Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (30): 4855-4863.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0946
Previous Articles Next Articles
Hydroxyapatite ceramics in bone tissue engineering: research and extensive applications
Mao Wen-wen, Ru Jiang-ying
- Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Yangzhou University (Yangzhou First People’s Hospital), Yangzhou 225000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2018-04-09Online:2018-10-28Published:2018-10-28 -
Contact:Ru Jiang-ying, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Yangzhou University (Yangzhou First People’s Hospital), Yangzhou 225000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Mao Wen-wen, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Yangzhou University (Yangzhou First People’s Hospital), Yangzhou 225000, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the General Project of Jiangsu Provincial Health and Family Planning Committee, No. H201662; the Key Young Talent Project of Jiangsu Province, No. QNRC2016356; the Green Poplar/Golden Phoenix Plan of Yangzhou Municipality, No. yzlyjfjh2015YB106
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Mao Wen-wen, Ru Jiang-ying. Hydroxyapatite ceramics in bone tissue engineering: research and extensive applications[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(30): 4855-4863.
share this article
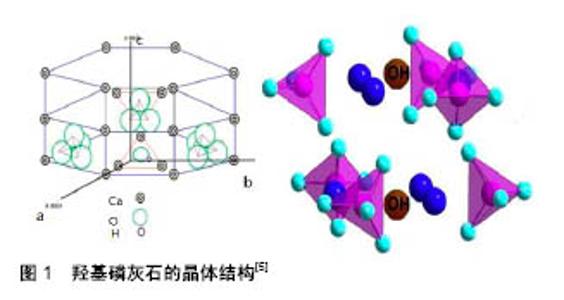
2.1 羟基磷灰石结构特点和力学性能 羟基磷灰石的化学式为Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2,其晶体周围是呈六方排列的Ca2+、PO43-、OH-。羟基磷灰石的晶体结构属于六维空间群(P63/m),晶胞尺寸为a=b=9.421 nm,c=6.884 nm,见图1。其中以两羟基连线为轴,形成立体六重对称性结构通道,羟基也作为活性离子交换基团,易与很多离子发生替换。准确模拟羟基磷灰石和磷酸钙中的阳离子和阴离子取代基,可以改变羟基磷灰石的晶粒尺寸、拓扑结构、化学成分、结晶度和表面电荷,最终影响到材料溶解速率、致密化行为、机械强度和生物相容性等[3]。目前研究较多的,银纳米粒子掺杂羟基磷灰石支架对不同类型的细菌菌株表现出良好的抗菌活性,例如大肠杆菌,并可防止骨植入物相关的细菌感染[4]。铌掺杂的陶瓷在不增加细胞毒性的基础上,较未修饰羟基磷灰石的晶体结构表现出更好的骨细胞生长分化[1],铁离子掺杂的羟基磷灰石的晶体结构,与未掺杂的羟基磷灰石的晶体结构相比骨矿化作用较显著[5],镁离子有促进血管生成的作用[6]。Sr2+增加骨诱导活性,Si4+诱导血管生成和骨矿化。SrO可增强(增加β-连环蛋白形成)成骨细胞的复制,刺激骨形成和抑制骨吸收。SiO2另外还是成骨细胞分化及增加骨矿化的关键因子,与纯羟基磷灰石的晶体结构相比,由于硅掺杂的羟基磷灰石的晶体结构表面上负电荷增强,Si-羟基磷灰石的晶体结构可募集更多的钙离子,接着磷酸根离子吸附形成磷灰石,使得Si-羟基磷灰石晶体结构周围的骨可以较快重塑并达到较高的骨沉积速率[3,7],增加了陶瓷材料的弯曲强度和抗断裂韧性[8-9]。 作为骨组织缺损部位的移植物,尤其在承重部位,这对移植物的机械强度就有一定的要求。天然骨骼抗压强度变化为:松质骨4-12 MPa,皮质骨130-180 MPa,具体数值随骨骼所在部位、年龄的变化而变化,目前纯羟基磷灰石支架的压缩强度为(30.2±6.0) MPa,天然骨骼通过内部松质骨和外部皮质骨,这种材质梯度的形式来维持机械强度。而羟基磷灰石或其他磷酸钙类陶瓷在制备过程中产生的裂纹会扩展,导致硬质材料结构被破坏,增加了材料的脆性[10]。陶瓷材料本身固有的脆性和低断裂韧性(抵抗裂纹扩展能力)限制了其在承重条件下的使用[11-12]。此外为了保持陶瓷类移植物较高的生物活性和骨传导性,需要有高孔隙率及较大孔径值来支持,这就进一步降低了陶瓷材料的机械稳定性,同时也增加了陶瓷类材料制造的复杂性。正是这些固有缺陷,单纯利用羟基磷灰石治疗各种骨缺损疾病未能取得理想的效果。而机械稳定性可以通过新形成骨之间的相互交锁、植入物的宏观设计、硬度和界面应力,以及界面摩擦和骨-植入物间隙尺寸来影响[1],如对于孔隙的形成可加以控制,通过限制孔隙的大小及数量来限制裂纹的生长,增强生物陶瓷强度[10]。 提高韧性简单有效的方法是陶瓷材料与聚合物涂层相结合,形成具有生物活性的微结构。掺入的聚合物还可作为生长因子和治疗药物的载体,强化陶瓷材料的生物学功能。通过用韧性聚合物涂覆或渗透移植材料也是对骨和牙齿本质结构(羟基磷灰石和有机胶原纤维组成)的一种模拟。其中聚合物主要包括两类,合成型(为主),常见的有聚己酸内酯、聚乙丙交酯、聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物等;另一类为天然聚合物,如明胶、丝、藻酸盐、胶原和壳聚糖等。以聚己酸内酯涂层为例,聚己酸内酯涂层纳米羟基磷灰石颗粒抗压强度几乎增加了10倍;与未涂覆的支架相比,聚己酸内酯涂层的β-磷酸三钙支架强度增加了约2倍,韧性增加了约5倍[13]。