration rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1699-1704. |
| [5] | Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Chen Xiaoxu, Yang Kun. Extracellular matrix and tissue engineering regeneration and repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1785-1790. |
| [6] | Li Junqi, Tian Guangzhao, Chen Mingxue, Wang Hao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Li Ming, Guo Quanyi. Regulatory effect of acellular cartilage extracellular matrix on phenotype of mouse macrophage line [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1512-1516. |
| [7] | Guo Haoyu, Li Weiquan, Liu Kaiyuan, Xiao Ruifen, Sun Denglong, Xi Jiaoya. Recent research progress in construction of biomimetic engineered cardiac tissue based on extracellular matrix [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1577-1584. |
| [8] | Wu Ming, Zhang Yan. Related factors regulating osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 116-122. |
| [9] | Cao Xuhan, Bai Zixing, Sun Chengyi, Li Yanle, Sun Weidong. Application of robot in orthopedic surgery: reliability and room for improvement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1416-1421. |
| [10] | Liu Chunyu, Han Xiaoyan, Wang Lin. Basic science related to tendinopathy: microbiomechanics and stress shielding [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 766-772. |
| [11] | Wang Zhihao, Wu Cong, Wu Sihua, Shi Hongcan. Application and characteristics of decellularization technology in tissue engineered trachea [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(35): 5695-5700. |
| [12] | Yang Wenxiao, Yang Ning, Liu Yao. Immunomodulation of extracellular matrix and its role in tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(35): 5701-5707. |
| [13] | He Jing, Ao Qiang. Research hotspots in tissue decellularization method for manufacturing extracellular matrices [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5413-5420. |
| [14] | Cheng Xue, Fang Hong, Zhang Yunke, Wu Yingen. Interventional mechanism of Feibi prescription on extracellular matrix transformation in a mouse model of pulmonary fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 5038-5043. |
| [15] | Liu Guoming, Wang Qinfen, Lin Kefeng, Zhou Shiguo, Chen Zuxing, Lin Shishui. Whole body application of nerve growth factor promotes early healing of tibial shaft fracture and improves expression of bone morphogenetic protein-2 and vascular endothelial growth factor in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(29): 4680-4685. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||