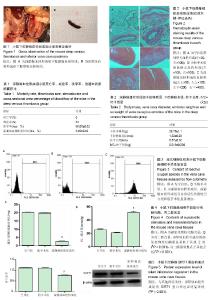
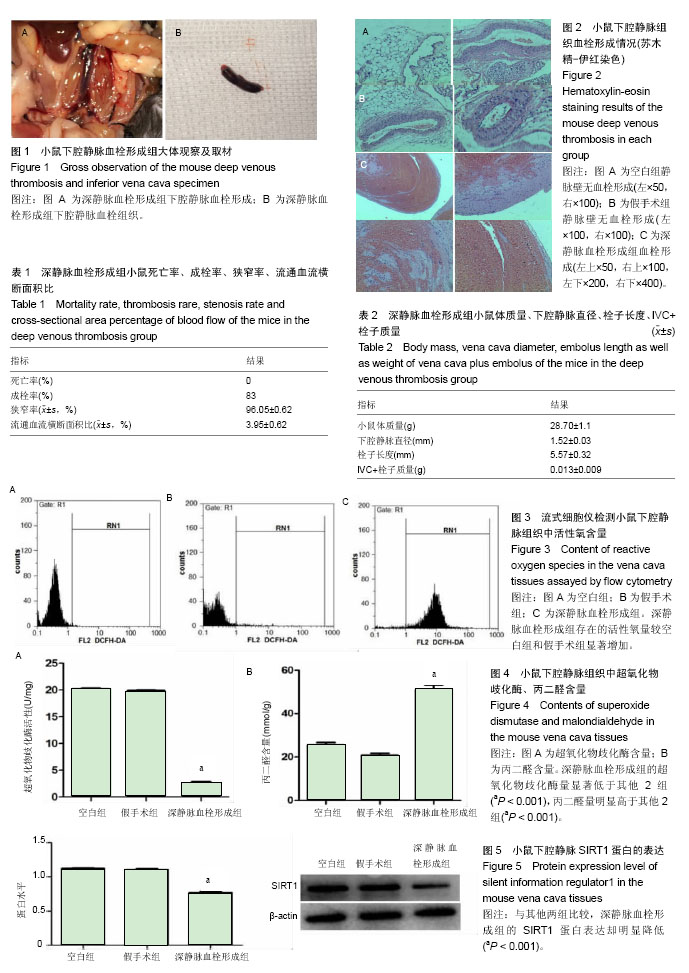
| [1] 中华医学会骨科学分会.中国骨科大手术静脉血栓栓塞症预防指南[J].中华骨杂志,2016,36(2):65- 71[2] Beckman MG, Hooper WC, Critchley SE,et al.Venous thromboembolism: a public health concern.Am J Prev Med, 2010;38(4):495-501. [3] Ashrani AA,Heit JA.Incidence and cost burden of post-thrombotic syndrome.J Thromb Thrombolysis.2009; 28(4):465-476. [4] Hill J,Treasure T,Guideline Development Group.Reducing the risk of venous (deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism)in patients admitted to hospital:summary of the NICE guideline.Hear.2010;96(11):879-882. [5] Laporte S,Mismetti P,Décousus H,et al.Clinical predictors for fatal pulmonary embolism in 15,520 patients with venous thromboembolism:findings from the Registro Informatizado de la Enfermedad TromboEmbolica venosa(RIETE) Registry. Circulation. 2008;117(13):1711-171 6.[6] Ho KM,Burrell M,Rao S,et al.Incidence and risk factors for fatal pulmonary embolism after major trauma:a nested cohort study.Br J Anaesth.2010;105(5): 596-602.[7] López JA,Chen J.Pathophysiology of venous thrombosis.Thromb Res.2009;123(Suppl 4):S30-34.[8] Wakefield TW,Myers DD,Henke PK.mechanisms of venous thrombosis and resolution.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2008;28(3):387-391.[9] Guo H,Chen Y,Liao L,et al.Resveratrol protects HUVECs from oxidized-LDL induced oxidative damage by autophagy upregulation via the AMPK/SIRT1 pathway.Cardiovasc Drugs ther.2016; 27(3):189-198.[10] Hu YX,Cui H,Fan L,et al.Resveratrol attenuates left ventricular remodeling in old rats with COPD induced by cigarette smoke exposure and LPS instillation.Can J Physiol pharmacol. 2013;91(12):1044-1054.[11] Li Y,Wang K,Feng Y,et al.Novel role of silent information regulator 1 in acute endothelial cell oxidative stress injury.Biochim Biophys Acta.2014;1842(11):2246-2256.[12] Brandl A,Meyer M,Bechmann V,et al.Oxidative stress induces senescence in human mesenchymal stem cells.Exp Cell Res. 2011;317(11):1541-1547.[13] 李文,胡继红,李兴国,等.KLF6通过上调TGF-β1诱导静脉内皮细胞endoglin,P-selectin表达,引发血小板黏附、聚集,促进TDVT形成的实验研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(16): 1365-1368.[14] 李兴国,郑宏宇,李文,等.