各种离子或氧化物等添加剂也可改变羟基磷灰石的机械性能,如氧化钙(CaO)、氧化铝(Al2O3)或氧化硅(SiO2)是已被广泛应用于基于羟基磷灰石陶瓷的代表添加剂,有研究将CaO-Al2O3-SiO2(CAS)三元氧化物体系作为液相引入羟基磷灰石陶瓷,发现与单纯羟基磷灰石陶瓷相比,压缩强度和断裂韧性分别达到(22.22±0.77) MPa(提高105%)和(1.68±0.06) MPa•m1/2(提升63%),维氏硬度为(4.47±0.05) GPa(增加了11%),在模拟体液中浸泡后14 d,磷灰石几乎完全覆盖羟基磷灰石陶瓷表面,也证实了含CAS羟基磷灰石陶瓷优异的生物活性[14]。骨髓干细胞在碳纳米管/丝素蛋白纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66支架表面培养表现出良好的黏附和增殖能力。纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66多孔支架(平均孔径约500 μm,满足骨组织再生最小孔径大于100 μm的要求)可很好地模拟天然骨,经过碳纳米管/丝素蛋白修饰后,它保留了原始孔结构(孔隙率约为62%),抗压强度为5.4 MPa,单位体积支架上的骨髓干细胞存活百分比值约27.54%[15]。 2.2 羟基磷灰石类陶瓷的吸收与降解 骨骼再生取决于多种相互依赖的因素,如健康状况、遗传背景、药物、解剖结构、大小和位置。所有这些因素直接或间接地影响骨移植替代物的再吸收率,因此实际上很难选择出具有精确适应个体患者需要的移植骨替代物[16]。天然骨的重塑过程是以基本的多细胞单位来进行的。一个多细胞单位是一个圆柱形的路径(约2 mm长,150-200 μm宽),每天运动速度为20-40 μm穿过骨组织。多细胞单位前面的破骨细胞向主导方向挖掘一个圆形隧道,在多细胞单位结束时,成骨细胞形成新的骨组织[12]。理想的陶瓷支架不仅需要具有与宿主组织相似的机械性能,而且能够在体内随时间以可控的速率而降解,最终产生新生骨组织所需的生长空间。另外,天然骨被包围在组织液中,并在体内不断循环维持体内平衡。因此,植入的骨替代物总是与体液保持动态平衡状态。有研究使用蠕动泵循环装置来模拟组织内流动环境,监测多孔磷酸钙陶瓷在动态条件下的降解过程发现,与静态条件下模拟体液不同的是,第1天钙离子释放急剧增加,7 d后逐渐减慢,磷离子浓度也明显上升。动态条件下的溶解速率高于静态条件下的溶解速率,表明动态环境通过不断更新陶瓷表面钙磷等离子浓度,显著促进了生物材料的降解[17]。但由于羟基磷灰石高度结晶结构在生理环境下溶解非常有限,一旦植入体内需要很长时间才能吸收[3,11]。另外目前许多骨替代品是基于牛松质骨或珊瑚,它们经过烧结过程以除去所有机物质,并且从中消除了抗原性和潜在的感染性污染,以获得较纯净的无机物产物(主要是羟基磷灰石晶体形式的磷酸钙)。尽管在植入后,新形成的骨会长入这些材料的孔隙并覆盖骨小梁,但烧结后遗留的矿物很难被吸收,甚至根本不吸收。这主要归因于:在烧结过程中微小的(< 60 nm)初级骨矿物晶体,重新结晶成更大的晶体,其对破骨细胞的溶解作用更具抗性;覆盖表面的新骨替代材料阻断破骨细胞的进入[18]。相比之下,磷酸三钙溶解比羟基磷灰石快得多,现有磷酸钙类陶瓷的溶解度随着β-磷酸三钙用量的增加而增加,即β-磷酸三钙>双相磷酸钙(即羟基磷灰石与β-磷酸三钙的混合物)>羟基磷灰石,在人胫骨缺损部位植入β-磷酸三钙的病例随访发现,在体内环境中大约2年β-磷酸三钙即可近乎完全降解。β-磷酸三钙在体内的降解及其转化为新骨的过程可分为两个阶段:第一阶段是通过增加原有骨骼的降解,并在β-磷酸三钙支架中形成新骨来进行的,此阶段β-磷酸三钙骨架内新出现的是皮质骨;第二阶段的特征是β-磷酸三钙骨架的再吸收和骨的重塑,这期间骨架内密度降低[12,16]。 含有钙磷元素的材料在体内的降解可是以下过程的组合:①物理因素,材料的磨损、断裂、崩解。另外材料孔隙率增加,比表面积的增大(粉末>多孔固体>致密固体),结晶度和晶粒尺寸减小,生物降解速率也会增大;②化学因素,取决于材料中的组成(构成材料的钙磷比)和离子的取代。磷酸钙相的溶解速率与其钙磷比直接相关,β-磷酸三钙比例为1.5,较羟基磷灰石更易溶解;磷酸钙相的溶解度还受离子取代基团的影响,羟基磷灰石特殊的晶体结构含有几个高度可交换的位点,很多阴离子和阳离子均可取代,随之其溶解度也发生相应的变化[11]。如Si-羟基磷灰石,Si离子的半径较小,在羟基磷灰石结构中磷与硅的替换导致PO4-四面体变形,晶体结构的完整性被打破,与纯羟基磷灰石相比,Si-羟基磷灰石因硅酸盐离子掺入,羟基磷灰石晶体结晶度下降,晶粒界限增多,导致Si-羟基磷灰石溶解速率增加。与未掺杂的羟基磷灰石相比,类似的锶或镁取代的羟基磷灰石也表现出更大的溶解度。此外这些发生离子替换的羟基磷灰石还具有协同增强骨诱导性能的潜力[3,11];③生物因素,生物降解过程主要涉及两步:其一,破骨细胞溶解矿物质,如磷酸钙或磷酸镁是基于局部释放的Ⅱ型碳酸酐酶,其催化二氧化碳和水转化为碳酸氢盐和质子,形成酸性环境,增加了矿物质的溶解度;其二,由巨噬细胞发挥吞噬作用(颗粒大于10 μm)和细胞内消化作用(通过溶酶体分解为小颗粒或运输到邻近组织如淋巴结,多是直径小于10 μm的颗粒)[6,19]。近期还有研究发现,新形成的骨和陶瓷降解之间类似于骨重塑过程,而这个过程是由骨形态发生蛋白支持的。体内的骨形态发生蛋白7可增强破骨细胞活性,以往的实验也观察到小鼠模型中存在骨形态发生蛋白7时陶瓷降解增强,利用骨形态发生蛋白7可高度选择性地降解磷酸三钙组分,实现植入物的可调节性降解[20]。由于磷酸三钙溶解较羟基磷灰石快,调节骨替代物吸收最简单有效的方法是通过改变羟基磷灰石和β-磷酸三钙构成比例,形成一种新的紧密混合物,组成双相磷酸钙。体外一项测定体外双相磷酸钙(具有57∶43的羟基磷灰石与β-磷酸三钙比率和92%的孔隙率)溶解实验发现,经过5.0 mmol/L乙二胺四乙酸浸泡,22 h后残余材料质量(70.2±6.7)%,体积降至65%,孔隙度保持在89.2%。X射线衍射数据显示富含羟基磷灰石(羟基磷灰石与β-磷酸三钙的比率变为65∶35),表明β-磷酸三钙相已被选择性地溶解,证实β-磷酸三钙与羟基磷灰石相比具有更高的溶解度。植入缺损组织后,随着β-磷酸三钙的溶解,而剩余的羟基磷灰石颗粒仍然保持固体结构,这也是陶瓷移植物在初始降解阶段保持机械稳定的原因。而在体内,由于体液的灌注,新生骨在植入物上的沉积及破骨细胞的作用,导致体内吸收降解过程更为复杂[18]。总之生物陶瓷降解的主要过程是,通过被动溶解和活性破骨细胞的溶解作用及在巨噬细胞吞噬作用下,伴随着骨的重塑过程逐渐进行[6]。而羟基磷灰石和β-磷酸三钙具有相似的化学组成,但它们具有不同的生物再吸收能力。羟基磷灰石的生物活性相对较低,几乎不吸收,β-磷酸三钙是近乎于完全吸收的物质。通过控制羟基磷灰石与β-磷酸三钙比例,不仅可调节陶瓷移植物的吸收速率,而且可影响骨细胞附近的离子释放,改善陶瓷移植物生物学活 性[16,21]。"

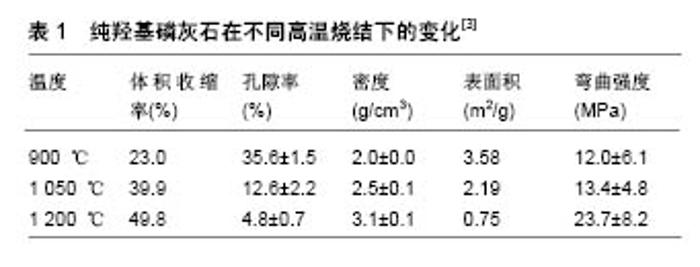
