Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (20): 3250-3255.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0808
Previous Articles Next Articles
Growth factors in platelets promote soft and hard tissue healing in oral implantology
Wang Jun-ling, Shao Miao-miao, He Jian-ya, Hu Shu-hai, Li Xiao-jie
- School of Stomatology of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116044, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2017-11-30Online:2018-07-18Published:2018-07-18 -
Contact:Li Xiao-jie, Master, Lecturer, School of Stomatology of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116044, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Wang Jun-ling, Master, Physician, School of Stomatology of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116044, Liaoning Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Jun-ling, Shao Miao-miao, He Jian-ya, Hu Shu-hai, Li Xiao-jie. Growth factors in platelets promote soft and hard tissue healing in oral implantology[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(20): 3250-3255.
share this article
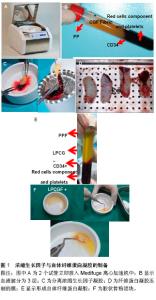
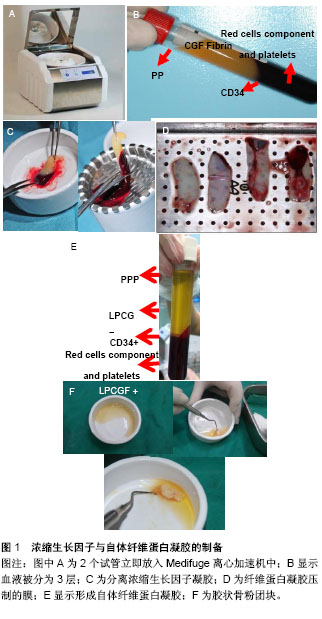
由此可知,骨创伤的类型及部位并不会影响较后期的骨组织的愈合状态[2]。而经研究发现,在种植手术中,植体与骨发生的骨结合也经过了类似的过程,而差别主要在于对种植手术来说最重要的是临时基质及新生血管的形成,这取决于在植体表面能否出现骨的生成及再塑,即植体的存活率。因此,保证血液的供应及新生血管的形成对于软硬组织的愈合而言尤为重要,这个条件无论是在骨损伤还是种植手术中都是无可厚非的[11]。无论是拔牙创还是种植手术在愈合的初期对于血液的供应及新生血管的要求,都是一样的严格。 以骨组织为例,当骨组织受伤后,血管即刻进行收缩,纤维蛋白基质与血小板迅速形成的血栓堵住出血处。接着,补体系统开始活化,血小板释放炎症物质以改变血管张力增加其通透性。与此同时,大量的生长因子例如转化生长因子、成纤维细胞生长因子、表皮生长因子等会被释放至受伤部位[12],开始进行组织的修复。当然,不同结构组成的生长因子发挥的作用也各不相同。 2.2 血小板浓缩技术的研究背景 1974年,Ross等[13]通过研究发现,血小板中所含的生长因子具有强效促进组织再生的功能。在随后的数十年中,国内外科学家针对生长因子进行了一系列试验,研究生长因子在愈合机制中所扮演的角色。 Arora等[14]通过研究发现从人的血浆中可以分离出含有多种生长因子的富血小板血浆。1993年,Hood等[15]将自体的全血离心后产生的凝胶与氯化钙和牛凝血酶混合,研究出一种含有高度浓缩的血小板及其纤维素原的改良纤维素凝胶,即“富血小板血浆凝胶”。研究发现,在凝血酶启动活化血小板后,大量的生长因子便会立即从血小板中被释放出来,发挥其促进软组织与硬组织愈合的作用。早期科学家对于富血小板血浆的研究和应用局限于促进软组织的愈合上,富血小板血浆凝胶只作为一种生物凝胶和屏障应用于临床。而富血小板血浆对硬组织的作用,包括剂量、安全性、效能等诸多问题,仍有待探讨。 2001年,Choukroun等[16]在1代血小板浓缩技术,即富血小板血浆凝胶的基础上进行改良,研究制作出了2代浓缩血小板-富血小板纤维蛋白。富血小板纤维蛋白是由患者静脉血制作而成的一种富纤维蛋白凝胶,它在制备过程中无需任何生物添加剂的处理,即刻便能形成一种具有纤维网络结构的胶状凝块,大幅度减少了二次交叉感染的风险。而且在此过程中,一旦血小板被启动活化,大量生长因子,包括隐藏在其细胞因子中的白细胞,都会立即从颗粒细胞中被释放出来,同时针对炎症和止血发挥作用,减轻术后的疼痛和水肿,从而加速组织的愈合和血管的生成。组织学评估表明,富血小板纤维蛋白能够缩短骨形成的时间。 Saccol[17]首先研发出来的浓缩生长因子是目前为止最新一代血小板浓缩技术。浓缩生长因子与富血小板纤维蛋白一样,均是由患者自体静脉血液制备而成,但两者的离心速度有所不同。富血小板纤维蛋白采用的是为时10 min的3 000 r/min的定速离心技术;而浓缩生长因子采用的是为时12 min的变速离心技术,离心速度是从2 400 r/min到3 000 r/min变化进行。因此,二者分离出的成分是有所差异的,后者能够准确效率将静脉血中的细胞分层,同时相比富血小板血浆与富血小板纤维蛋白技术,能够分离出浓度更高的生长因子,这包括血小板衍生生长因子、转化生长因子β、血管内皮生长因子、成纤维细胞生长因子、表皮生长因子、胰岛素样生长因子、骨形态发生蛋白及CD34干细胞等有效成分[18]。 作为造血干细胞、髓系及淋巴系细胞的表面抗原,CD34干细胞在血管的维护与再生、组织的新生与修复及免疫调节等方面都起到了不可或缺的作用。由于浓缩生长因子中富含丰富的纤维蛋白凝块,因此其在愈合过程中能够显示出极强的再生力和多变性,尤其是当浓缩生长因子被压制成生物膜时,将具有更高的抗张强度、更多的生长因子、更好的黏性、更高的黏合强度以及更多含量的纤维蛋白,可以当做barrier membrane来使 用[19]。因此,浓缩生长因子生物膜常被当作隔膜在临床中被应用,甚至将其与骨移植物混合以加快软硬组织的愈合与重建。