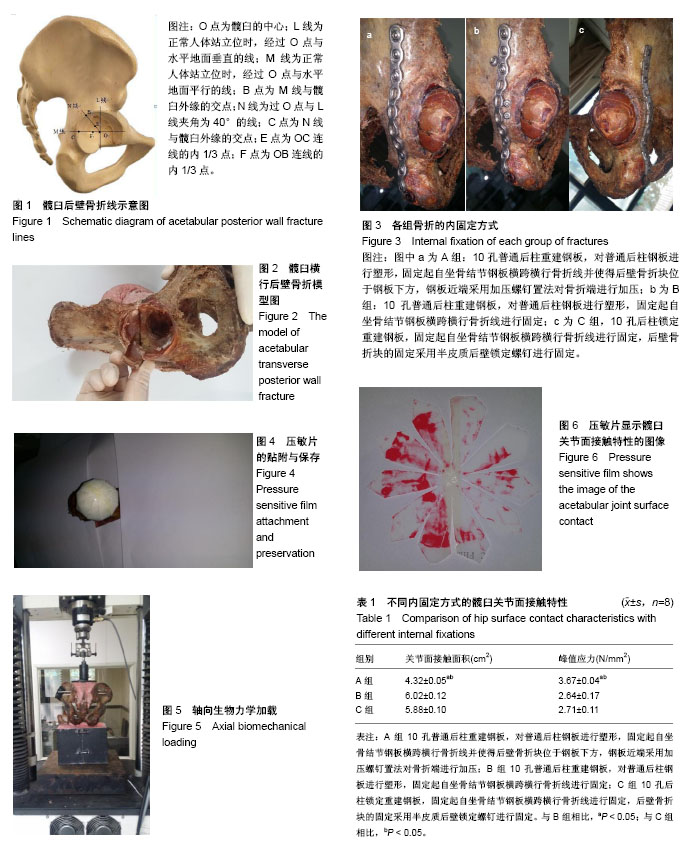
| [1] Judet R, Judet J, Letournel E. Fractures of the acetabulum: classification and surgical approaches for open reduction. Preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1964;46:1615-1646.[2] Letournel E. Acetabulum fractures: classification and management. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1980;(151):81-106.[3] 马爱国,裴宝瑞,庞智寅,等.锁定重建钢板应用于髋臼横行后壁骨折的生物力学研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2016,30(11): 1354-1357.[4] 马爱国,裴宝瑞,刘斌,等.髋臼横行后壁骨折不同内固定方式的生物力学研究[J].成都医学院学报,2016,11(6):738-741,746.[5] Grubor P, Krupic F, Biscevic M, et al. Controversies in treatment of acetabular fracture. Med Arch. 2015;69(1):16-20. [6] 王庆贤,张英泽,潘进社,等.髋臼横断骨折不同内固定方法臼顶负重区的应力分布[J].中华创伤杂志,2004,20(12):743-746.[7] 王钢,汪祎然,陈鸿奋,等.髋臼骨折后柱螺钉内固定治疗策略[J].临床外科杂志,2016,24(5):340-342.[8] Stöckle U, Hoffmann R, Nittinger M, et al. Screw fixation of acetabular fractures. Int Orthop. 2000;24(3):143-147.[9] Wu X, Chen W, Zhang Q, et al. The study of plate-screw fixation in the posterior wall of acetabulum using computed tomography images. J Trauma. 2010;69(2):423-431.[10] 高烁,王雷,吴啸波,等.髋臼横行骨折四种内固定方式的生物力学研究[J].中国临床研究,2016,29(4):444-447.[11] 马爱国,裴宝瑞,庞智寅,等.锁定重建钢板应用于髋臼横行后壁骨折的生物力学研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2016,30(11): 1354-1357.[12] Olson SA, Bay BK, Pollak AN, et al. The effect of variable size posterior wall acetabular fractures on contact characteristics of the hip joint. J Orthop Trauma. 1996;10(6):395-402.[13] Malkani AL, Voor MJ, Rennirt G, et al. Increased peak contact stress after incongruent reduction of transverse acetabular fractures: a cadaveric model. J Trauma. 2001;51(4):704-709.[14] Cahueque M, Martínez M, Cobar A, et al. Early reduction of acetabular fractures decreases the risk of post-traumatic hip osteoarthritis? J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2017;8(4):320-326.[15] Haefeli PC, Marecek GS, Keel MJ, et al. Patients undergoing surgical hip dislocation for the treatment of acetabular fractures show favourable long-term outcome. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-B(4):508-515.