2.3 羟基磷灰石类陶瓷材料的制备及孔隙结构 至今随着生产技术和设备不断的更新换代,羟基磷灰石的制备方法已经达数十余种,其中主要分为湿法和干法两大类。湿法主要有:水热法、沉淀法、溶胶-凝胶法等。干法主要有:烧结法、喷雾法、超声波法、仿生合成法等。根据植入的环境需要,很多时候是两种或多种制备方法相结合,来生产出满足需要的陶瓷类植入材料。每种方法优缺点也各有不同,如沉淀法,生产过程简单,操作温度低,以合理的成本达到高产率,但有时不完全的反应和沉淀,导致化学计量学变化,导致混入不需要的杂质。溶胶-凝胶法可将各种分子均匀混合,与其他方法相比可较好地产出纳米尺寸的颗粒,但起始材料非常昂贵,而且形成的前体通常对湿度极其敏感,增添了生产的难度[22]。不同方法制造出的陶瓷支架,其孔隙率、孔径结构、比表面积、致密化行为、材料的收缩和形态等也不同,这直接影响到了生物活性的表达和具体适用范围。如烧结法的优势是在烧结后压缩更多的空间,得到较高的孔隙率,但孔径和孔与孔间的互相连通性(大部分孔径小于10 μm以下的微孔,在烧结温度在1 200 ℃或以上时关闭,这也是大多经高温烧结法制备的磷酸钙多孔陶瓷不能诱导异位骨形成的主要原因),产物的尺寸难以掌控[23]。对于纯羟基磷灰石,烧结温度在900,1 050,1 200 ℃时,随着温度升高(β-磷酸三钙相逐渐增加),晶粒明显生长,致使其体积逐步扩大,平均晶粒尺寸约800 nm,孔隙率、表面积、弯曲强度变化见表1[3,12]。 现阶段为了制备含有大孔径及高孔隙率的生物陶瓷,简单而又快速的方法为加入明胶的烧结法。明胶作为羟基磷灰石粉末的黏合剂,有机组分在烧结过程中消退,产生相应空隙,该法制得的羟基磷灰石孔隙率大于60%,孔径近似为100-200 μm,平均抗压强度达 7.59 MPa,满足人骨替代物要求[10]。目前模拟皮质骨的生物材料及研究相对较少,其显著特征是在骨修复时出现蜂窝状的排列结构,通过藻酸盐溶胶-凝胶过程产生类似的平行排列孔道结构。通过该法制备的纳米羟基磷灰石不仅强度高,还很好地模拟了天然骨的结构[24]。在联合制备方式中,以选择性激光烧结结合液相烧结法为例。选择性激光烧结可控制产出物的形状,并可控制多孔支架的内部结构。然而,由于选择性激光烧结激光束与材料之间的作用时间短(0.2-200 ms),难以实现较高的致密度。液相烧结法能够使得固体颗粒重排和聚集,再通过溶液沉淀粗化,实现高致密化,以提高陶瓷的机械性能。有研究采用选择性激光烧结法,与CaO-P2O5作为液相联合烧结制备β-磷酸三钙支架,支架的孔隙可均匀控制在0.8 mm,最大维氏硬度、抗压强度和刚度分别为4.89 GPa,21.32 MPa和264.32 MPa;在体外模拟体液中浸泡14 d后,可见整个支架表面上形成均匀的磷灰石层;将人成骨样细胞MG-63细胞加入到支架中,培养4 h后可见MG-63细胞牢固附着并铺展在支架表面,培养3 d后形成延伸的丝状伪足,可见在机械性能提高的同时,仍可保持着良好的细胞相容性[14,25]。目前为了模拟天然骨外层为致密皮质骨、内层为松质骨的这种梯度结构,失蜡铸造技术提供了一种制备具有内部有孔结构和外部为紧密结构的β-磷酸三钙支架优良方法。使用3D打印机将孔隙率、孔的尺寸和外部致密层的数据调节至目标值,以制造用于铸造过程的蜡模,以此生产出的支架外层和内层孔隙率可达(31.4±0.4)%,(55.6± 0.9)%,抗压强度分别为(192±7),(36±2) MPa,大孔尺寸为500 μm,微孔尺寸高达10 μm,且多孔结构互相联通。而普通β-磷酸三钙支架的这两项数值仅为(66.9± 0.4)%和(9±1) MPa[12]。 陶瓷植入物被完全整合到宿主组织过程中,因为材料逐渐降解会形成不规则表面边界,使得更大范围的包含植入材料被暴露,增加了植入物和周围组织之间界面的接触面积,因此为其发挥骨诱导活性及血管诱导活性等相关生物活性提供了便利。另外骨细胞的生长及缺损部位的修复需要适宜的营养及氧分要求,细胞和生长因子需要进入到植入区域,这就要求支架多孔化成为必须,以利于这些营养物质和生长必要成分的输送,以及细胞代谢废物的排除。由于陶瓷降解形成了更大的多孔结构,这些间隙可作为血管向内生长和成骨细胞进入的活性通道,促进了植入材料内的新骨生长,产生促进新骨形成的积极效果[26-28]。 天然骨中皮质骨大部分是致密结构,在其内部总孔隙率为10%,小梁骨是一种高度多孔的结构,典型的孔隙率在50%-90%之间(具体数值取决于骨组织所在的部位和年龄)。这些多孔区域允许骨结构的血管化和细胞浸润。已证实至少40 μm的孔隙尺寸才能有骨骼生长的可能,而100-350 μm的孔隙尺寸被认为是适合骨骼生长的范围[29]。高孔隙率和足够的孔径数值是有效骨替代材料的重要因素[23]。具有高孔隙率及孔径值的支架允许骨的向内生长并支持新生血管形成。多孔生物活性支架诱导材料内部形成新的骨组织主要涉及以下3个过程:①新形成的骨组织,在材料表面向中心开始长入,利用相互连通的孔隙网络侵入内部,多孔结构有利于新骨组织和骨髓的定植;②在材料内部,血管细胞和成骨细胞会结合成毛细血管轴,孔隙结构作为所需的营养物质通道来促进这一过程;③材料本身通过降解产出各种含钙、磷等的微量元素(高水平的Ca和P可刺激成骨细胞基因表达,抑制破骨细胞活性),创造出适合周围组织生长所需的微环境,便于骨髓中所含的成骨细胞前体进一步分化[30]。支架增强成骨信号表达和支持新骨形成的能力,在很大程度上取决于支架的孔径和孔隙率。孔径和孔隙率除了能够促进体内骨传导和血管化,还影响细胞附着效率,影响细胞接种密度、分布和迁移。此外孔径和孔隙率影响体内和体外细胞信号转导,进而影响间充质干细胞的成骨细胞分化和细胞外基质蛋白质的产生[29]。具体合适的孔径值,所需的孔结构与待修复的材料、组织缺损位置及个体患者的状态这些因素有关,这导致了不能定义孔径大小的最佳值。换句话说,确定最佳支架结构是一个相对的概念,达到某一个特定功能可能只能找到一个真正的最优值[24]。目前常用的作为人骨移植材料方面替代物,是具有孔径分布为35-150 μm的70%孔隙率复合支架,在保证较高的抗压强度的同时,还具有一定的生物活性,如基于明胶-壳聚糖-羟基磷灰石支架,粒径分布在40-105 nm之间,平均值为70 nm,70%孔隙率,平均抗压强度3.5 MPa,符合松质骨抗压强度区间。另外其中壳聚糖提供了一个有利于成骨细胞黏附和增殖的表面,以加速骨再生过程。明胶具有生物相容性,抗原性极低,它在骨架上含有不同的肽键和游离羧基,增强了蛋白吸收能力。该支架上培养的间充质干细胞,在第14天时从细胞骨架延伸的板状伪足,随着培养时间的延长慢慢扩散[31]。 虽然大孔(>100 μm)有益于细胞附着、增殖和血管形成,但也有研究表明微孔(<20 μm)通过改善骨分布在双相磷酸钙陶瓷支架中的均匀性来增强骨再生。目前研究发现微孔隙可产生毛细作用力,当基质与细胞悬液接触时,在体外陶瓷底物的微孔能够吸引细胞,而体内支架的微孔与缺陷处的生理液体接触,微孔诱导的毛细作用力将细胞和流体吸入到支架大孔和微孔中,来提升植入支架的效果。在3组植入猪骨缺损的双相磷酸钙陶瓷支架实验中,与浸入磷酸盐缓冲盐水中的双相磷酸钙陶瓷(液体填充孔隙,以抑制微孔诱导的毛细管现象)与无微孔的双相磷酸钙陶瓷支架相比,有微孔双相磷酸钙陶瓷支架中骨质分布更加均匀,微孔中还有均匀染色无核细胞,形态与在大孔血管中发现的红细胞一致(无核细胞,如红细胞,缺乏核而无法积极迁移),均匀的骨分布意味着在整个支架中已形成了广泛的脉管系统,降低了缺损中心组织坏死的风险。