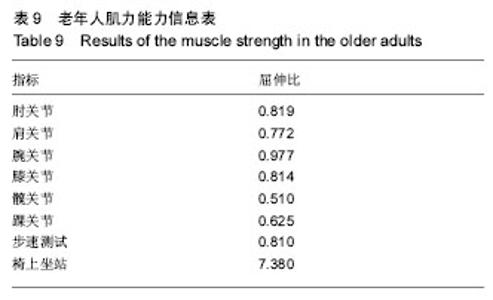
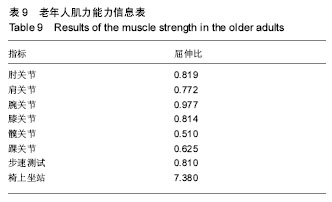
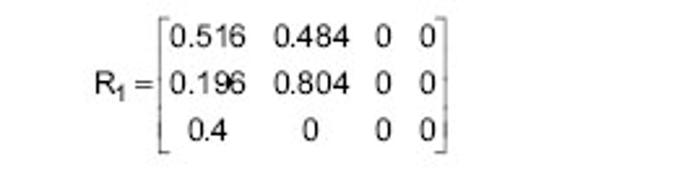
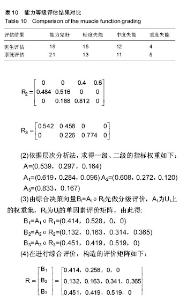
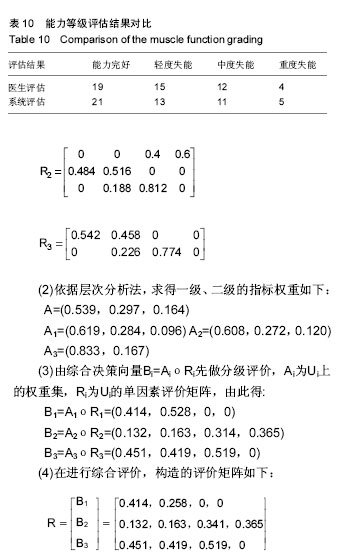
| [1] 王金营.21世纪中国面临的人口问题再认识以及应对策略[J].人口学刊, 2008(3):3-9.[2] 中华人民共和国民政部. MZ/T[S],039-2013,中华人民共和国民政行业标准:老年人能力评估.北京: 中华人民共和国民政部,2013.[3] 吴伟峰,糜迅.等速肌力测试和训练技术在我国康复医学领域应用现[J].中国伤残医学,2014,22(9):44-47.[4] 唐玉成,吴卅. 国外老年人肌肉力量评价指标综述[J]. 中国运动医学杂志, 2012, 5(5):456-461.[5] 杨茗,蒋皎皎,罗理,等.基于老年人群编制的失能评估量表[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2014,29(4):395-398[6] 胡秀英,龙纳,吴琳娜,等. 中国老年人健康综合功能评价量表的研制[J]. 四川大学学报(医学版),2013,44(4):610-613.[7] 胡娴亭,黄治物,陈建勇,等. 听力障碍筛查量表用于老年人群听力筛查分析[J]. 听力学及言语疾病杂志,2014,19(3):230-234.[8] Janssen I. Evolution of sarcopenia research. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2010, 35(5):707-712.[9] 胡水清,米奕翔,蒋云飞. Isomed 2000测试系统的等速向心测试方法的可信度分析[J].中国体育科技,2014, 50(5):100-106.[10] 俞捷,左群.老年人健身走对下肢肌力的影响[J]中国体育科技, 2008, 44 (2):76-80.[11] Lovell DI, Cuneo R, Gass GC. The effect of strength trainingand short-term detraining on maximum force and therate of force development of older men. Eur J Appl Physiol.2010;109(3):429-435.[12] 徐晓敏.层次分析法的运用[J].统计与决策,2008, 1:156-158.[13] 许顺国,牟瑞芳,张雪梅模糊数学综合评判法在水质评价中的应用一以成都市府河为例[J].唐山师范学院学报,2007,29(2):68-70.[14] Lin CC, Lin PY, Lu PK, et al.A Healthcare Integration System for DiseaseAssessment and Safety Monitoringof Dementia Patients. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed. 2008;12(5):579-586.[15] Ghassemian M, Auckburaully SF, Pretorius M, et al.Remote Elderly Assisted Living System-A preliminary research, development and evaluation.2011 IEEE 22nd International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications:2219-2223.[16] 李颖娟,赵中奇. 层次分析法中的判断向量法[J]. 系统工程, 2002,20(2): 83-87. [17] 丁俭,王华,赵敏. 一种简明的群体决策AHP模型及新的标度方法[J].管理工程学,2000,14(1):16-18. [18] Saaty TL.Decision making-the analytic hierarchy and network processes(AHP/ANP).J Syst Sci Syst Eng.2004;13(1):1-35. [19] 黄淑兰.旅行社核心竞争力模糊综合评价[J]. 新疆职业大学学报,2009, 17(2):26-29[20] 吴耀兴,陈政辉.模糊综合评价法在工程项目评标中的运用[J].建筑经济,2009, (10):64-67.[21] 程小飞,高曙.模糊综合评判理论在研究性学习系统中的研究及应用[J].电脑知识与技术,2009,5(25):7293-7294[22] Chen MS, Wang SW. Fuzzy Clustering Analysis for Optimizing Fuzzy Membership Functions.Fuzzy Sets Syst.1999;103(4):239-254.