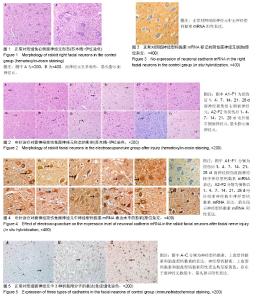
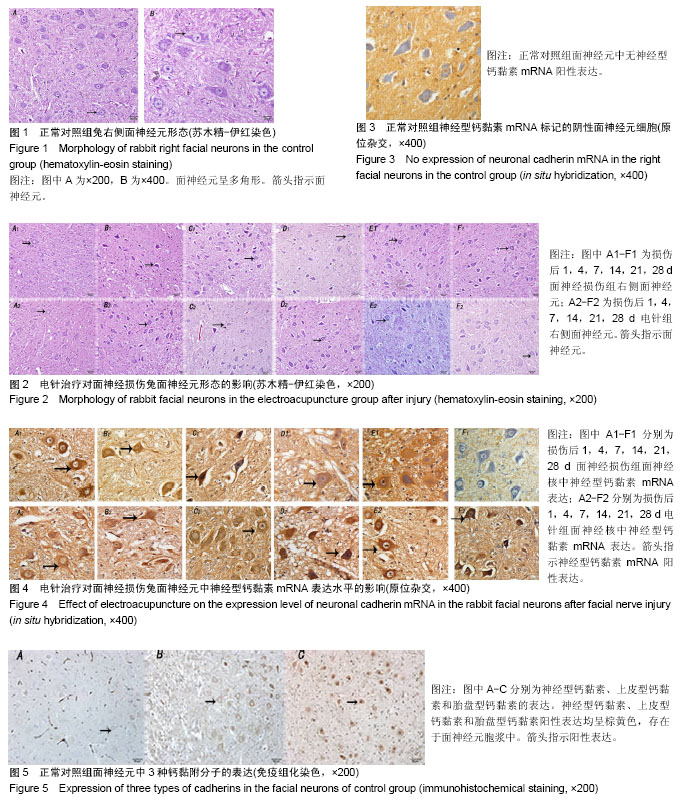
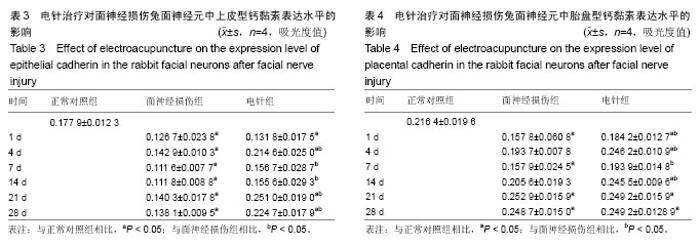
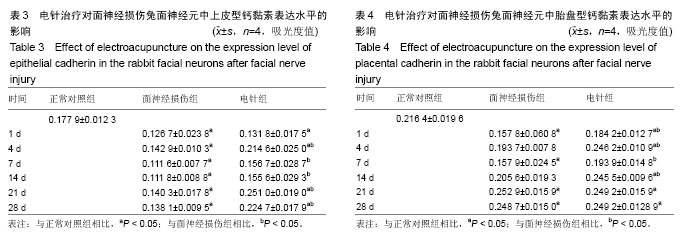
| [1] 田勇泉.耳鼻咽喉-头颈外科学[M].8版.北京:人民卫生出版社, 2013.[2] 李坚将,刘辉.针灸治疗面瘫及对口唇?甲襞微循环的影响[J].上海针灸杂志,2001,20(5):16-18.[3] 卫彦,寇吉友.电针对兔实验性周围性面瘫干预作用量效关系的影响[J].上海针灸杂志,2014,33(6):589-591.[4] 李雷激,骆文龙,曾卫东,等.穴位电针对面神经损伤后面神经核中黏附分子CD56表达的影响[J].重庆医学, 2006,35(24):2239-2241.[5] 牟鸿.单核细胞趋化蛋白-1?细胞间粘附分子-1在病毒性面瘫小鼠脑干面神经核团的动态表达及意义[D].济南:山东大学,2015.[6] 牙祖蒙,王建华,李忠禹,等.面神经损伤后穴位电针刺激对面神经核中几种神经营养因子mRNA表达的影响[J].中国中西医结合耳鼻咽喉科杂志, 2001,9(5):209-211.[7] 张微.电针对面神经损伤修复的雪旺细胞形态学及CNTF表达影响的研究[D].成都:成都中医药大学,2012.[8] 李雷激,骆文龙,伍宗惠,等.面神经损伤后面神经核中黏附分子CD44表达与穴位电针刺激的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007,11(27): 5369-5373.[9] 李斐,江普查,袁先厚,等.N-cadherin?E-cadherin及β-catenin在胶质瘤中的表达及意义[J].中国临床神经外科杂志, 2007,12(9):536-539.[10] 孙力超.结肠癌肝转移诊断?治疗相关分子靶标的研究[D].北京:中国医学科学院,2009.[11] Gwak GY, Yoon JH, Yu SJ, et al. Anti-apoptotic N-cadherin signaling and its prognostic implication in human hepatocellular carcinomas. Oncol Rep. 2006;15(5):1117-1123.[12] Lin S, Stonyanova T, Kono E, et al. Abstract LB-279: N-cadherin promotes castration-resistant prostate cancer progression by enhancing stem cell properties of prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2016;76(14 Supplement):LB-279.[13] Horne HN, Oh H, Sherman ME, et al. Abstract 3451: Breast cancer risk factor associations by loss of E-cadherin tumor tissue expression: A pooled analysis of 5,896 cases in 12 studies from the Breast Cancer Association Consortium (BCAC).Cancer Res.2016;76(14 Supplement): 3451.[14] Li B, Shi H2, Wang F1, et al. Expression of E-, P- and N-Cadherin and Its Clinical Significance in Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Precancerous Lesions. PLoS One. 2016;11(5):e0155910. [15] Rebman JK, Kirchoff KE, Walsh GS. Cadherin-2 Is Required Cell Autonomously for Collective Migration of Facial Branchiomotor Neurons. PLoS One. 2016;11(10):e0164433. [16] Xu C, Funahashi Y, Watanabe T, et al. Radial Glial Cell-Neuron Interaction Directs Axon Formation at the Opposite Side of the Neuron from the Contact Site. J Neurosci. 