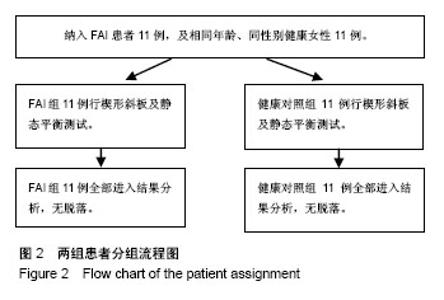
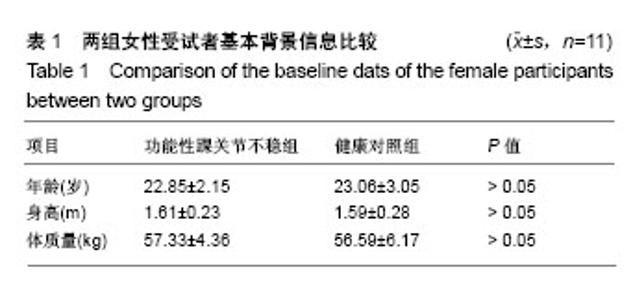
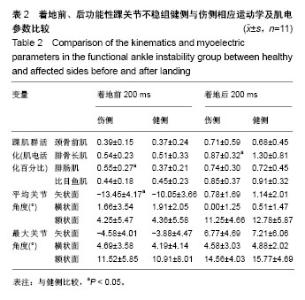
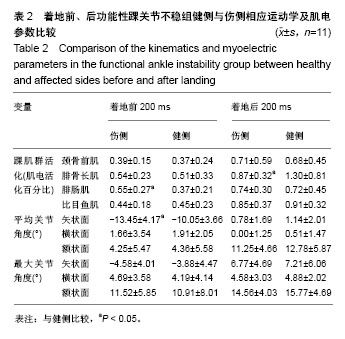
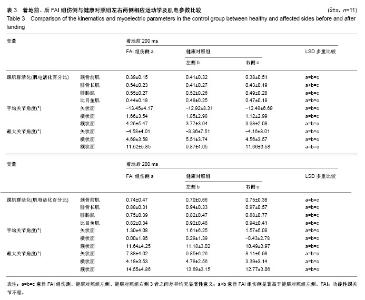
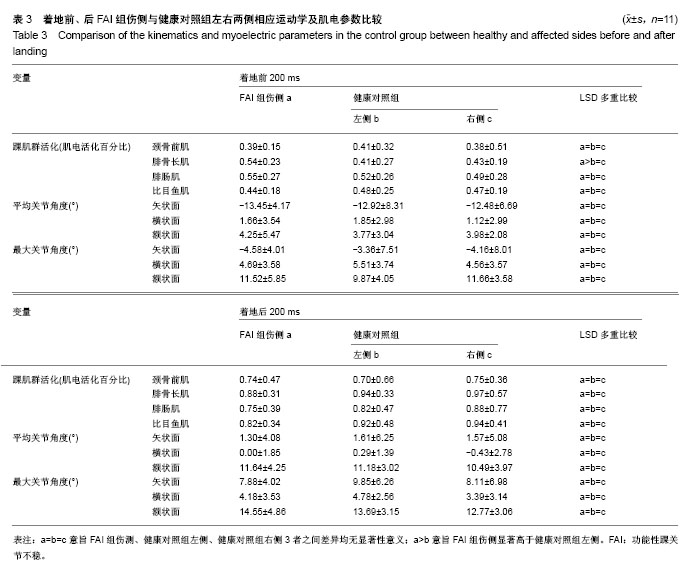
| [1] Freeman MA.Instability of the foot after injuries to the lateral ligament of the ankle. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1965;47(4): 669-677.[2] Lohrer H, Nauck T, Gehring D, et al. Differences between mechanically stable and unstable chronic ankle instability subgroups when examined by arthrometer and FAAM-G. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10:32.[3] 尹彦,罗冬梅,刘卉,于冰. 功能性踝关节不稳者姿势稳定性的研究进展[J].体育科学,2016,36(4):61-67.[4] Doherty C,Delahunt E,Caulfield B, et al.The incidence and prevalence of ankle sprain injury: A systemmatic review and meta analysis of prospective epidemiological studies. Sports Med. 2014;44(1):123-140.[5] Gerber JP, Williams GN, Scoville CR, et al. Persistent disabilityassociated with ankle sprains: A prospective examination of an athletic population. Foot Ankle Int. 1998; 19(10):653-660.[6] Hughes T, Rochester P. The effectsof propr ioc ept ive exercise and taping onproprioception in subjects with functional ankleinstability: A review of the literature. Phys Ther Sport. 2008;9(3):136-147.[7] Hirai D, Docherty CL, Schrader J. Severity of functional and mechanical ankleinstability in an active population.Foot Ankle Int. 2009;30(11):1071-1077.[8] Brown CN, Padua DA, Marshall SW, et al.Variability of motionin individuals with mechanical or functional ankleinstability during a stop jump maneuver. Clin Biomech. 2009;24(9):762-768.[9] Wu HW, Chang YW, Liu CW, et al. Biomechanical analysis of landing fromcounter movement jump and vertical jump withrun-up in the individuals with functional ankleinstability. Int J Sport Exerc Sci. 2010;2(2):43-48.[10] Yoshida M, Taniguchi K, Katayose M. Analysis of muscle activity and ankle jointmovement during the side-hop test. J Strength Cond Res. 2011;25(8):2255-2264.[11] Wikstrom EA, Arrigenna MA, Tillman MD, et al. Dynamic postural stabilityin subjects with braced, functionally unstableankles. J Athl Train. 2006;41(3):245-250.[12] Gutierrez GM, Kaminski TW, Douex AT. Neuromuscular control and ankleinstability. Phys Med Rehabil. 2009;1(4): 359-365.[13] Delahunt E, Monaghan K, Caulfield B. Ankle function during hopping in subjectswith functional instability of the ankle joint Scandinavian. J Med Sci Sports. 