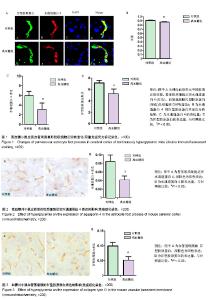
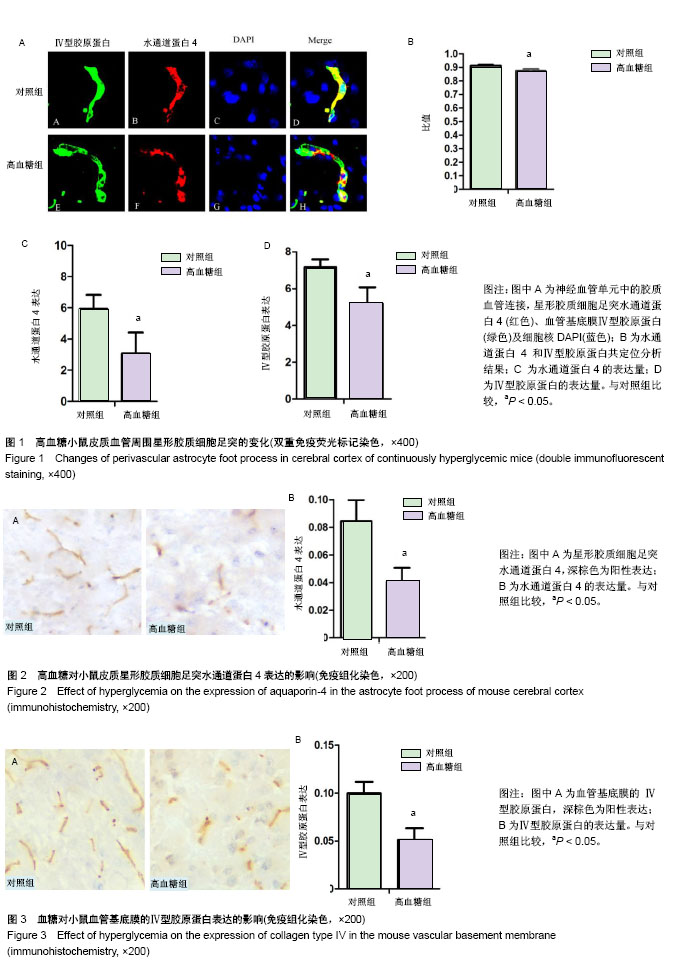
| [1] Reusch JE, Manson JE. Management of type 2 diabetes in 2017: Getting to Goal. JAMA.2017;317(10):1015-1016.[2] Wang L, Gao P, Zhang M, et al. Prevalence and ethnic pattern of diabetes and prediabetes in China in 2013.JAMA.2017; 317(24):2515-2523.[3] Hagg S, Thorn LM, Forsblom CM, et al. Different risk factor profiles for ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Stroke.2014;45(9):2558-2562.[4] Koekkoek PS, Kappelle LJ, van den Berg E, et al. Cognitive function in patients with diabetes mellitus: guidance for daily care. Lancet Neurol.2015;14(3):329-340.[5] Stirban A. Microvascular dysfunction in the context of diabetic neuropathy. Curr Diab Rep.2014;14(11):541.[6] Bogush M, Heldt NA, Persidsky Y. Blood brain barrier injury in diabetes: unrecognized effects on brain and cognition. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol.2017;12(4):593-601.[7] Zlokovic BV. Neurovascular pathways to neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease and other disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011;12(12):723-738.[8] Moskowitz MA, Grotta JC, Koroshetz WJ, et al. The NINDS stroke progress review group final analysis and recommendations. Stroke.2013;44(8):2343-2350.[9] Kisler K, Nelson AR, Montagne A, et al. Cerebral blood flow regulation and neurovascular dysfunction in Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurosci.2017;18(7):419-434.[10] Marie Simard GA, Takahiro Takano, Qing Song Liu, and Maiken Nedergaard. Signaling at the gliovascular interface. J Neurosci.2003;23(27):9254-9262.[11] Giaume C, Koulakoff A, Roux L, et al. Astroglial networks: a step further in neuroglial and gliovascular interactions. Nat Rev Neurosci.2010;11(2):87-99.[12] Iadecola C. Neurovascular regulation in the normal brain and in Alzheimer's disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004;5(5): 347-360.[13] Andreone BJ, Lacoste B, Gu C. Neuronal and vascular interactions. Annu Rev Neurosci.2015;38:25-46.[14] Jukkola P, Gu C. Regulation of neurovascular coupling in autoimmunity to water and ion channels. Autoimmun Rev. 2015;14(3):258-267.[15] Dunn KM, Hill-Eubanks DC, Liedtke WB, et al. TRPV4 channels stimulate Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release in astrocytic endfeet and amplify neurovascular coupling responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci US A.2013;110(15):6157-6162.[16] Pappas AC, Koide M, Wellman GC. Astrocyte Ca2+ Signaling Drives Inversion of Neurovascular Coupling after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. J Neurosci.2015;35(39): 13375-13384.[17] Merlini M, Meyer EP, Ulmann-Schuler A, et al. Vascular beta-amyloid and early astrocyte alterations impair cerebrovascular function and cerebral metabolism in transgenic arcAbeta mice. Acta Neuropathol.2011;122(3): 293-311.[18] MacVicar BA, Newman EA. Astrocyte regulation of blood flow in the brain. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.2015,7(5). pii: a020388.[19] Chen Y, Mancuso J, Zhao Z, et al. Vasodilation by in vivo activation of astrocyte endfeet via two-photon calcium uncaging as a strategy to prevent brain ischemia. J Biomed Opt.2013;18(12):126012.[20] Zhang M, Zhang L, Hu J, et al. MST1 coordinately regulates autophagy and apoptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy in mice. Diabetologia.2016;59(11):2435-2447.[21] Di Benedetto B, Malik VA, Begum S, et al. Fluoxetine Requires the Endfeet Protein Aquaporin-4 to Enhance Plasticity of Astrocyte Processes. Front Cell Neurosci.2016; 10:8.[22] Rajkowska G, Hughes J, Stockmeier CA, et al. Coverage of blood vessels by astrocytic endfeet is reduced in major depressive disorder. Biol Psychiatry.2013;73(7):613-621.