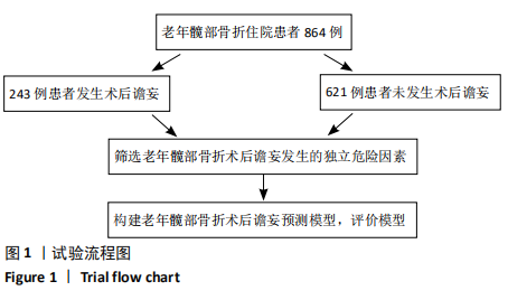
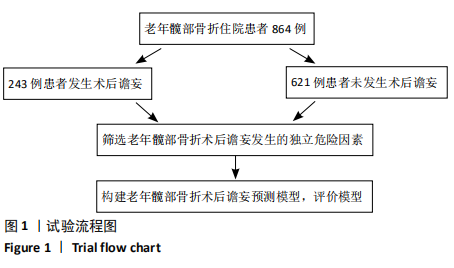
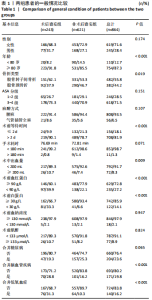
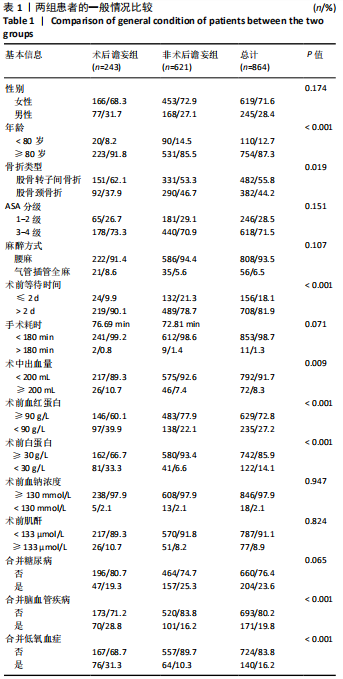
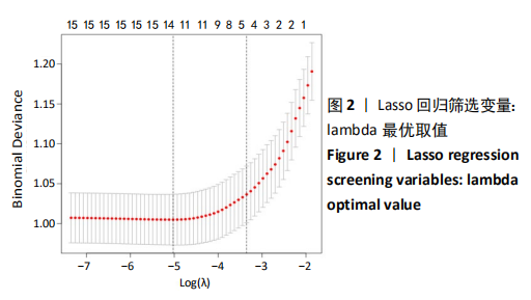
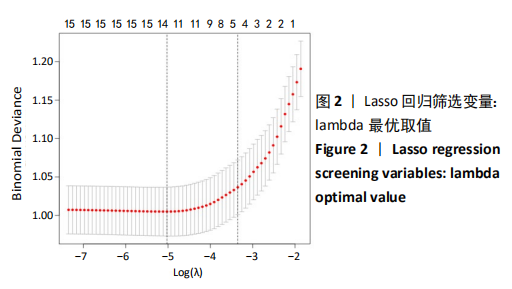
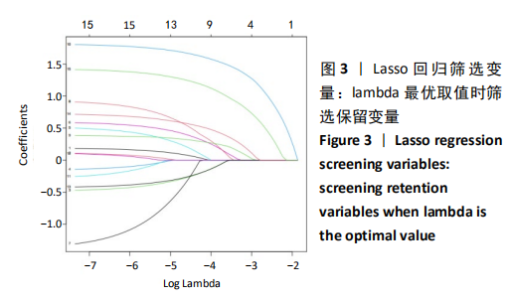
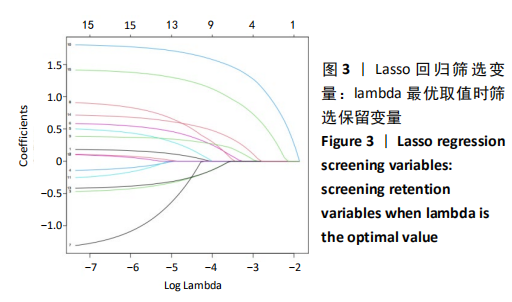
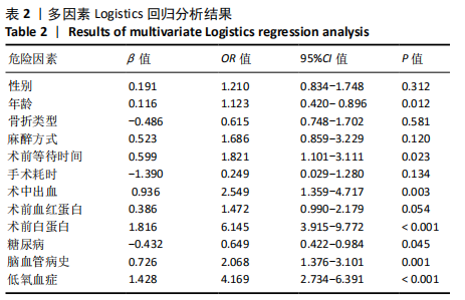
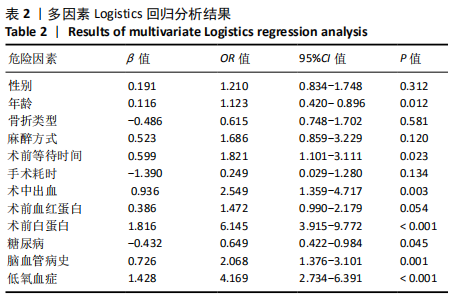
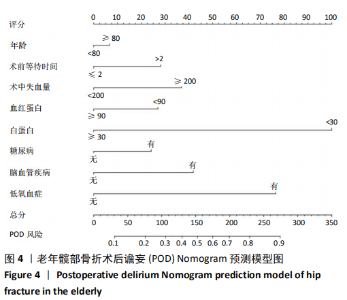
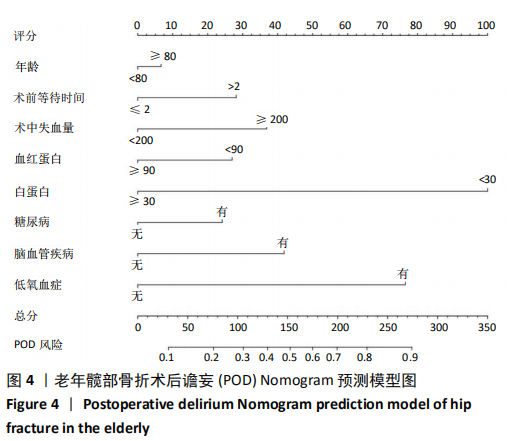
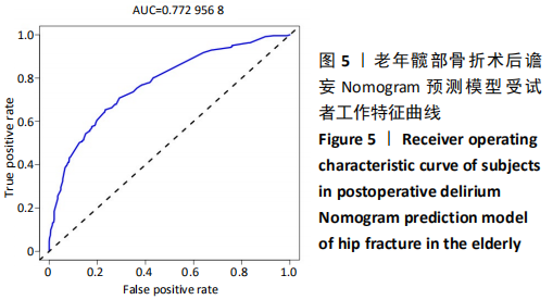
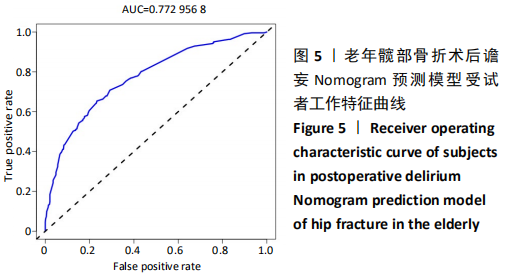
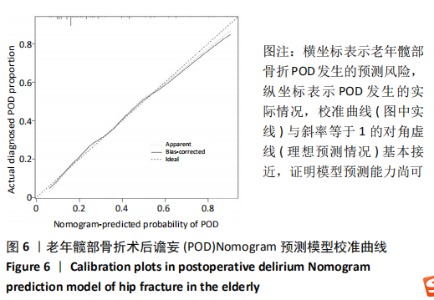
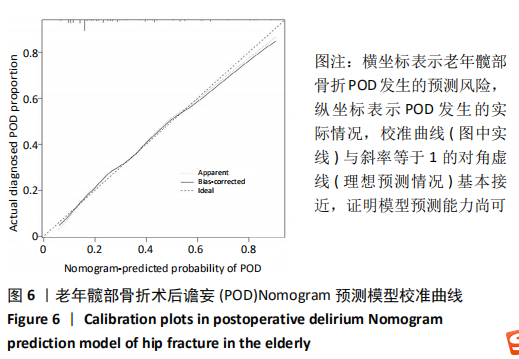
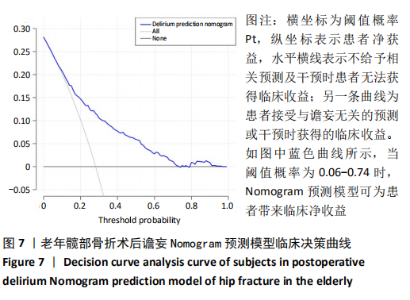
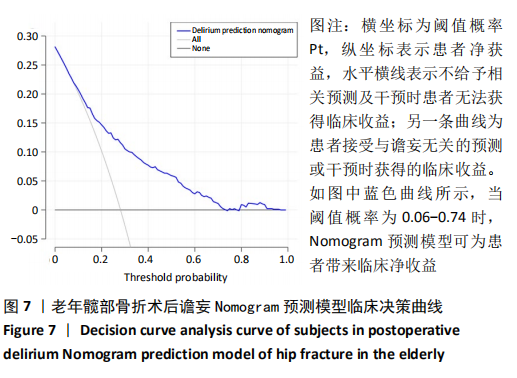
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (24): 3844-3849.doi: 10.12307/2021.090
Previous Articles Next Articles
Construction of a Nomogram prediction model for postoperative delirium after hip fracture in the elderly based on medical records from a hospital
Su Baotong1, Wang Hanyu2, Xu Yilang1, Xie Yajuan1, Cheng Zhian3
- 1Second Clinical School of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 2Xiangyang Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Xiangyang 441000, Hubei Province, China; 3Department of Orthopedics, Guangdong Province Traditional Chinese Medical Hospital, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2020-09-14Revised:2020-09-16Accepted:2020-10-30Online:2021-08-28Published:2021-03-08 -
Contact:Cheng Zhian, Chief physician, MD, Professor, Department of Orthopedics, Guangdong Province Traditional Chinese Medical Hospital, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Su Baotong, Master candidate, Second Clinical School of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Su Baotong, Wang Hanyu, Xu Yilang, Xie Yajuan, Cheng Zhian. Construction of a Nomogram prediction model for postoperative delirium after hip fracture in the elderly based on medical records from a hospital[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3844-3849.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] 张长青,张伟.对老年髋部骨折救治绿色通道建设的思考与展望[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2015,17(2):95-96. [2] 吴新宝,杨明辉.老年髋部骨折诊疗专家共识(2017)[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2017,19(11):921-927. [3] SEZGIN EA, MARKEVIČIŪTĖ V, ŠIRKA A, et al. Combined fracture and mortality risk evaluation for stratifying treatment in hip fracture patients: A feasibility study. Jt Dis Relat Surg. 2020;31(2):163-168. [4] RUDOLPH JL, MARCANTONIO ER. Review articles: postoperative delirium: acute change with long-term implications. Anesth Analg. 