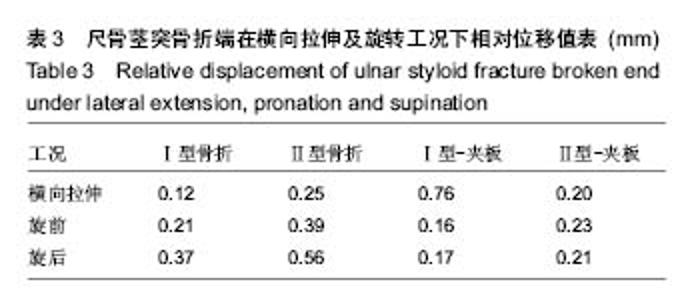
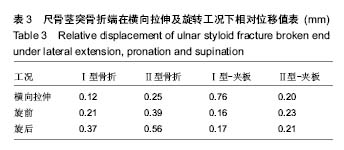
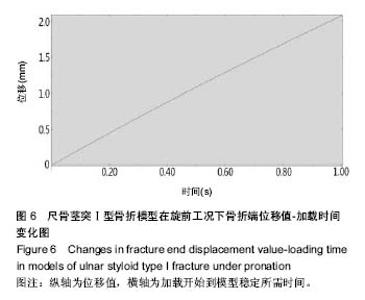
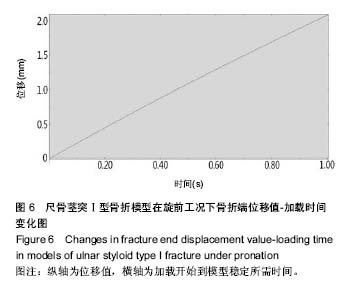
| [1] May MM, Lawton JN, Blazar PE. Ulnar styloid fractures associated with distal radius fractures: incidence and implications for distal radioulnar joint instability. J Hand Surg Am.2002;27(6): 965-971.[2] Rikli DA, Regazzoni P. Fractures of the distal end of the radius treated by internal fixation and early function. A preliminary report of 20 cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996;78(4):588-592.[3] Henry MH. Management acute triangular fibrocartilage complex injury of the wrist. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2008,16(6): 320-329.[4] Anderson ML, Larson AN, Moran SL, et al. Clinical comparison of arthroscopic versus open repair of triangular fibrocartilage complex tears. J Hand Surg Am. 2008;33(5):675-682.[5] Abe Y, Moriya A, Tominaga Y, et al. Dorsal tear of triangular fibrocartilage complex: clinical features and treatment. J Wrist Surg. 2016; 5(1):42-46.[6] 杨焕,王斌,李浩,等.尺骨茎突解剖特点与骨折分型及治疗方法[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2012,30(5):564-567.[7] Woo SJ, Jegal M, Park MJ. Arthroscopic-assisted repair of triangular fibrocartilage complex foveal avulsion in distal radioulnar joint injury. Indian J Orthop.2016;50(3):263-268.[8] Moritomo H. The distal interosseous membrane: current concepts in wrist anatomy and biomechanics. J Hand Surg Am.2012; 37(7): 1501-1507.[9] Zlatkin M B, Rosner J. MR imaging of ligaments and triangular fibrocartilage complex of the wrist. Radiol Clin North Am.2006; 44(4):595-623.[10] 尚峥辉,黄富国,岑石强,等.三角纤维软骨复合体损伤后腕关节稳定性的生物力学分析[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2008,22(7):820-823.[11] 张光辉.桡骨远端骨折合并的尺骨茎突骨折内固定与否对腕关节功能的影响[J].临床医药文献电子杂志, 2016,3(41):8162-8164.[12] Ayalon O, Marcano A, Paksima N, et al. Concomitant ulnar styloid fracture and distal radius fracture portend poorer outcome. Am J Orthop.2016;45(1):34-37.[13] Yilmaz S, Cankaya D, Karakus D. Ulnar styloid fracture has no impact on the outcome but decreases supination strength after conservative treatment of distal radial fracture. 2015; 20(8):1497-1502.[14] Krämer S, Meyer H, O'Loughlin P F, et al. The incidence of ulnocarpal complaints after distal radial fracture in relation to the fracture of the ulnar styloid. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2013; 38(7): 710-717.[15] Shirakawa K, Shirota M.T.A.C. Pin fixation for basal ulnar styloid fractures associated with distal radius fractures. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg. 2013; 17(3):158-161.