另外,浓缩生长因子的制备过程简单,无需任何生物添加剂(例如凝血酶或抗凝剂)的处理,是由患者的静脉血制作而成,因此不存在潜在的免疫原性的危险及交叉感染。 2.3 浓缩生长因子与自体纤维蛋白凝胶(autologous fibrin glue,AFG)的制备 准备2支真空采血试管,其中一支含有硅涂层,将同一患者被采集的静脉血分别置于2支试管中;迅速将2支试管放入Medifuge离心加速机中(Silfradent,意大利,如图1A),并经过2 400-3 000 r/min的变速离心;12 min后,含硅涂层的采血管里的血液被分为3层,分别是PPP、浓缩生长因子及含有血球细胞及凝血因子的红色细胞层(如图1B);部分血清PPP被分离出以储存在特定器皿中;而含有丰富纤维蛋白、血小板、相关细胞及生长因子的浓缩生长因子将被分离并储在稀释的抗生素溶液中(如图1C),以供临床应用,另外,将纤维蛋白凝胶压制成膜以作为屏障能加快手术区组织的愈合(如图1D),在临床上的应用也较为广泛;最后,底层的红色细胞层因含有血小板、凝血因子等其他基本元素,可混合自体骨或其他生物材料,作为填料来使用。 除此之外,在经过同样离心过程的另一支真空采血管中的浓缩生长因子层则是以液态形式存在的,称为液态浓缩生长因子(Liquid Phase CGF,LPCGF),如图1E),即自体纤维蛋白凝胶(AFG)。有实验证明,将约 3 mL量的液态浓缩生长因子及CD34与动物骨粉或自体骨混合并静置5-10 min后能得到一种胶状骨粉团块(如图1F),此种胶状骨粉团块是由骨粉颗粒与液态浓缩生长因子的纤维蛋白网络凝结而成的,因此具有一定的强度,即使使用一般的手术镊子也不容易将其打散,在临床操作上具有诸多优势;另外纤维蛋白交织的网络也会阻止软组织进入骨粉团块,加速软硬组织的愈合;其次, 险[20] (图1)。"
| [1] Ntounis A,Geurs N,Vassilopoulos P,et al. Vassilopoulos and M. Reddy.2015.Clinical assessment of bone quality of human extraction sockets after conversion with growth factors. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2015;(1):196-201.[2] Choukroun J, Adda F, Schoeffler C, et al. Une opportunitéen paro-implantologie:Le PRF. Implantodontie.2001;42:55-62. [3] Rodella LF, Favero G, Boninsegna R,et al.Growth factors, CD34 positive cells, and fibrin network analysis in concentrated growth factors fraction.Microsc Res Tech.2001; 74(8):772-777.[4] Zhao Y,Zhang S,Zeng D,et al.rhPDGF-BB promotes proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells from streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats through ERK pathway.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:637415.[5] Semichev EV, Baikov AN, Shevtsova NM, et al. Morphofunctional Changes of Spleen After Hemostasis by Nonequilibrium Plasma.Vestn Ross Akad Med Nauk.2015; (5):592-598.[6] Wang Xiaoxu, Zhai R, Yang Juntao, et al.[Effect of hamstring tendon transfected with adenovirus- mediated transforming growth factor β1 gene on histomorphology of tendon-bone interface healing after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in rabbits. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2015;29(12):1488-1493.[7] Zheng L, Cai Y, Zhou L, et al.Benzoquinone from Fusarium pigment inhibits the proliferation of estrogen receptor-positive MCF-7 cells through the NF-kappaB pathway via estrogen receptor signaling.Int J Mol Med.2017;39(1):39-46.[8] 陈庆.成纤维细胞生长因子在骨修复中的作用和应用[J].中国组织化学与细胞代学杂志,2001,10(13):337-339.[9] Nässel DR, Vanden Broeck J.Insulin/IGF signaling in Drosophila and other insects: factors that regulate production, release and post-release action of the insulin-like peptides. CellMol Life Sci..2016;73(2):271-290.[10] Zhuang YF, Li J.Serum EGF and NGF levels of patients with brain injury and limb fracture.Asian Pac J Trop Med.2013;6(5): 383-386.[11] 毛亚丽,韩纪举,王云.血小板聚集初期形状变化与聚集的关系及其影响因素分析[J].山东医药,2014,54(24):1-3.