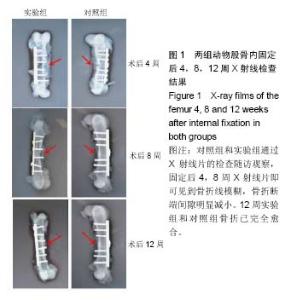
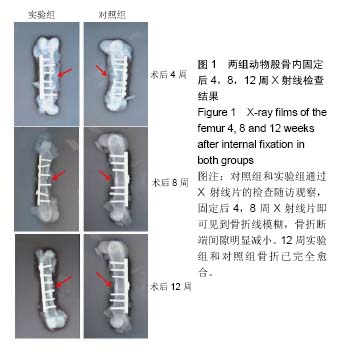
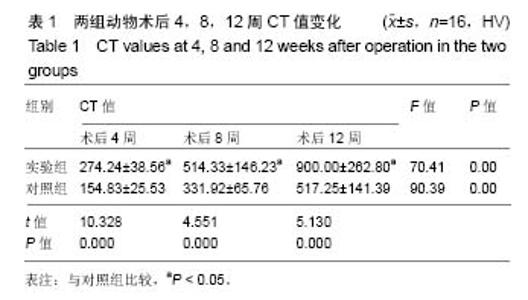
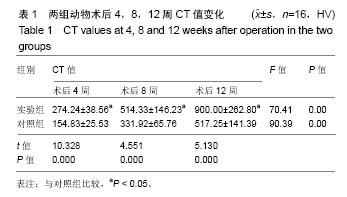
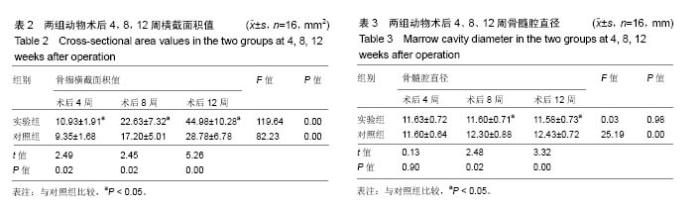
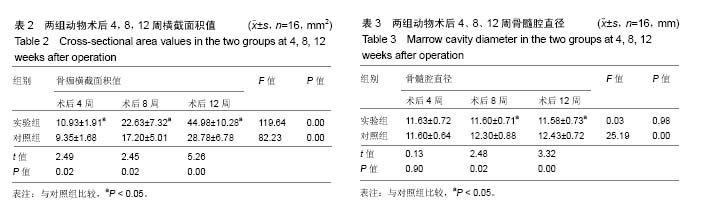
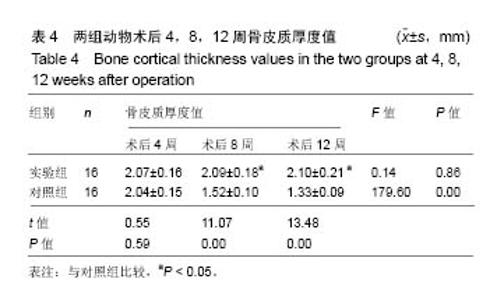
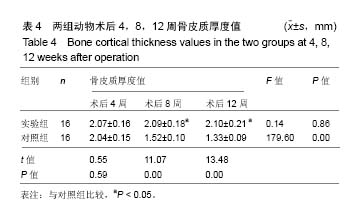
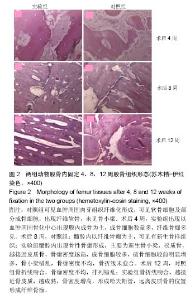
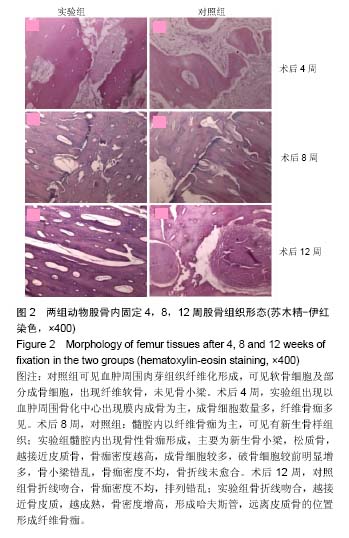
| [1] 周江军,肖春林,赵敏,等.新型组合式锁定加压钢板生物力学性能的三维有限元分析[J].中华生物医学工程杂志,2016,20(1):1-6.[2] 张耀,胡林,谢增如.微创钢板与交锁髓内钉内固定治疗成人股骨干骨折的疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2015,30(8): 797-800.[3] 谷雨,次仁伦珠.滑槽植骨结合 LCP 固定治疗股骨骨折术后骨不连的疗效观察[J].医学临床研究,2016,33(6):1044-1047.[4] 王飞达,高耀祖,苑伟,等.附加锁定加压钢板联合植骨治疗股骨干骨折髓内钉固定术后无菌性骨不连[J].中国骨伤, 2014,27(10): 815-818.[5] 王昌俊,郑欣,邱旭升,等.影响骨折愈合的生物物理学因素研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(10):898-901.[6] 赵烽,熊鹰,张仲子,等.桥接组合式内固定治疗股骨骨折的效果及生物力学特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(13):2127-2132.[7] 孙志波,杨述华,禹志宏,等.桥接组合式内固定系统治疗股骨骨折内固定术后再骨折[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2016,13(5): 19-20.[8] Chan DS, Nayak AN, Blaisdell G, et al. Effect of distal interlocking screw number and position after intramedullary nailing of distal tibial fractures: a biomechanical study simulating immediate weight-bearing. J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29(2):98-104.[9] 常晓,张保中,张万利,等.组合式外固定支架治疗胫骨远端骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2016,18(4):346-350.[10] Singh SD, Manohar PV, Butala R. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in management of distal tibia fractures. J Appl Ichthyol. 2015;28(28):687-691. [11] El-Rosasy MA, El-Sallakh SA. Distal tibial hypertrophic nonunion with deformity: treatment by fixator-assisted acute deformity correction and LCP fixation. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2013;8(1):31-35. [12] 吕志强,李兴华,王爱国.