与微米尺寸的羟基磷灰石相比较,纳米羟基磷灰石颗粒更容易分散在聚合物基质中,形成规则的孔隙。由此也可看出,磷酸钙类陶瓷表面的微米和纳米级形态可强烈地影响成骨细胞和干细胞的黏附、增殖和分化。明确设计和使用骨支架,诱导其中的成骨细胞、毛细血管生成,在更大程度上有助于大而复杂骨缺损的治疗[32-33]。总的来说,大孔通过增加成骨细胞和骨原细胞迁移到支架中来促进骨样形成和矿化,而相互关联的微孔可增强骨重建过程中的血管形成和营养扩散。 2.4 羟基磷灰石的骨诱导及骨传导活性 尽管目前生物材料诱导骨生成的研究很热门,但确切机制仍不完全清楚。事实上,目前较为大家认可的是,微观结构表面特性(包括晶粒尺寸,微孔率,表面粗糙度和比表面积,这些参数决定了陶瓷与蛋白质结合的能力)可能是骨诱导的关键因素之一。根据陶瓷的合成方式、大隙、晶粒大小和表面粗糙度的不同,导致不同的骨诱导潜能。如微/大孔双相磷酸钙陶瓷颗粒可以诱导肌肉部位的异位骨形成或骨部位的骨形成。在生物材料植入之后蛋白质吸附即可发生,这会影响种植体周围局部微环境中细胞的黏附、增殖和分化。因此,对磷酸钙类陶瓷骨诱导机制的一个普遍解释是:材料微孔结构会导致各种内源性骨生长因子在内孔表面的高度吸附和积累,刺激间充质干细胞分化进入成骨细胞,最终实现成骨诱导。一项比较间充质干细胞在具有相同羟基磷灰石/β-磷酸三钙比例、而不同颗粒尺寸的双相磷酸钙陶瓷上的培养情况实验发现,生长在小颗粒状双相磷酸钙陶瓷上的间充质干细胞比块状双相磷酸钙陶瓷上的数量更多。细胞在小颗粒双相磷酸钙陶瓷上增殖程度更高。且在基础培养基中双相磷酸钙陶瓷上的间充质干细胞中骨形成相关基因(如RUNX-2)的表达上调,表明小颗粒双相磷酸钙陶瓷具有的骨诱导潜能更高[34]。此外,陶瓷的表面形貌和释放的无机离子也可能是成骨分化和骨形成的直接触发因素。如羟基磷灰石在体内溶解时产生的钙磷等离子可刺激成骨基因的表达。另外已证明在植入异位部位时,骨植入物表面上的重复凹陷可促进骨形成。陶瓷在生产过程中产生出颗粒表面的凹陷,这在体外可诱导表面矿化,在体内可异位诱导骨形成。凹面尺寸直接影响表面矿化的程度(凹面尺寸减少4倍,导致钙摄取增加约123倍)。凹面类似于破骨细胞形成过程中产生的半骨质沟,以此引发骨诱导活性,且表面矿化过程优先开始在凹陷内而不是在陶瓷的平坦表面上[33]。而骨传导是指骨缺损边缘向表面向内生长或向下进入生物材料的孔隙,生物材料作为支架或模板来指导新骨组织的形成。这种现象的影响因素主要取决于材料的内在特性(几何形状,孔隙度)和生物因素(如对生长因子或蛋白质及细胞的吸引黏附作用)。将双相磷酸钙陶瓷(羟基磷灰石与β-磷酸三钙组成比3∶7,孔隙度70%)植入小鼠大腿肌肉45 d后,在内部孔周围形成了小块新骨;90 d时新骨占有面积的(5.26±4.31)%,羟基磷灰石或者β-磷酸三钙总是表现出对骨形态发生蛋白2很高的吸附性,溶液中约90 d的形态发生蛋白2可以结合到材料表面,且不受其他血清蛋白的影响[21,23]。 Albee和Morrison在1920年首次报道了磷酸钙用于骨修复[35]。天然骨是胶原蛋白和羟基碳酸磷灰石的复合物,具有10%-30%的多孔硬外层(皮质骨),30%-90%的多孔内部(松质骨)。其中无机成分主要是30%无定形的磷酸钙 Ca3(PO4)2,70%的羟基磷灰石。作为正常骨组织骨盐的主要成分之一,其中尤其是β-磷酸三钙,具有优异的生物相容性、骨传导性和骨诱导活性,并且其相关衍生物也不引起细胞毒性作用[18,36],为骨修复和替代提供了巨大的潜力[37-38]。羟基磷灰石被认为是能够与活组织形成直接化学键,无毒和骨传导性的生物活性材料,因此被广泛用作牙科、颌面外科和矫形外科手术修复骨缺损的植入材料,并作为金属植入物的涂层材料。以前的研究涉及体外和体内研究报道,与非涂层植入物相比,羟基磷灰石涂层有助于更快的骨附着,产生更高的整合率。钙和磷酸盐是能够成功诱导新骨生成的主要因素,在细胞水平上,羟基磷灰石可触发干细胞或骨祖细胞向成骨方向分化,其释放的钙和磷酸根离子在植入部位具有较强的多种细胞趋化性,并且在植入物空隙中加速新形成骨的矿化。在分子水平上,羟基磷灰石还与骨诱导蛋白具有很高的亲和力,增加了细胞活性[35]。简单说来就是,低结晶度陶瓷部分地解离成简单信号分子(即钙和磷酸根离子),其诱导骨髓间充质干细胞内骨诱导蛋白生长因子(骨形态发生蛋白2)的产生和分泌,来进行诱导新骨生成[38]。而骨髓间充质干细胞是具有高自我更新能力的多潜能细胞,并且有可能分化为多种细胞类型,包括骨、软骨和脂肪。在天然骨骼发育过程中,骨髓间充质干细胞分化形成骨骼;在组织工程领域,骨髓间充质干细胞在骨骼再生修复骨缺损方面也具有极其重要的地位[39]。因而骨诱导可被定义为各种物理或化学生物因素刺激人骨髓间充质干细胞分化为成骨细胞,诱导骨的生成[9]。 有研究将羟基磷灰石纳米颗粒溶液与丝素溶液混合,通过冻干法制备丝素蛋白/羟基磷灰石复合支架,实现羟基磷灰石颗粒的均匀分布,测定在纯丝和不同含量丝素蛋白/羟基磷灰石(羟基磷灰石比例分别为:0,20%,40%)复合支架上培养干细胞的分化与增殖。在相同的培养时间,丝素蛋白/羟基磷灰石复合支架表达出最高水平的碱性磷酸酶活性;支架上生成的矿物比纯丝高约10倍;培养第7天时的Runx2及骨钙素表达水平较其他组支架为最高。随着羟基磷灰石颗粒含量的增加,骨髓基质干细胞的成骨分化增强[37,40]。 在兔颅骨缺损部位植入相同孔隙及颗粒形状的双相磷酸钙陶瓷及β-磷酸三钙约4周后,组织形态学分析显示再生骨平均值约为49.2%和52.4%,两组之间没有明显差异,且植入部位未出现细胞炎性浸润或异物反应的迹象,展示出双相磷酸钙陶瓷及β-磷酸三钙与周围组织良好的物质结合,以及良好的骨传导性[16]。近来还有研究指出生物聚集体,一种新型的硅酸钙纳米微粒生物陶瓷,通过抑制破骨细胞形成(生物聚集体直接抑制RAW264.7细胞向破骨细胞分化)和骨吸收来显著诱导骨骼和牙周再生[41]。纳米陶瓷和聚合物复合材料已被广泛研究用于骨组织建设,促进骨组织生成。如和纯羟基磷灰石相比,羟基磷灰石-岩藻依聚糖复合材料在兔子的胫骨中观察到显著的矿化[42]。一项动物实验在雄性新西兰兔胫骨制作2个圆形临界尺寸缺陷(6 mm直径),植入多孔Si-Ca-P-单相陶瓷,通过比较植入前后的扫描电子显微镜图像来评估材料变化,新的骨层厚度在15 d时为(13±10) μm,30 d后增加到(30±7) μm,60 d后增加到(50±4) μm,表明植入物被很好地整合到宿主组织中,并刺激新骨生成[27]。使用硅磷酸盐支架植入胫骨干骺端,在组织切片中观察到,3个月时具有成骨细胞的类骨质薄层,以及侵入支架的骨髓和血管毛细血管成分;6个月时,观察到许多骨细胞陷窝,植入材料完全被新骨组织包裹,整个过程中未检测到炎性细胞(巨噬细胞和淋巴细胞)的存在。支架颗粒被新形成的骨包围,其呈现出成熟的骨特征,并且在对不同时间点残余支架EDS元素分析中,在骨界面材料中的Si离子浓度从10.77下降到6.89,这一发现表明,Ca和Si离子从生物材料逐渐扩散到组织与植入物界面上,且构成新骨的组成部分[30]。 2.5 羟基磷灰石作为药物,植入物涂层载体 用于生物医学应用的生物陶瓷或陶瓷的概念,不仅仅限于硬组织的恢复,生物活性磷酸钙和生物活性玻璃已被广泛用作药物递送的基质[43]。