[23] Holland PR, Searcy JL, Salvadores N, et al. Gliovascular disruption and cognitive deficits in a mouse model with features of small vessel disease. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2015;35(6):1005-1014.[24] Duncombe J, Lennen RJ, Jansen MA, et al. Ageing causes prominent neurovascular dysfunction associated with loss of astrocytic contacts and gliosis. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2017;43(6):477-491.[25] Bragg F, Holmes MV, Iona A, et al. Association between diabetes and cause-specific mortality in rural and urban areas of China. JAMA.2017;317(3):280-289.[26] Feher J, Taurone S, Spoletini M, et al. Ultrastructure of neurovascular changes in human diabetic retinopathy. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol.2018;31:394632017748841.[27] Gardner TW, Davila JR. The neurovascular unit and the pathophysiologic basis of diabetic retinopathy. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol.2017;255(1):1-6.[28] Kolibabka M, Friedrichs P, Dietrich N, et al. Dicarbonyl Stress Mimics Diabetic Neurovascular Damage in the Retina. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes.2016;124(7):437-439.[29] Zhao Z, Nelson AR, Betsholtz C, et al. Establishment and Dysfunction of the Blood-Brain Barrier. Cell.2015; 163(5): 1064-1078.[30] Min LJ, Mogi M, Shudou M, et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma activation with angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockade is pivotal for the prevention of blood-brain barrier impairment and cognitive decline in type 2 diabetic mice. Hypertension. 2012;59(5): 1079-1088.[31] Pak RW, Hadjiabadi DH, Senarathna J, et al. Implications of neurovascular uncoupling in functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) of brain tumors. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017:271678X17707398.[32] Kimbrough IF, Robel S, Roberson ED, et al. Vascular amyloidosis impairs the gliovascular unit in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Brain.2015;138(Pt 12):3716-3733.[33] Nicchia GP, Pisani F, Simone L, et al. Glio-vascular modifications caused by Aquaporin-4 deletion in the mouse retina. Exp Eye Res.2016;146:259-268.[34] Thomsen MS, Routhe LJ, Moos T. The vascular basement membrane in the healthy and pathological brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.2017;37(10):3300-3317.[35] Huang J, Sun SQ, Lu WT, et al. The internalization and lysosomal degradation of brain AQP4 after ischemic injury. Brain Res.2013;1539:61-72.[36] de Senna PN, Xavier LL, Bagatini PB, et al. Physical training improves non-spatial memory, locomotor skills and the blood brain barrier in diabetic rats. Brain Res.2015;1618:75-82.[37] Skucas VA, Mathews IB, Yang J, et al. Impairment of select forms of spatial memory and neurotrophin-dependent synaptic plasticity by deletion of glial aquaporin-4. J Neurosci.2011;31(17):6392-6397.[38] Zeppenfeld DM, Simon M, Haswell JD, et al. Association of perivascular localization of aquaporin-4 with cognition and alzheimer disease in aging brains. JAMA Neurol.2017; 74(1):91-99.[39] Xu Z, Xiao N, Chen Y, et al. Deletion of aquaporin-4 in APP/PS1 mice exacerbates brain Abeta accumulation and memory deficits. Mol Neurodegener.2015;10:58.[40] Wijesekara N, Ahrens R, Sabale M, et al. Amyloid-beta and islet amyloid pathologies link Alzheimer's disease and type 2 diabetes in a transgenic model. Faseb J.2017;31(12): 5409-5418.[41] Michalicova A, Banks WA, Legath J, et al. Tauopathies-focus on changes at the neurovascular unit. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2017;14(7):790-801.[42] Szu JI, Binder DK. The role of astrocytic aquaporin-4 in synaptic plasticity and learning and memory. Front Integr Neurosci.2016;10:8. |