[12] Zhao Y,Zhang S,Zeng D,et al.rhPDGF-BB promotes proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells from streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats through ERK pathway.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:637415.[13] Ross R, Glomset J, Kariya B,et al. A platelet- dependent serum factor that stimulates the proliferation of arterial smooth muscle cells in vitro.Proc Natl AcadSci U S A.1974; 71(4):1207-1210.[14] Arora NS, Ramanayake T, Ren YF, et al. Platelet-rich plasma: a literature review.Implant Dent.2009;18(4):303-310.[15] Hood AG,Hill AG,Reeder GD.Perioperative autologous sequestration.III:A new physilolgic glue with wound healing properties.Proc Am Acad Cardiovasc Perfusion.1993;14:126.[16] Choukroun J, Diss A, Simonpieri A,et al.Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part IV: clinical effects on tissue healing.OralSurg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod.2006;101(3):e56-60.[17] Saccol L. International academy of implant prosthesis and osteoconnection.Lecture.2006.12.4[18] AlTurki A, Proietti R, Birnie DH,et al. Management of antithrombotic therapy during cardiac implantable device surgery.J Arrhythm.2016;32(3):163-169.[19] Sharma V, Sharma S, Dudeja P, et al. Endodontic management of nonvital permanent teeth having immature roots with one step apexification, using mineral trioxide aggregate apical plug and autogenous platelet-rich fibrin membrane as an internal matrix: Case series.Contemp Clin Dent.2016;7(1):67-70.[20] Dohan Ehrenfest DM, Rasmusson L, Albrektsson T. Classification of platelet concentrates: from pure platelet-rich plasma (P-PRP) to leucocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF). Trends Biotechnol.2009;27(3):158-167.[21] Jang SH, Ha JK, Lee DW,et al.Fibrin clot delivery system for meniscal repair.Knee Surg Relat Res.2011;23(3):180-183.[22] Boyne PJ,James RA.Grafting of the maxillary sinus floor with autogenous marrow and bone.J Oral Sury.1980;38(8): 613-616.[23] Lee JS, Jung JS, Im G, et al. Ridge regeneration of damaged extraction sockets using rhBMP-2: an experimental study in canine.J Clin Periodontol. 2015;42(7):678-687.[24] Zechner WS,Tangl G,Tepper G,et al. Influence of platelet-rich plasma on osseous healing of dental implants: a histologic and histomorphometric study in minipigs.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2003;18(1):15-22.[25] Weibrich G, Gnoth SH, Otto M, et al.[Growth stimulation of human osteoblast-like cells by thrombocyte concentrates in vitro].Mund Kiefer Gesichtschir. 2002;6(3):168-174.[26] Toffler M, Toscano N, Holtzclaw D.Osteotome-mediated sinus floor elevation using only platelet-rich fibrin: an early report on 110 patients.Implant Dent.2010;19(5):447-456.[27] Thorat M,Pradeep AR,Pallavi B.Clinical effect of autologous platelet-rich fibrininthe treatment of intra-bony defects;a controlled clinicaltrial.Clin Periodontol.2011;39(10):925-932.