CaP被认为是合适的药物载体,因为它们利用陶瓷基质的硬化学性质,有效地保护承载的药物分子免受酶降解或体内酸碱度或温度等因素诱导的变性,具有并入和保留活性物质的能力,随着时间的推移以受控的方式局部递送,逐渐降解并被新形成的骨替代。使用这种方法目标药物浓度在骨水平更容易达到,同时也降低或消除血浆药物浓度,避免二次作用或一般毒性。CaP支架的局部药物释放可根据两种主要机制进行:扩散通过CaP载体的多孔网络和通过其渐进的生物降解。基于这些机制,各种支架特征及负荷剂量都参与了释放剂量的输送动力学和控制[44]。目前应用的聚合物涂覆生物陶瓷或生物活性玻璃支架就是基于以上特性,作为局部药物递送载体,并且对药物递送具有选择性,由此增强支架的内在生物活性。迄今为止,已有一系列不同的药物被纳入到支架中[13]。如在对关节结核治疗上,使用含二氧化硅纳米粒子的多孔β-磷酸三钙生物陶瓷,异烟肼和利福平的载药率分别达71%和63.7%。体外模拟体液实验中,异烟肼首日释放量约为总装载量 (1 mg)的约25%,大约80%的药物在84 d后被释放出来。体内实验中,异烟肼药物浓度在第7天达到最大值(约105 mg/L)且保持在有效最小抑制浓度(异烟肼: 10 mg/L;利福平:5 mg/L)超过8周[45]。作为药物载体,羟基磷灰石纳米颗粒具有pH依赖性溶解度和低毒性的优点,近年来开发出混合羟基磷灰石中空微粒,通过组合羟基磷灰石中空微粒和脱乙酰壳多糖/藻酸钠,使其具有高比表面积、高载药和持续的pH依赖性药物释放能力,其载药率为高达90.0%(固体羟基磷灰石微粒39.6%),在可控药物递送的新型药物载体方面具有很大的潜力[46]。 已知将植入物放置在活的生物体内后,细菌细胞可黏附于其表面,导致生物膜形成,造成持续性感染。因此,现在的植入物表面不仅应具有良好的生物相容性,还应具有抗菌性能。载有抗生素的羟基磷灰石植入物涂层可以允许局部递送抗生素,以防止手术植入后的感染或炎症反应。用真空等离子喷涂技术在钛样品上制备了不同浓度银的羟基磷灰石-Ag涂层,这种涂层对人体细胞没有细胞毒性,对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌显示出抗菌活性。通过电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法分析羟基磷灰石-Ag中释放Ag(浓度为1 000 ppm)的量,开始时7.11 g/24 h,释放达最高,在4 d内连续降低,直到达到0.2-0.41 g/24 h几乎恒定的值,15 d内的总释放量被确定为12.61 g。第1天内Ag有效释放,降低了细菌对种植体表面的初始黏附,与无涂层羟基磷灰石相比大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌存活率小于0.001%[4,47]。有研究将聚己内酯与四环素混合在溶剂中,并将其涂覆到多孔羟基磷灰石支架(孔隙尺寸为150-200 μm,孔隙率87%),与直接局部使用四环素相比未出现明显爆发性释放,机械性能由聚己内酯涂层补足。类似的含硫酸妥布霉素聚己内酯-羟基磷灰石支架在体外维持了10周的杀菌活性[48]。 2.6 羟基磷灰石的临床应用 目前已有很多生物陶瓷的临床实际应用,有一项回顾性研究通过在股骨头坏死的减压手术后用双相陶瓷(含有75%硫酸钙和25%磷酸钙的复合物与β-磷酸三钙混合)作填充物评测相关的吸收动力学。术后生物陶瓷的密度平均值与皮层骨相当,从而提供了足够的机械强度,以防止骨质减压后骨坏死性股骨头的进一步塌陷;术后1年,检测材料密度的大幅度下降,主要是由于CaSO4溶解造成的,其留下的开放孔结构,使得新血管的浸润和沉积;术后2年时,平均密度进一步降低,直至与小梁骨水平相当[26]。还有研究利用羟基磷灰石或双相磷酸钙的生物相容性、生物活性和骨传导性,将CaP水泥应用于腰椎间融合达到94%的融合率,这与使用髂骨移植物(93%)或局部骨移植物(95%)相似[28]。为了增强磷酸钙陶瓷支架的骨再生成功概率,常用方法如预先添加生长因子、细胞因子、干细胞和抗感染药物到支架上。磷酸钙陶瓷支架在矫形和牙科应用方面预先添加的有:骨形态发生蛋白(例如骨形态发生蛋白2、骨形态发生蛋白7)、人生长激素、血小板衍生生长因子、转化生长因子β3、成纤维细胞生长因子2、富血小板血浆和血管内皮生长因子。虽然许多磷酸钙陶瓷支架-生长因子的组合已在动物身上进行了测试,目前在临床上仅有的商用磷酸钙陶瓷支架-生长因子产品:GEM21S®(Osteohealth),它通过提供血小板衍生生长因子以可控的方式输送用于牙科领域[9]。羟基磷灰石已在使用各种类型的(生物)聚合物或生物大分子来递送抗生素,在治疗骨感染疾病中得到应用,它不仅提供了完美的供抗生素附着的载体,利用其生物相容性、骨传导性以提高骨整合,而且防止植入物磨损颗粒与界面处的接触,避免了免疫应答和围绕手术部位被使用,包括用于治疗感染骨缺损部位的可生物降解藻酸盐载体系统和可再吸收的聚-L-乳酸药物载体[49]。此外随着近年来3D打印技术的迅速发展已成功应用于机械制造和科学研究的许多领域,利用3D打印技术可得到不同患者自体特定的解剖数据,而生产出符合不同个体需要的植入物、组织工程支架,以达到为个体化精准治疗的实现提供便利[50]。 "
| [1] Capanema NSV,Mansur AAP,Carvalho SM,et al.Niobium-Doped Hydroxyapatite Bioceramics: Synthesis, Characterization and In Vitro Cytocompatibility. Materials(Basel).2015;8(7): 4191-4209.[2] Tamaddon M,Samizadeh S,Wang L,et al.Intrinsic Osteoinductivity of Porous Titanium Scaffold for Bone Tissue Engineering.Int J Biomater. 2017.2017:5093063.[3] Fuh LJ,Huang YJ,Chen WC,et al.Preparation of micro-porous bioceramic containing silicon-substituted hydroxyapatite and beta-tricalcium phosphate.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;75: 798-806.[4] Vollmer NL,Spear JR,Ayers RA.Antimicrobial activity and biologic potential of silver-substituted calcium phosphate constructs produced with self-propagating high-temperature synthesis.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2016;27(6):104.