桥接组合式内固定与金属锁定接骨板钉系统修复股骨干骨折的生物力学比较[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(17):24515-24521.[13] 赵凯,努尔波力•哈里木,杨晶,等.可吸收材料在骨折治疗中的研究进展[J].中华生物医学工程杂志,2015,21(2):192-194.[14] 徐振东,刘曦明.微动促进骨折愈合的机制及临床应用研究现状[J].创伤外科杂志,2017,3(19):228-230.[15] 马信龙.生物力学在骨折愈合过程中的作用[J].中国中西医结合外科杂志,2012,18(6):555-556.[16] 周炎,刘世清,余铃,等.有限切开复位结合前外侧L形锁定加压接骨板内固定治疗胫骨远端干骺端骨折[J].创伤外科杂志, 2015, 17(5):441-444.[17] 武进华,冯志斌,段晓亮,等.肩外侧入路锁定接骨板内固定治疗肱骨近端骨折[J].实用骨科杂志,2016,22(1):43-46.[18] 施建辉,柳明忠,许志通.微创接骨板内固定治疗胫骨远端骨折的切口并发症相关危险因素分析[J].中国现代医学杂志, 2016, 26(5):110-114.[19] 高哲辰,周方,田耘,等.锁定接骨板内固定治疗股骨远端骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2016,18(11):965-969.[20] 林梁,唐亚辉,吾路汗,等.骨折愈合过程中原始骨折血肿的潜在作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(46):7386-7390.[21] 徐可林,殷渠东.对侧皮质锁定技术治疗股骨远端骨折的研究近况[J].中国现代医学杂志,2016,26(7):48-53.[22] 徐凤松,李力更,吴啸波,等.髋臼横行骨折K-L入路不同内固定方式的生物力学稳定性比较[J].山东医药,2016,56(16):52-54.[23] Gupta SKV, Parimala SP. Supracutaneous Locking Compression Plate for Grade I & II Compound Fracture Distal Tibia-A Case Series. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2013;3(2): 106-109.[24] Paluvadi SV, Lal H, Mittal D, et al. Management of fractures of the distal third tibia by minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis A prospective series of 50 patients. J Appl Ichthyol. 2014;5(3): 129-136.[25] 杨岳聪,何晖,甘秀天,等.桥接组合式内固定系统治疗成年肱骨干骨折的疗效分析[J].广西医学,2015,37(12):1821-1823.[26] [刘月驹,杨宗酉,张奇,等.一项新型应力分散微创接骨板[J].河北医科大学学报,2013,34(8):950-950.[27] 范志航,熊雁,杜全印,等.新型点式接触锁定加压接骨板在治疗四肢长骨骨折中的临床应用[J].创伤外科杂志, 2014,16(3): 240-243.[28] 刘磊,孙家元,陈伟,等.自定位微创钢板与普通锁定钢板内固定治疗山羊股骨干骨折的疗效比较[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2014, 16(5):433-436.[29] Menon RR, Subramanian V. Functional outcome of distal femoral fractures treated by, minimally invasive surgery using locking condylar plate. J Orthop. 2014;15(1):117-120.[30] 徐建民,王兆朋,王恒孝.骨形态发生蛋白-2在兔骨折愈合过程中的作用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(10):920-925. |