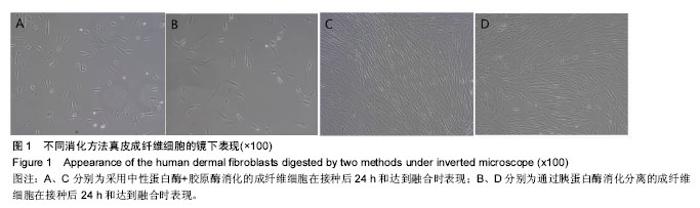
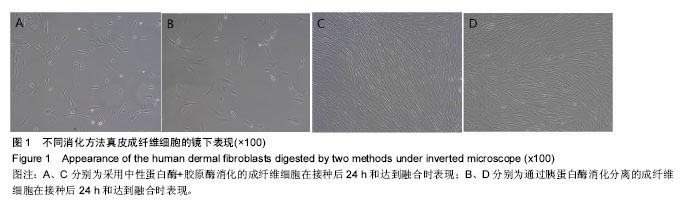
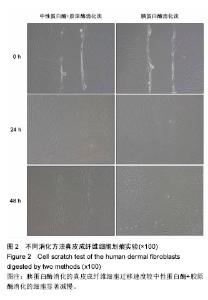
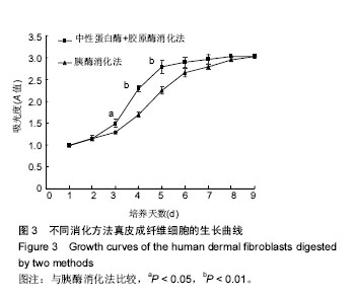
| [1] Duffield JS, Lupher M, Thannickal V J, et al. Host responses in tissue repair and fibrosis. Annu Rev Pathol.2013;8:241-276.[2] Rouabhia M, Park HJ, Zhang Z. Electrically Activated Primary Human Fibroblasts Improve In Vitro and In Vivo Skin Regeneration. J Cell Physiol. 2016;231(8):1814-1821.[3] Nithiananthan S, Crawford A, Knock JC, et al. Physiological Fluid Flow Moderates Fibroblast Responses to TGF-beta1. J Cell Biochem.2016.[4] Pilling D, Vakil V, Cox N, et al. TNF-alpha-stimulated fibroblasts secrete lumican to promote fibrocyte differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(38):11929-11934.[5] Alase AA, El-Sherbiny YM, Vital EM, et al.IFNlambda Stimulates MxA Production in Human Dermal Fibroblasts via a MAPK-Dependent STAT1-Independent Mechanism. J Invest Dermatol.2015;135(12):2935-2943.[6] Kendall RT, Feghali-Bostwick CA. Fibroblasts in fibrosis: novel roles and mediators. Front Pharmacol.2014;5:123.[7] Jang YH, Koo GB, Kim JY, et al.Prolonged activation of ERK contributes to the photorejuvenation effect in photodynamic therapy in human dermal fibroblasts. J Invest Dermatol.2013; 133(9):2265-2275.[8] Sriram G, Bigliardi PL, Bigliardi-Qi M. Fibroblast heterogeneity and its implications for engineering organotypic skin models in vitro. Eur J Cell Biol. 2015;94(11):483-512.[9] Takashima A. Establishment of fibroblast cultures. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 2001;Chapter 2:1-2.[10] Nahm WK, Zhou L, Falanga V. Sustained ability for fibroblast outgrowth from stored neonatal foreskin: a model for studying mechanisms of fibroblast outgrowth. J Dermatol Sci.2002; 28(2):152-158.[11] Hsia LT, Ashley N, Ouaret D, et al. Myofibroblasts are distinguished from activated skin fibroblasts by the expression of AOC3 and other associated markers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2016;113(15):E2162-E2171.[12] 张卓然. 培养细胞学与细胞培养技术[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2004.[13] 谭玉珍. 实用细胞培养技术[M].北京: 高等教育出版社, 2010.[14] 章静波. 组织和细胞培养技术[M]. 3版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2014.[15] 医疗机构管理条例[J]. 中华人民共和国国务院公报, 1994,(3): 83-89.[16] Pandamooz S, Hadipour A, Akhavan-Niaki H, et al. Short exposure to collagenase and coculture with mouse embryonic pancreas improve human dermal fibroblast culture. Biotechnol Appl Biochem.2012;59(3):254-261.[17] Attia-Vigneau J, Terryn C, Lorimier S, et al. Regeneration of human dermis by a multi-headed peptide. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134(1):58-67.[18] Myllyla RM, Haapasaari KM, Lehenkari P, et al. Bone morphogenetic proteins 4 and 2/7 induce osteogenic differentiation of mouse skin derived fibroblast and dermal papilla cells. Cell Tissue Res.2014;355(2):463-470.[19] Wang H, Van Blitterswijk CA, Bertrand-De HM, et al.Improved enzymatic isolation of fibroblasts for the creation of autologous skin substitutes. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim.2004; 40(8-9):268-277.[20] 宋瑞,卞徽宁,赖文,等. 碱性成纤维细胞生长因子对增生性瘢痕与正常皮肤成纤维细胞胶原、纤维连接蛋白表达的影响(英文)[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(41):7784-7790.[21] Chang Y, Guo K, Li Q, et al. Multiple Directional Differentiation Difference of Neonatal Rat Fibroblasts from Six Organs. Cell Physiol Biochem.2016;39(1):157-171.[22] Stenn KS, Link R,Moellmann G,et al.Dispase, a neutral protease from Bacillus polymyxa, is a powerful fibronectinase and type IV collagenase. J Invest Dermatol.1989;93(2): 287-290.[23] Yamato M, Utsumi M, Kushida A, et al. Thermo-responsive culture dishes allow the intact harvest of multilayered keratinocyte sheets without dispase by reducing temperature. Tissue Eng.2001;7(4):473-480.[24] Schaefer BM, Wallich R,Schmolke K, et al. Immunohistochemical and molecular characterization of cultured keratinocytes after dispase-mediated detachment from the growth substratum. Exp Dermatol.2000;9(1):58-64.[25] 陆新,韩春茂.皮肤组织工程进展[J].中华烧伤杂志, 2003,19(z1): 72-74.[26] 李伟,伍津津,吴国选,等. 人角质形成细胞库的建立[J]. 第三军医大学学报, 2004,26(11):987-989.[27] 毛一雷,徐海峰. 创口的处理与难点[J].中国实用外科杂志, 2011, 31(1):69-71.[28] Patriota LL, Procopio TF, de Souza MF, et al. A Trypsin Inhibitor from Tecoma stans Leaves Inhibits Growth and Promotes ATP Depletion and Lipid Peroxidation in Candida albicans and Candida krusei. Front Microbiol.2016;7:611.[29] 王志强,梁锐,陈明清,等. 胰蛋白酶消化法和组织块法原代培养人包皮成纤维细胞的比较[J]. 生命科学研究, 2012,16(3): 242-247.[30] Sinclair JA, Henderson C, Tettey JN, et al.The influence of the choice of digestion enzyme used to prepare rat hepatocytes on xenobiotic uptake and efflux. Toxicol In Vitro.2013;27(1): 451-457.[31] Agley CC, Rowlerson AM, Velloso CP, et al.Isolation and quantitative immunocytochemical characterization of primary myogenic cells and fibroblasts from human skeletal muscle.J Vis Exp.2015;(95):52049. |