[5] Gomes S,Kaur A,Grenèche JM,et al.Atomic scale modeling of iron-doped biphasic calcium phosphate bioceramics.Acta Biomater. 2017;50:78-88.[6] Blum C,Brückner T,Ewald A,et al.Mg:Ca ratio as regulating factor for osteoclastic in vitro resorption of struvite biocements. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;73:111-119.[7] Ke D,Dernell W,Bandyopadhyay A,et al.Doped tricalcium phosphate scaffolds by thermal decomposition of naphthalene: Mechanical properties and in vivo osteogenesis in a rabbit femur model.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2015;103(8):1549-1559.[8] Schumacher TC,Treccani L,Rezwan K.Effect of silica on porosity, strength, and toughness of pressureless sintered calcium phosphate–zirconia bioceramics.Biomed Mater. 2015;10(4):045020.[9] Denry I,Kuhn LT.Design and characterization of calcium phosphate ceramic scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.Dent Mater. 2016;32(1): 43-53.[10] Mbarki M,Sharrock P,Fiallo M,et al.Hydroxyapatite bioceramic with large porosity. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;76:985-990.[11] Yatongchai C,Placek LM,Curran DJ,et al.Investigating the addition of SiO2–CaO–ZnO–Na2O–TiO2 bioactive glass to hydroxyapatite: Characterization, mechanical properties and bioactivity. J Biomater Appl.2015;30(5):495-511.[12] Lindner M,Bergmann C,Telle R,et al.Calcium phosphate scaffolds mimicking the gradient architecture of native long bones.J Biomed Mater Res A.2014;102(10):3677-3684.[13] Philippart A,Boccaccini AR,Fleck C,et al.Toughening and functionalization of bioactive ceramic and glass bone scaffolds by biopolymer coatings and infiltration: a review of the last 5 years.Expert Rev Med Devices.2015;12(1):93-111.[14] Duan S,Feng P,Gao C,et al.Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties Improvement in Liquid-Phase-Sintered Hydroxyapatite by Laser Sintering.Materials(Basel). 2015;8(3):1162-1175.[15] Yao MZ,Huang-Fu MY,Liu HN,et al.Fabrication and characterization of drug-loaded nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide 66 scaffolds modified with carbon nanotubes and silk fibroin. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016;11: 6181-6194.[16] Kunert-Keil C,Scholz F,Gedrange T,et al.Comparative study of biphasic calcium phosphate with beta-tricalcium phosphate in rat cranial defects--A molecular-biological and histological study. Ann Anat.2015;199:79-84.[17] Xie L,Yu H,Deng Y,et al.Preparation, characterization and in vitro dissolution behavior of porous biphasic alpha/beta-tricalcium phosphate bioceramics. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;59: 1007-1015.[18] de Wild M,Amacher F,Bradbury CR,et al.Investigation of structural resorption behavior of biphasic bioceramics with help of gravimetry, muCT, SEM, and XRD.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2016; 104(3):546-553.[19] Lu J,Descamps M,Dejou J,et al.The biodegradation mechanism of calcium phosphate biomaterials in bone.J Biomed Mater Res. 2002; 63(4):408-412.