2011;112(5):1202-1211. [5] AMARILLA-DONOSO FJ, LÓPEZ-ESPUELA F, RONCERO-MARTÍN R, et al. Quality of life in elderly people after a hip fracture: a prospective study. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2020;18(1):71. [6] ZENILMAN ME. Delirium: An Important Postoperative Complication. JAMA. 2017;317(1):77-78. [7] EASTHAM JA, KATTAN MW, SCARDINO PT. Nomograms as predictive models. Semin Urol Oncol. 2002;20(2):108-115. [8] WEI LA, FEARING MA, STERNBERG EJ, et al. The Confusion Assessment Method: A Systematic Review of Current Usage. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2008;56(5):823-830. [9] LEE SR, HA YC, KANG H, et al. Morbidity and mortality in Jeju residents over 50-years of age with hip fracture with mean 6-year follow-up: a prospective cohort study. J Korean Med Sci. 2013;28(7):1089-1094. [10] SCHOLTENS RM, VAN MUNSTER BC, VAN FAASSEN M, et al. Plasma melatonin levels in hip fracture patients with and without delirium: A confirmation study. Mech Ageing Dev. 2017;167:1-4. [11] OH ES, SIEBER FE, LEOUTSAKOS JM, et al. Sex Differences in Hip Fracture Surgery: Preoperative Risk Factors for Delirium and Postoperative Outcomes. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2016;64(8):1616-1621. [12] WITLOX J, EURELINGS LS, de JONGHE JF, et al. Delirium in elderly patients and the risk of postdischarge mortality, institutionalization, and dementia: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2010;304(4):443-451. [13] ZYWIEL MG, HURLEY RT, PERRUCCIO AV, et al. Health economic implications of perioperative delirium in older patients after surgery for a fragility hip fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(10):829-836. [14] 王晓伟,孙天胜,刘智,等.老年髋部骨折后发生谵妄的研究现状[J].中华骨科杂志,2016,36(13):871-875. [15] WANG Y, SHEN X. Postoperative delirium in the elderly: the potential neuropathogenesis. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2018;30(11):1287-1295. [16] MALDONADO JR. Pathoetiological Model of Delirium: a Comprehensive Understanding of the Neurobiology of Delirium and an Evidence-Based Approach to Prevention and Treatment. Crit Care Clin. 2008;24(4): 789-856. [17] BEHRENDS M, DEPALMA G, SANDS L, et al. Association between intraoperative blood transfusions and early postoperative delirium in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2013;61(3):365-370. [18] 李呈凯,白树财,宋秀钢,等.