[23] 王中胜,李敏强,寇纪淞. 层次分析法判断矩阵不一致性的形成机理和一种修正方法[J]. 系统工程理论与实践,1995,15(9):36-43.[24] 陈培友,李星.模糊综合评判算法的改进[J].黑龙江科技学院学报,2006, 16(6):396-399.[25] Li J,Min QW,Li WH.Evaluation of water resources conserved by forests in the Hani rice terraces system of Honghe County, Yunnan, China: an application of the fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model.J Mountain Sci.2016;4:744-753.[26] IsIam Z,Metternicht G.The performance of fuzzy operators on fuzzy classification of urbanland covers. Photogramm Eng Rem S. 2005; (1):59-68.[27] Zhao X, Xiao DY .FaultDiagnosis of Nonlinear Systems Based on Modular Fuzzy NeuralNetworks. Control Theory & Appl. 2001;(6): 395-400.[28] Steve F, Kenneth JO, James SG, et al.Short physical performance battery in hospitalized older adults.Aging Clin Exp Res.2009;21(6): 445-452.[29] Lovell DI, Cuneo R, Gass GC. The effect of strength trainingand short-term detraining on maximum force and therate of force development of older men. Eur J Appl Physiol.2010;109(3):429-435.[30] Persad CC,Cook S,Giordani B. Assessing falls in the elderly:should we use simple screening tests or a comprehensive fall risk evaluation. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2010;46(2):249-259.[31] Foldvari M, Clark M, Laviolette L, et al. Association ofmuscle power with functional status in community-dwelling elderly women.J Gerontol. 2000;55 (4):M192-199.[32] Cuoco A, Callahan DM, Sayers S,et al.Impact of musclepower and force on gait speed in disabled older men andwomen. J Gerontol. 2004;59(11):1200-1206.[33] Henwood TR,Taaffe DR. Short-term resistance trainingand the older adult:the effect of varied programmes forthe enhancement of muscle strength and functional performance.Clin Physiol Funct Imaging.2006;26(5):305-313.[34] 袁俊锋,徐宏,游国鹏,等. ISOMED等速肌力测试仪检测高脚竞速运动员各关节肌力的灰色关联分析[J]. 贵州体育科技,2012,(1):53-56.[35] John R, Justin W L K. Power Training: Can it improve functional performance in older adults. A systematic review. Int J Exerc Sci.2009; 2(2):131-151.[36] Trappe S,Williamson D,Godard M,et al.Effect of resistance training on single muscle fiber contractile function in older men.J Appl Physiol. 2000; 89(1):143-152. |