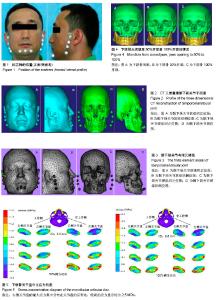
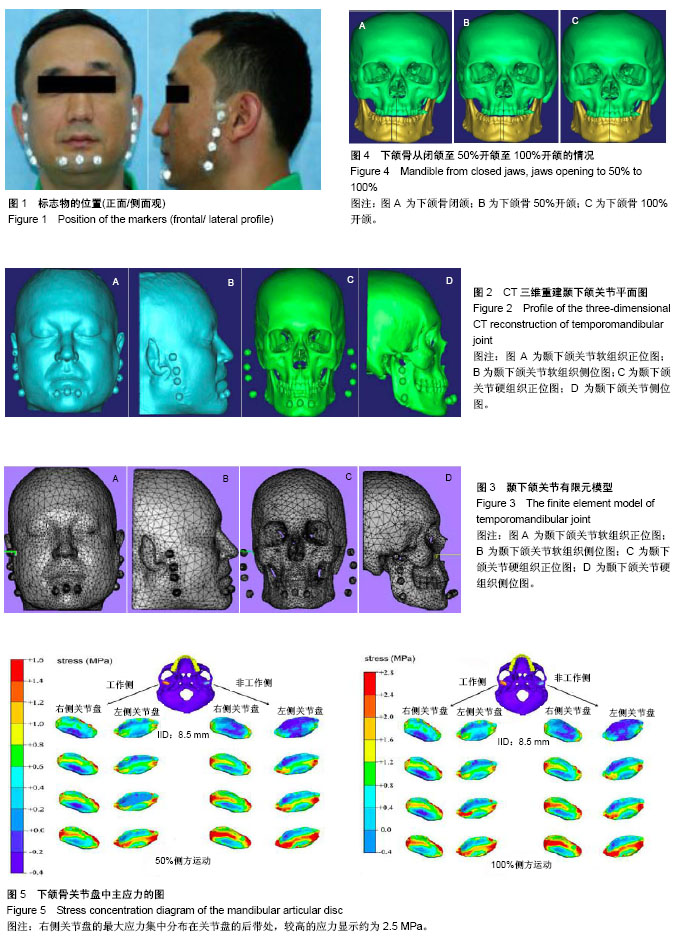
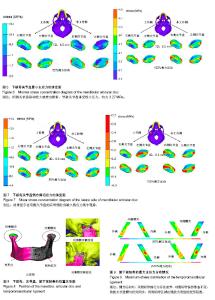
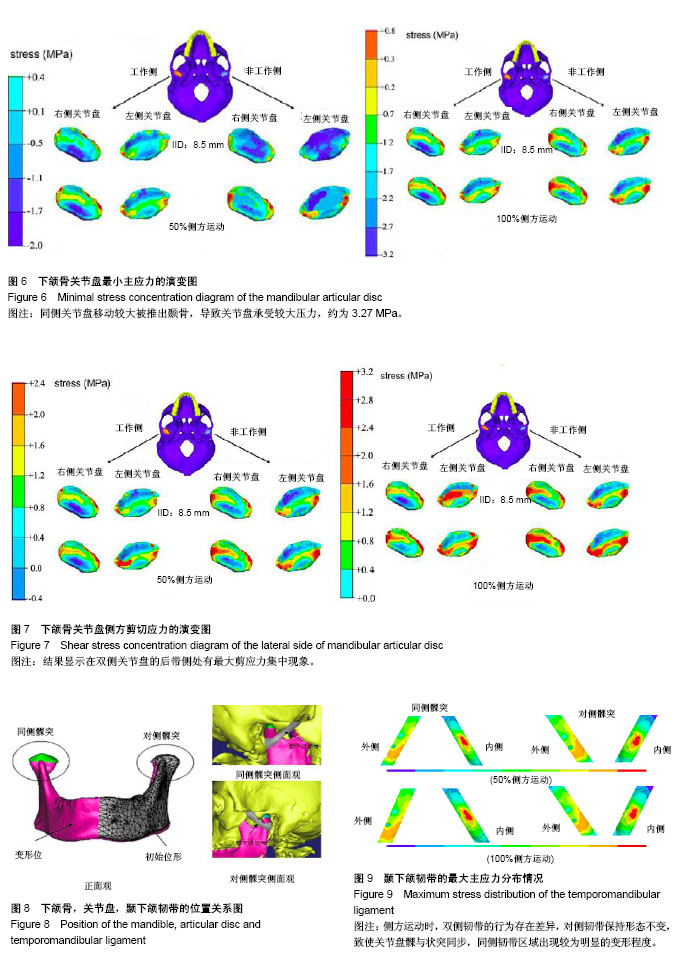
| [1] 孔亚阁.口腔解剖生理学[M].郑州:郑州大学出版社,2013. [2] 金翩翩,舒真谛,夏婉,等.关节松动术配合理疗治疗颞下颌关节紊乱综合征的疗效评估[J].中国康复医学杂志,2016, 31(7): 775-778.[3] 郁春华, 钱海馨, YUChun-hua,等.稳定性牙合垫、手法及物理治疗对颞下颌关节盘不可复性移位的短期疗效评价[J]. 上海交通大学学报:医学版, 2016, 36(6):850-855.[4] 韩建辉,雷杰,刘木清,等.颞下颌关节盘不可复性前移位患者骨关节病表现的锥形束CT观察[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2017,52(1):22-26.[5] 向国林,龙星,邓末宏,等.创伤性颞下颌关节外强直10例临床分析[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2016, 32(3):438-440.[6] 陈维维,桑婷,黄臻,等.Herbst双期拔牙矫治对颞下颌关节骨性结构影响的锥形束CT研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志, 2016,34(5): 498-501.[7] 杨驰.颞下颌关节盘前移位与髁突骨吸收的关系及联合诊疗模式的探索[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2017, 52(3):157-160.[8] 夏文棣,傅开元.颞下颌关节盘前移位对下颌功能和形态的影响及其生物学机制的研究进展[J].中华口腔医学杂志, 2016, 51(3):182-184.[9] 夏文棣,傅开元,陆文昕,等. 口腔医学本科生颞下颌关节紊乱病症状及其与心理、睡眠关系的问卷调查[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2016,51(9):521-525.[10] 毛凯平,邹璟,李解,等.氦氖激光对兔退变颞下颌关节髁突软骨基质表达的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志,2017,32(9):984-988.[11] Won HS, Liu HF, Kim JH,et al.Intermuscular aponeuroses between the flexor muscles of the forearm and their relationships with the ulnar nerve. Surg Radiol Anat. 2016; 38(10):1183-1189. [12] Stavness I,Hannam AG,Lloyd JE, et al.An integrated dynamic jaw and laryngeal model constructed from CT data.Lecture Notes in Computer Science.2006;4072:169-177.[13] Lpez-Jornet P,Camacho-Alonso F,Leon-Espinosa S. Burning mouth syndrome, oral parafunctions, and psychological profile in a longitudinal case study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2009;23(3):363-365. [14] Long H, Liao Z, Wang Y, et al. Efficacy of botulinum toxins on bruxism: an evidence-based review. Int Dent J. 2012;62(1): 1-5. [15] Dao TT,Lavigne GJ.Oral splints: the crutches for temporomandibular disorders and bruxism? Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1998;9(3):345-361.[16] Ateshian GA,Soltz MA,Mauck RL,et al.The role of osmotic pressure and tension-compression nonlinearity in the frictional response of articular cartilage.Transport in Porous Media.2003, 50(1):5-33. [17] Rintakoski K, Kaprio J. Legal psychoactive substances as risk factors for sleep-related bruxism: a nationwide finnish twin cohort study. Alcohol Alcohol. 2013;48(4):487-494.[18] 罗宁洁,李自力,伊彪,等.口内入路髁突切除同期正颌术后颞下颌关节结构变化的影像学观察[J].中华口腔医学杂志, 2016,51(6): 350-356.[19] 李晨,李永刚,冯雪,等.骨性II类高角成年女性颞下颌关节骨性结构的三维研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志, 2016,32(2):239-243.[20] 鄢荣曾,胡敏.颞下颌关节三维有限元建模相关因素分析[J].医用生物力学,2016,31(2):182-187.[21] 盛潇,朱敏.颞下颌关节三维有限元建模方法进展[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2011,21(1):68-71. [22] 朱赴东,石珏,宋恩,等.数字化全牙列下颌骨三维解剖建模[J]. 解剖学报, 2014,45(4):536-539. [23] Hirose M,Tanaka E,Tanaka M,et al.Three-dimensional finite element model of the human temporomandibular joint disc during prolonged clenching. Eur J Oral Sci. 2006;114(5): 441-448. [24] Spilker RL,Nickel JC,Iwasaki LR.A biphasic finite element model of in vitro plowing tests of the temporomandibular joint disc. Ann Biomed Eng. 2009;37(6):1152-1164. [25] Osborn JW.The temporomandibular ligament and the articular eminence as constraints during jaw opening. J Oral Rehabil. 1989;16(4): 323-333.[26] Schreppers GJ,Sauren AA,Huson A.A model of force transmission in the tibio-femoral contact incorporating fluid and mixtures. Proc Inst Mech Eng H.1991;205(4):233-241.[27] Wang DJ,Cheng HY,Pan YN,et al.Research on biomechanical behavior of three-dimensional bilateral temporomandibular disorder models.J Exp Cli Med.2013;5(1):17-21. |