老年髋部骨折患者术后谵妄相关危险因素的回顾性研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2018,38(4):250-256. [19] YANG Y, ZHAO X, DONG T, et al. Risk factors for postoperative delirium following hip fracture repair in elderly patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2017;29(2):115-126. [20] LAKSTYGAL AM, KOLESNIKOVA TO, KHATSKO SL, et al. DARK Classics in Chemical Neuroscience: Atropine, Scopolamine, and Other Anticholinergic Deliriant Hallucinogens. ACS Chem Neurosci.2019;10(5): 2144-2159. [21] 沈亚骏,范磊,王云华,等.老年髋部骨折术后谵妄危险因素分析[J].实用老年医学,2019,33(10):979-982. [22] MAHESHWARI K, PLANCHARD J, YOU J, et al. Early Surgery Confers 1-Year Mortality Benefit in Hip-Fracture Patients. J Orthop Trauma. 2018;32(3):105-110. [23] GOTTSCHALK A, HUBBS J, VIKANI AR, et al. The Impact of Incident Postoperative Delirium on Survival of Elderly Patients After Surgery for Hip Fracture Repair. Anesth Analg. 2015;121(5):1336-1343. [24] BELLAS N, STOHLER S, STAFF I, et al. Impact of Preoperative Specialty Consults on Hospitalist Comanagement of Hip Fracture Patients. J Hosp Med. 2020;15(1):16-21. [25] MUSALLAM KM, TAMIM HM, RICHARDS T, et al. Preoperative anaemia and postoperative outcomes in non-cardiac surgery: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2011;378(9800):1396-1407. [26] YANG Q, WANG J, HUANG X, et al. Incidence and risk factors associated with postoperative delirium following primary elective total hip arthroplasty: a retrospective nationwide inpatient sample database study. BMC Psychiatry. 2020;20(1):343. [27] VAN DER ZANDEN V, BEISHUIZEN SJ, SWART LM, et al. The Effect of Treatment of Anemia with Blood Transfusion on Delirium: A Systematic Review. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2017;65(4):728-737. [28] YANG L, YAN J, JIN X, et al. Screening for Dementia in Older Adults: Comparison of Mini-Mental State Examination, Mini-Cog, Clock Drawing Test and AD8. PLoS One. 2016;11(12):e168949. [29] CHONG E, TAY L, CHONG MS. Identifying phenomenological differences and recovery of cognitive and non-cognitive symptomatology among delirium superimposed upon dementia patients (DsD) versus those without dementia (DaD) in an acute geriatric care setting. Int Psychogeriatr. 2015;27(10):1695-1705. [30] LIN R, ZHANG F, XUE Q, et al. Accuracy of regional cerebral oxygen saturation in predicting postoperative cognitive dysfunction after total hip arthroplasty: regional cerebral oxygen saturation predicts POCD. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(3):494-497. [31] VAN ROMPAEY B, ELSEVIERS MM, SCHUURMANS MJ, et al. Risk factors for delirium in intensive care patients: a prospective cohort study. Crit Care. 2009;13(3):R77. [32] ZIPSER CM, DEUEL J, ERNST J, et al. The predisposing and precipitating risk factors for delirium in neurosurgery: a prospective cohort study of 949 patients. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2019;161(7):1307-1315. [33] DUNCAN DG, BECK SJ, HOOD K, et al. Using dietetic assistants to improve the outcome of hip fracture: a randomised controlled trial of nutritional support in an acute trauma ward. Age Ageing. 2006;35(2):148-153. [34] 熊昌军,姜学明,左云周,等.老年髋部骨折患者术后出现谵妄的危险因素分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2020,35(2):162-164. [35] XIE SY, XIE M. Effect of dexmedetomidine on postoperative delirium in elderly patients undergoing hip fracture surgery. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2018;31(5(Special)):2277-2281. [36] OH ES, LI M, FAFOWORA TM, et al. Preoperative risk factors for postoperative delirium following hip fracture repair: a systematic review. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2015;30(9):900-910. [37] 吴斗,郝海虎,朱剑,等.老年髋部骨折术后谵妄的危险因素分析[J].中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志,2015,1(1):34-38. doi:10.3877/cma.j.issn.2096-0263.2015.01.008 [38] FEINKOHL I, WINTERER G, PISCHON T. Diabetes is associated with risk of postoperative cognitive dysfunction: A meta‐analysis. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2017;33(5). doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2884. [39] GUO Y, JIA P, ZHANG J, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of postoperative delirium in elderly hip fracture patients. J Int Med Res. 2016;44(2): 317-327. [40] LEE JK, PARK YS. Delirium after spinal surgery in Korean population. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(18):1729-1732. [41] 陆小川,宋晓华,俞瑞东,等.老年患者髋关节术后早期谵妄的危险因素分析[J].老年医学与保健,2019,25(3):335-338. [42] OTOMO S, MAEKAWA K, GOTO T, et al. Pre-existing cerebral infarcts as a risk factor for delirium after coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2013;17(5):799-804. [43] CHUNG KS, LEE JK, PARK JS, et al. Risk factors of delirium in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2015;60(3): 443-447. |
| [1] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [2] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [3] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [4] | Wang Dasai, Zhang Yang, Cheng Yin, Wang Qiang. Efficacy and safety of staged versus simultaneous unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis#br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3929-3936. |