[16] Sebaaly A, Riouallon G, Zaraa M, et al. The added value of intraoperative CT scanner and screw navigation in displaced posterior wall acetabular fracture with articular impaction. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2016;102(7):947-950.[17] Sen RK, Tripathy SK, Aggarwal S, et al. A safe technique of anterior column lag screw fixation in acetabular fractures. Int Orthop. 2012;36(11):2333-2340. [18] 白哲.改良Stoppa入路与髂腹股沟入路手术治疗骨盆和髋臼骨折的临床效果比较[J].中国现代医生,2016,54(22):64-66.[19] 崔后春,王金光,王汝渔,等.Judet-Letournel分型个体化手术入路内固定与选择性植骨治疗髋臼骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2017,32(6):573-576.[20] 李军,荆珏华.无明显移位的髋臼骨折可以保守治疗吗?[J].临床骨科杂志,2017,20(1):37.[21] 石永新,李富琴,谭文甫,等.髋臼横型骨折的单一手术入路选择[J].创伤外科杂志,2017,19(2):129-132.[22] 王雷,吴啸波,王永斌,等.髋臼四边体骨折3种内固定方式的生物力学评价[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2015,33(6):690-695.[23] Maini L, Kumar S, Batra S, et al. Evaluation of the muscle morphology of the obturator externus and piriformis as the predictors of avascular necrosis of the femoral head in acetabular fractures. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2016;11(2):105-111. [24] Boudissa M, Ruatti S, Kerschbaumer G, et al. Part 2: outcome of acetabular fractures and associated prognostic factors-a ten-year retrospective study of one hundred and fifty six operated cases with open reduction and internal fixation. Int Orthop. 2016;40(10):2151-2156. [25] 夏广,杨晓东,樊仕才,等.经腹直肌外侧小切口入路辅助经皮后柱顺行拉力螺钉固定技术治疗髋臼前后柱骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2015,17(8):656-662.[26] 邓少林,杨延伟,潘显明,等.切线位拉力螺钉内固定治疗累及四边体的髋臼骨折疗效观察[J].四川医学,2015,36(1):104-106.[27] 张彬,李涛,麦奇光,等.经腹直肌外侧入路钢板结合后柱拉力螺钉内固定治疗髋臼前后柱骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2017, 32(4):337-340.[28] 牟晓伟,沈志敏,王国胜,等.锁定钢板与人工肱骨头置换治疗成人肱骨近端骨折疗效的Meta分析[J].临床和实验医学杂志, 2014, 13(7):535-540.[29] 谢志坚,杨星华,官正华.锁定钢板外置治疗胫骨骨折临床疗效分析[J].西部医学,2013,25(8):1176-1177.[30] 范志远,陆骅.锁定钢板治疗股骨远端骨折的研究进展[J].骨科, 2017,8(4):334-336.[31] 刘晓冬.非甾体类药预防性治疗肘部外伤术后并发骨化性肌炎[J].创伤外科杂志,2011,13(4):322-323.[32] 郭振业,段王平,卫小春.骨化性肌炎的研究新进展[J].实用骨科杂志,2013,19(7):629-632.[33] 柏进社,张英泽,彭阿钦,等.髋臼骨折后创伤性关节炎全髋关节置换疗效研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2008,16(2):81-83. |