2007;17(6): 641-648.[14] De Vries JS, Kingma I, Blankevoort L, et al. Difference in balance measures between patients with chroni cankle instability and patients after an acuteankle inversion trauma. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18(5): 601-606.[15] Urguden M, Kizilay F, Sekban H, et al. Evaluationof the lateral instability of the ankle by inversions imulation device and assessment of therehabilitation program.Acta Orthop Traumatol Turcica. 2010;44(5):365-377.[16] Palmieri-Smith RM, Hopkins JT, Brown TN. Peroneal activation deficits in personswith functional ankle instability. Am J Sports Med. 2009;37(5): 982-988.[17] 钱思佑,吴忠政,张怡雯.踝关节不稳定之排球选手过网拦网动作的下肢肌电讯号分析[J].大专体育学刊,2012,14(1):100-108.[18] Ross SE, Guskiewicz KM, Gross MT, Yu B. Balance measures for discriminating between functionally unstable and stable ankles. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2009;41:399-407.[19] Suda EY, Amorim CF, Sacco Ide C. Influence of ankle functional instability on the ankle electromyography during landing after volleyball blocking. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2009;19:e84-93.[20] Raugust JD. The effect of functional ankle instability on peroneal reflex latency. Uni Alb Health Sci J. 2006;3(1):16-19.[21] Kazemi K, Arab AM, Abdollahi I, et al. Electromiography comparison of distal and proximal lower limb muscle activity patterns during external perturbation in subjects with and without functional ankle instability. Hum Mov Sci. 2017;55: 211-220.[22] Baumhauer JF, Alosa DM, Renström AF,et al. A prospectivestudy of ankle injury risk factors. American J Sports Med. 1995;23(5): 564-570.[23] Hagen M, Lemke M, Lahner M. Deficits in subtalar pronation and supination proprioception in subjects with chronic ankle instability. Hum Mov Sci. 2018; 57: 324-331.[24] Hirai D, Docherty CL, Schrader J. Severity of functional and mechanical ankle instability in an active population. Foot Ankle Int. 2009;30(11):1071-1077.[25] 李育铭,李恒儒.不同方向的跃起着地对下肢矢状面关节运动学、动力学和能量学的影响[J].体育学报,2013,46(1):33-43.[26] Allet L, Zumstein F, Eichelberger P, et al. Neuromuscular control mechanisms during single-leg jump landing in subacute ankle sprain patients: a case control study. PM R. 2017;9(3): 241-250.[27] Caulfield BM, Garrett M. Changes inground reaction force during jump landing insubjects with functional instability of the ankle joint. Clin Biomech. 2004;19(6):617-621. |