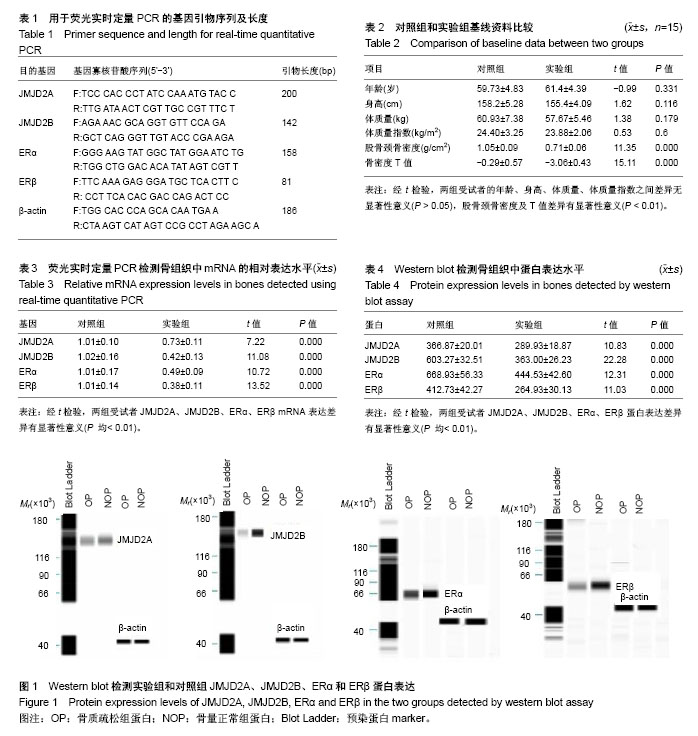
| [1] Erdogan MO, Y?ld?z H, Artan S, et al. Association of estrogen receptor alpha and collagen type I alpha 1 gene polymorphisms with bone mineral density in postmenopausal women. Osteoporos Int. 2011;22(4):1219-1225.[2] Movérare S, Venken K, Eriksson AL, et al. Differential effects on bone of estrogen receptor alpha and androgen receptor activation in orchidectomized adult male mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(23):13573-13578.[3] Lanyon L, Armstrong V, Ong D, et al. Is estrogen receptor alpha key to controlling bones' resistance to fracture. J Endocrinol. 2004; 182(2):183-191.[4] Lv H, Ma X, Che T, et al. Methylation of the promoter A of estrogen receptor alpha gene in hBMSC and osteoblasts and its correlation with homocysteine. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011;355(1-2): 35-45.[5] Kawazu M, Saso K, Tong KI, et al. Histone demethylase JMJD2B functions as a co-factor of estrogen receptor in breast cancer proliferation and mammary gland development. PLoS One. 2011; 6(3):e17830.[6] Greer EL, Shi Y. Histone methylation: a dynamic mark in health, disease and inheritance. Nat Rev Genet. 2012;13(5):343-357.[7] Bannister AJ, Schneider R, Kouzarides T. Histone methylation: dynamic or static. Cell. 2002;109(7):801-806.[8] Shi Y, Lan F, Matson C, et al. Histone demethylation mediated by the nuclear amine oxidase homolog LSD1. Cell. 2004;119(7): 941-953.[9] Tsukada Y, Fang J, Erdjument-Bromage H, et al. Histone demethylation by a family of JmjC domain-containing proteins. Nature. 2006;439(7078):811-816.[10] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会.原发性骨质疏松诊治指南(2011年)[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2011,4(1): 2-17.[11] 中华医学会骨科学分会.骨关节炎诊治指南(2007 年版)[J].中华骨科杂志,2007,10(27):793-796.[12] Wolski H, Drw?ska-Matelska N, Seremak-Mrozikiewicz A, et al. The role of Wnt/β-catenin pathway and LRP5 protein in metabolism of bone tissue and osteoporosis etiology. Ginekol Pol. 2015;86(4):311-314.[13] Black DM, Rosen CJ. Clinical Practice. Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(3):254-262.[14] Rivenbark AG, Strahl BD. Molecular biology. Unlocking cell fate. Science. 2007;318(5849):403-404.[15] Tian Y, Jia Z, Wang J, et al. Global mapping of H3K4me1 and H3K4me3 reveals the chromatin state-based cell type-specific gene regulation in human Treg cells. PLoS One. 2011;6(11): e27770.[16] 唐宏宇,郭承,董路珏,等.组蛋白去甲基化酶JMJD2 在绝经后骨质疏松症表达分析[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2016,22(1):24-29.[17] Labbé RM, Holowatyj A, Yang ZQ. Histone lysine demethylase (KDM) subfamily 4: structures, functions and therapeutic potential. Am J Transl Res. 2013;6(1):1-15.[18] Klose RJ, Yamane K, Bae Y, et al. The transcriptional repressor JHDM3A demethylates trimethyl histone H3 lysine 9 and lysine 36. Nature. 2006;442(7100):312-316.[19] Berry WL, Shin S, Lightfoot SA, et al. Oncogenic features of the JMJD2A histone demethylase in breast cancer. Int J Oncol. 2012; 41(5):1701-1706.[20] Kawazu M, Saso K, Tong KI, et al. Histone demethylase JMJD2B functions as a co-factor of estrogen receptor in breast cancer proliferation and mammary gland development. PLoS One. 2011; 6(3):e17830. [21] Shi L, Sun L, Li Q, et al. Histone demethylase JMJD2B coordinates H3K4/H3K9 methylation and promotes hormonally responsive breast carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011; 108(18):7541-7546.[22] Gaughan L, Stockley J, Coffey K, et al. KDM4B is a master regulator of the estrogen receptor signalling cascade. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41(14):6892-6904. |