氧化应激和Rac1/2对静脉壁的影响及在创伤性深静脉血栓形成中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(11): 2033-2038.[15] 李兴国,郑宏宇,李文,等.深静脉血栓形成模型大鼠股静脉内皮组织中核转录因子kappa B1和组织因子的表达[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(7):1245-1250.[16] Diaz JA,Obi AT,Myers DD Jr,et al.Critical review of mouse s of venous thrombosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.2012;32(3): 556-562.[17] 娄振凯,彭志,周如丹,等.P选择素、P选择素糖蛋白配体1在大鼠深静脉血栓模型中的表达变化[J].中国急救医学,2016,36(2): 142-146.[18] Yao H and Rahman I.Perspectives on translational and therapeutic aspects of SIRT1 in inflammaging and senescence.Biochem Pharmacol.2012;84(10):1332-1339.[19] Stavrou EX,Fang C,Merkulova A,et al.Reduced thrombosis in Klkb1-/- mice is mediated by increased Mas receptor, prostacyclin, Sirt1,and KLF4 and decreased tissue factor. Blood.2015;125(4):710-719.[20] Vassallo PF,Simoncini S,Ligi I,et al.Accelerated senescence of cord blood endothelial progenitor cells in premature neonates is driven by SIRT1 decreased expression.Blood. 2014;123(13):2116-2126.[21] Kao CL , Chen LK , Chang YL ,et al.Resveratrol protects human endothelium from H(2)0(2) -induced oxidative stress and senescence via SirT1 activation.Atheroscler Thromb. 2010;17(9):970-979.[22] 张敏,朱颖,胡波,等.α-actinin-4与多柔比星肾病大鼠氧化应激状态的关系[J].实用儿科临床杂志,2009,24(5):358-360.[23] 廖永晖,汤雨,千年松,等.氧化应激与细胞凋亡[J].新乡医学院学报,2011,28(1):110-113.[24] Choy JC,Granville DJ,Hunt DW,et al.Endothelial cell apoptosis:biochemical characteristics and potential implications for atherosclerosis.J Mol Cell Cardiol.2001;33(9):1673-1690.[25] Li AE,Ito H,Rovira II,et al.A role for reactive oxygen species in endothelial cell anoikis. Circ Res,1999,85(4):304-310.[26] Turrens JF.Mitochondrial formation of reactive oxygen species. Physiol.2003;552(Pt 2):335-344.[27] Zeng M,Wei X,Wu Z,et al.Reactive oxygen species contribute to simulated ischemia/reperfusio -n -induced autophagic cell death in human umbilical vein ehdothelial cells.Med Sci Monit.2014;19(20): 1017-1023.[28] Gül N,Bögels M,Grewal S,et al.Surgery-induced reactive oxygen species enhance colon carcinoma cell binding by disrupting the liver endothelial cell lining.Gut.2011;60(8):1 076-1086.[29] 娄振凯,李兴国,张福厚,等. PI3-K/Akt和MAPKs信号通路在氧化应激诱导人脐静脉内皮细胞凋亡中的作用[J].中国急救医学, 2016,36(1):78-82. |