[20] Roldán JC,Klünter T,Schulz P,et al.Bone Morphogenetic Protein-7 Enhances Degradation of Osteoinductive Bioceramic Implants in an Ectopic Model. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2017;5(6):e1375.[21] Bouler JM,Pilet P,Gauthier O,et al.Biphasic calcium phosphate ceramics for bone reconstruction: A review of biological response.Acta Biomater.2017;53:1-12.[22] Ghosh R,Sarkar R.Synthesis and characterization of sintered beta-tricalcium phosphate: A comparative study on the effect of preparation route.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;67:345-352.[23] Wang J,Chen Y,Zhu X,et al.Effect of phase composition on protein adsorption and osteoinduction of porous calcium phosphate ceramics in mice.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;102(12):4234-4243.[24] Despang F,Bernhardt A,Lode A,et al.Synthesis and physicochemical, in vitro and in vivo evaluation of an anisotropic, nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite bisque scaffold with parallel-aligned pores mimicking the microstructure of cortical bone.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015; 9(12):E152-166.[25] Feng P,Deng Y,Duan S,et al.Liquid phase sintered ceramic bone scaffolds by combined laser and furnace.Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(8): 14574-14590.[26] Civinini R,Capone A,Carulli C,et al.The kinetics of remodeling of a calcium sulfate/calcium phosphate bioceramic.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2017;28(9):137.[27] Rabadan-Ros R,VelásquezPA,Meseguer-Olmo L,et al.Morphological and Structural Study of a Novel Porous Nurse's A Ceramic with Osteoconductive Properties for Tissue Engineering. Materials (Basel). 2016;9(6).pii: E474. doi: 10.3390/ma9060474.[28] Sun H,Yang HL.Calcium phosphate scaffolds combined with bone morphogenetic proteins or mesenchymal stem cells in bone tissue engineering.Chin Med J (Engl). 2015;128(8):1121-1127.[29] Maté Sánchez de Val JE,Calvo-Guirado JL,Gómez-Moreno G,et al.Influence of hydroxyapatite granule size, porosity, and crystallinity on tissue reaction in vivo. Part A: synthesis, characterization of the materials, and SEM analysis.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2016;27(11): 1331-1338.[30] Ros-Tárraga P, Mazón P, Rodríguez MA,et al.Novel Resorbable and Osteoconductive Calcium Silicophosphate Scaffold Induced Bone Formation. Materials(Basel). 2016;9(9).pii: E785. doi:10.3390/ma9090785. [31] Maji K,Dasgupta S,Kundu B,et al.Development of gelatin-chitosan- hydroxyapatite based bioactive bone scaffold with controlled pore size and mechanical strength.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2015;26(16): 1190-1209.[32] Rustom LE,Boudou T,Lou S,et al.Micropore-induced capillarity enhances bone distribution in vivo in biphasic calcium phosphate scaffolds.Acta Biomater.2016;44:144-154.[33] Bianchi M,Urquia Edreira ER,Wolke JG,et al.Substrate geometry directs the in vitro mineralization of calcium phosphate ceramics.Acta Biomater.2014;10(2):661-669.[34] Lobo SE,Glickman R,da Silva WN,et al.Response of stem cells from different origins to biphasic calcium phosphate bioceramics.Cell Tissue Res.2015;361(2):477-495.