[28] Sharma V, Sharma S, Dudeja P, et al. Endodontic management of nonvital permanent teeth having immature roots with one step apexification, using mineral trioxide aggregate apical plug and autogenous platelet-rich fibrin membrane as an internal matrix: Case series.Contemp Clin Dent.2016;7(1):67-70.[29] 李琦,周延民,翟静捷.富血小板纤维蛋白修复兔颅骨骨缺损的实验研究[J].口腔医学研究,2011,27(7):587-589.[30] Nkenke E,Schlegel A,Schultze-Mosgau S,et al.The endoscopically controlled osteotome sinus floor elevation:A preliminary prospective study.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2001;17(4):557-566.[31] Sohn DS.Concentration of growth factors on the ridge on the increase.J Dent Dynamic.2009;12.[32] Cavicchia F, Bravi F, Petrelli G.Localized augmentation of the maxillary sinus floor through a coronal approach for the placement of implants.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2001;21(5):475-485.[33] Takeda Y, Katsutoshi K, Matsuzaka K, et al.The Effect of Concentrated Growth Factor on Rat Bone Marrow Cells In Vitro and on Calvarial Bone Healing In Vivo.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2015;30(5):1187-1196.[34] 张晓,董福生,任贵云.富自体CGF纤维蛋白膜对人牙龈成纤维细胞黏附及增殖的影响[J].现代口腔医学志,2014,28(4):197-201.[35] Yu B, Wang Z.Effect of concentrated growth factors on beagle periodontal ligament stem cells in vitro.Mol Med Rep.2014;9(1):235-242. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [3] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [4] | Wang Mengting, Gu Yanping, Ren Wenbo, Qin Qian, Bai Bingyi, Liao Yuanpeng. Research hotspots of blood flow restriction training for dyskinesia based on visualization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1264-1269. |
| [5] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [6] | Yuan Jun, Yang Jiafu. Hemostatic effect of topical tranexamic acid infiltration in cementless total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 873-877. |
| [7] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [8] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [9] | Xu Jianxia, Wang Zhaoxu, Wang Chunren. Blood compatibility of disposable blood perfusion device in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 588-592. |
| [10] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [11] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [12] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [13] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [14] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [15] | Lü Zexiang, Wu Jutai, Jiang Jian, Feng Xiao, Li Tengfei, Wang Yehua. Effect of tranexamic acid combined with carbazochrome sodium sulfonate on blood loss and safety after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 386-390. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||