[16] 靳家骋,张坤鹏,黄富国.合并尺骨茎突骨折对桡骨远端骨折预后影响的Meta分析[J].中国循证医学杂志, 2014,14(6):729-733.[17] 赵雪明,都晋江.前后石膏夹板固定治疗桡骨远端骨折68例疗效分析[J].临床医药实践,2009,18(9):719-720.[18] Kang YK, Park HC, Youm Y, et al. Three dimensional shape reconstruction and finite element analysis of femur before and after the cementless type of total hip replacement. J Biomed Eng.1993;15:497-504.[19] Lotz JC, Cheal EJ, Hayes WC. Fracture prediction for the proximal femur using finite element models: partl-linear analysis. J Biomech Engin.1991;11(2):353-360.[20] 徐永清,钟世镇,徐达传,等.腕关节韧带的解剖学研究[J].创伤外科杂志,2006,8(1):52-54.[21] 颜冰珊.尺骨茎突骨折与下尺桡关节稳定性关系的有限元分析[D].复旦大学,2009.[22] 郭欣,樊瑜波,李宗明.掌骨受轴向压力作用下的腕部生物力学分析[J].航天医学与医学工程,2008,21(1):45-49.[23] Anderson DD, Daniel TE. A contact-coupled finite element analysis of the radiocarpal joint. Semin Arthroplasty.1995;6(1): 30-36.[24] 周恩昌.塑形夹板治疗尺桡骨双骨折的生物力学实验研究[D].福建中医学院,2002.[25] 欧来良,王志彬,李林安,等.柳木夹板力学性能测试和优化分析.中国骨伤,2000,13(10):580-582.[26] Tencer AF, ViegasSF, Cantrell J, et al. Pressure distribution in the wrist joint. J Orthop Res.1998; 6(4):509-517.[27] 钦斌,黄永火,欧阳羽,等.轴向应力作用下的舟骨有限元分析[J].第三军医大学学报,2010,15(11):1213-1215.[28] 周晓宁.腕关节三维有限元模型的建立及桡骨远端骨折发生机制的生物力学分析[D].北京中医药大学,2014.[29] Schuind F, An KN, Berglund L, et al. The distal radioulnar ligaments: A Biomechanical study. J Hand Surg Am.1991;16(6): 1106-1114.[30] Short WH, werner FW, Fortino MD, et al. The stabilizing mechanism of the distal radioulnar joint during pronation and supination.J Hand Surg Am.1995;20(6):930-936.[31] Cheng HY, Lin CL, Lin YH, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of the modified Double-Plating fixation for the distal radius fracture. Clin Biomechanics (Bristol, Avon). 2007;22(5):510-517.[32] 李想.小夹板治疗老年桡骨远端骨折中夹板束缚力的量化研究[D].广州中医药大学,2011.[33] 兰美兵,敖俊,张美超.两种植骨方式治疗L-1椎体爆裂骨折的有限元研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2016,34(1):91-95.[34] Yu B, Chen W C, Lee P Y, et al. Biomechanical comparison of conventional and anatomical calcaneal plates for the treatment of intraarticular calcaneal fractures-a finite element study. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2016;19(13):1363-1370.[35] Burt LA, Macdonald HM, Hanley DA, et al. Bone microarchitecture and strength of the radius and tibia in a reference population of young adults: an HR-pQCT study. Arch Osteoporos. 2014;9(1):183.[36] Noda M, Saegusa Y, Takahashi M, et al. Biomechanical study using the finite element method of iInternal fixation in pauwels type Ⅲ vertical femoral neck fractures. Arch Trauma Res.2015; 4(3):e23167.[37] 林蔚莘.斜T型钢板内固定治疗桡骨远端骨折的有限元分析[D].南方医科大学,2004.[38] 李瑛,费攀,邹季.再议小夹板弹性固定骨折的先进性和科学性[J].中医外治杂志,2009,18(1):3-4. |