[35] Yu X,Tang X1,Gohil SV,et al.Biomaterials for Bone Regenerative Engineering.Adv Healthc Mater. 2015;4(9):1268-1285.[36] Roohani-Esfahani SI,No YJ,Lu Z,et al.A bioceramic with enhanced osteogenic properties to regulate the function of osteoblastic and osteocalastic cells for bone tissue regeneration. Biomed Mater.2016; 11(3):035018.[37] He F,Zhang J,Yang F,et al.In vitro degradation and cell response of calcium carbonate composite ceramic in comparison with other synthetic bone substitute materials.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015;50:257-265.[38] Cushnie EK,Ulery BD,Nelson SJ,et al.Simple Signaling Molecules for Inductive Bone Regenerative Engineering.PLoS One. 2014;9(7): e101627.[39] Harada N,Watanabe Y,Sato K,et al.Bone regeneration in a massive rat femur defect through endochondral ossification achieved with chondrogenically differentiated MSCs in a degradable scaffold. Biomaterials.2014;35(27):7800-7810.[40] Huang X,Bai S,Lu Q,et al.Osteoinductive-nanoscaled silk/HA composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering application. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2015;103(7):1402-1414.[41] Tian J,Qi W,Zhang Y,et al.Bioaggregate Inhibits Osteoclast Differentiation, Fusion, and Bone Resorption In Vitro.J Endod. 2015; 41(9):1500-1506.[42] Tae Young A,Kang JH,Kang DJ,et al.Interaction of stem cells with nano hydroxyapatite-fucoidan bionanocomposites for bone tissue regeneration.Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;93(PtB):1488-1491.[43] Arcos D,Vallet-Regí M.Bioceramics for drug delivery.Acta Materialia. 2013;61(3):890-911.[44] Parent M,Baradari H,Champion E,et al.Design of calcium phosphate ceramics for drug delivery applications in bone diseases: A review of the parameters affecting the loading and release of the therapeutic substance.J Control Release. 2017;252:1-17.[45] Zhu M,Li K,Zhu Y,et al.3D-printed hierarchical scaffold for localized isoniazid/rifampin drug delivery and osteoarticular tuberculosis therapy. Acta Biomater.2015;16:145-55.[46] Feng DS,Shi J,Wang XJ,et al.Hollow hybrid hydroxyapatite microparticles with sustained and pH-responsive drug delivery properties. RSC Adv.2013;3(47):24975.[47] Guimond-Lischer S,Ren Q,Braissant O,et al.Vacuum plasma sprayed coatings using ionic silver doped hydroxyapatite powder to prevent bacterial infection of bone implants. Biointerphases. 2016;11(2): 011012.[48] Brooks BD,Sinclair KD,Davidoff SN,et al.Molded polymer-coated composite bone void filler improves tobramycin controlled release kinetics.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2014;102(5): 1074-1083.[49] Zheng X,Shi Y,Chen Y,et al.Novel impurity-free hexagonal hydroxyapatite nanotubes for local delivery of antibiotics in orthopedic surgery: in vitro release validation.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(2): 2628-2634.[50] Chia HN,Wu BM.Recent advances in 3D printing of biomaterials.J Biol Eng.2015;9:4. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||