| [5] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [6] | Tian Kechao, Wang Lei, Tao Yong, Yao Tao. Proximal femoral nail antirotation combined with posteromedial wall reconstruction for the treatment of type A2 intertrochanteric fracture in the elderly [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3337-3342. |
| [7] | Zhang Mingyan, Liu Xiangyang, Chang Lei, Chen Jing, Shen Xiongjie, Liu Bin, Peng Shuai, Zhang Chao, Wu Huanyu, Zhu Feng, Mou Haipin . Relationship between the intraoperative endplate injury and cage retropulsion after lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2856-2862. |
| [8] | Zhang Tengfei, Wang Kun, Zhu Yanyu, Mei Wei, Wang Qingde. Meta-analysis of risk factors associated with adjacent segment degeneration after lumbar posterior fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1936-1943. |
| [9] | Zhao Yanxu, Zhang Zhao, Luo Dong, Li Manglai, Wang Jing, Fang Jie, Jiang Wen, Feng Yong, Peng Jiang, Xu Wenjing, Wang Yu, Wang Aiyuan, Zhang Minze. Risk factors for stress fracture of lower limbs and future research direction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1422-1429. |
| [10] | Qian Yuzhang, Wang Nan, Dong Yuqi, Xie Lin, Kang Ran. Factors for the recurrence of lumbar disc herniation after percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(36): 5886-5896. |
| [11] | Liu Zemin, Lü Xin, Liu Jinyuan, Wang Xiaohu. Epidemiological distribution characteristics of 2 342 cases of hip fracture: a single center analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(32): 5085-5091. |
| [12] | Zhang Jian, Wang Xiaojian, Qin Dean, Zhao Zhongtao, Liang Qingyuan, An Qijun, Song Jiefu. Risk factors for proximal junctional kyphosis after spinal deformity surgery: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(3): 460-468. |
| [13] | Wei Yong, Li Jun, Zhang Yong, Yu Hao, Xie Jia. Prevalence rate and high-risk factors of preoperative lower-limb deep venous thrombosis in patients with hip fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(27): 4338-4342. |
| [14] | Qin Zuoheng, Li Lijun, Ni Dongkui. Meta-analysis of independent risk factors for surgical site infection after spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(24): 3918-3924. |
| [15] | Zhao Jing, Yin Lian, Lei Xuemei, Li Miaomiao, Wang Kun, Zhang Tingran, Luo Jiong. KAASTU training for muscle fitness in the middle-aged and elderly adults: effects and strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(23): 3737-3743. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||