2015;35(43):14517-14532. [17] Liu Q, Londraville RL, Azodi E, et al. Up-regulation of cadherin-2 and cadherin-4 in regenerating visual structures of adult zebrafish. Exp Neurol. 2002;177(2):396-406.[18] Hatoko M, Tada H, Tanaka A, et al. The differential expression of N-cadherin in vascularized and nonvascularized nerve grafts: a study in a rat sciatic nerve model. Ann Plast Surg. 2001;47(3):322-327.[19] Tada H, Hatoko M, Tanaka A, et al. The difference in E-cadherin expression between nonvascularized and vascularized nerve grafts: study in the rat sciatic nerve model. J Surg Res. 2001;100(1):57-62.[20] 牙祖蒙,王建华,李忠禹,等.面神经损伤后穴位电针刺激对神经组织中神经营养因子-3及其受体表达的影响[J].中国中医基础医学杂志, 2000,6(1): 62-65.[21] Paxinos G, Watson C. The Rat Brain Stereotaxic Coordinates. Sydney: Reed Elsevier Group PLC. 2007:166-167. [22] 李雷激,徐超然,覃纲,等.面神经损伤后面神经核中神经型钙黏附分子及胎盘型钙黏附分子的表达[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(37):5978-5982.[23] 于亚楠,刘彦礼,徐振平,等.视网膜钙黏蛋白在中枢神经系统发育中的作用研究现状[J].新乡医学院学报,2015,32(9):804-806.[24] Paulson AF, Prasad MS, Thuringer AH, et al. Regulation of cadherin expression in nervous system development. Cell Adh Migr. 2014;8(1): 19-28. [25] Astick M, Tubby K, Mubarak WM, et al. Central topography of cranial motor nuclei controlled by differential cadherin expression. Curr Biol. 2014;24(21):2541-2547. [26] Redies C, Takeichi M. Expression of N-cadherin mRNA during development of the mouse brain. Dev Dyn. 1993;197(1):26-39.[27] Scheib J, Höke A. Advances in peripheral nerve regeneration. Nat Rev Neurol. 2013;9(12):668-676. [28] Faroni A, Mobasseri SA, Kingham PJ, et al. Peripheral nerve regeneration: experimental strategies and future perspectives. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;82-83:160-167. [29] Sun Z, Wei W, Liu H, et al. Acute Response of Neurons: An Early Event of Neuronal Cell Death After Facial Nerve Injury. World Neurosurg. 2018;109:e252-e257. [30] Zelano J, Wallquist W, Hailer NP, et al. Expression of nectin-1, nectin-3, N-cadherin, and NCAM in spinal motoneurons after sciatic nerve transection. Exp Neurol. 2006;201(2):461-469. [31] 张晓晖.电针治疗对坐骨神经损伤大鼠NGF?CNTF?BDNF?bFGF表达的影响[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2011. |