Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (32): 5085-5091.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2853
Epidemiological distribution characteristics of 2 342 cases of hip fracture: a single center analysis
Liu Zemin, Lü Xin, Liu Jinyuan, Wang Xiaohu
- Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2020-01-11Revised:2020-01-16Accepted:2020-03-04Online:2020-11-18Published:2020-09-24 -
Contact:Lü Xin, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Liu Zemin, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Zemin, Lü Xin, Liu Jinyuan, Wang Xiaohu. Epidemiological distribution characteristics of 2 342 cases of hip fracture: a single center analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(32): 5085-5091.
share this article
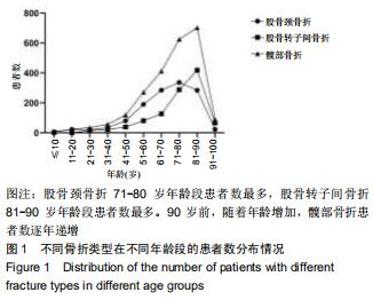
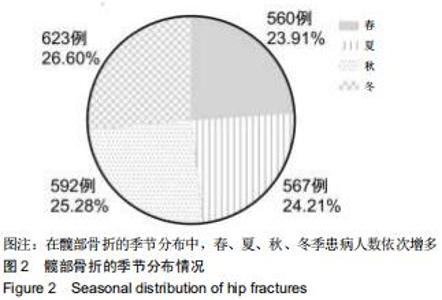
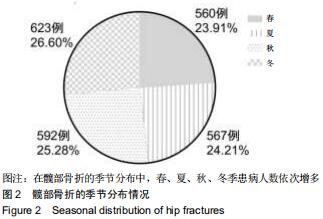
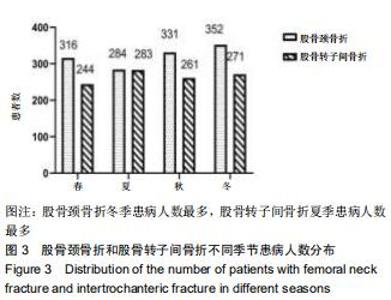
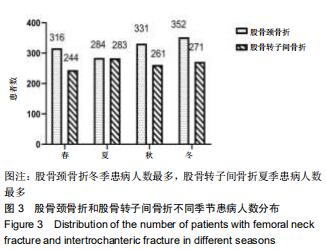
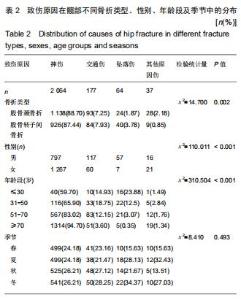
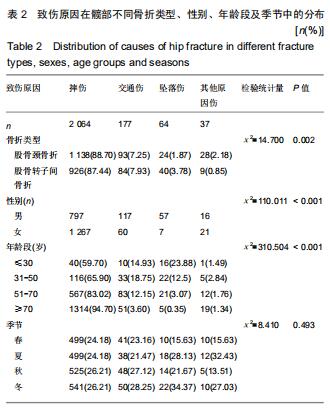
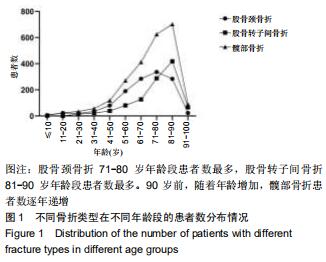
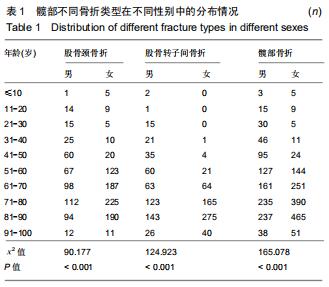
股骨颈骨折和股骨转子间骨折年龄分布差异有显著性意义(Z=-12.486,P < 0.001)。与股骨转子间骨折相比,股骨颈骨折女性患者明显多于男性患者,不同骨折类型间性别分布差异有显著性意义(χ2=12.890,P < 0.001)。股骨颈骨折高发年龄是50-90岁,其中70-80岁最多;股骨转子间骨折高发年龄是70-90岁,其中80-90岁最多,见图1。结果还显示,在不种骨折类型中,不同年龄层的性别分布差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表1。股骨颈骨折>50岁时女性患者数多于男性;其他年龄段男性患者数均多于女性。股骨转子间骨折>60岁以上的女性患者数多于男性;其他年龄段男性患者数均多于女性。 "
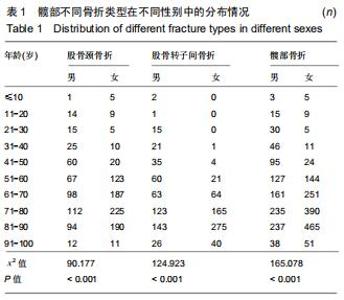
股骨颈骨折和股骨转子间骨折年龄分布差异有显著性意义(Z=-12.486,P < 0.001)。与股骨转子间骨折相比,股骨颈骨折女性患者明显多于男性患者,不同骨折类型间性别分布差异有显著性意义(χ2=12.890,P < 0.001)。股骨颈骨折高发年龄是50-90岁,其中70-80岁最多;股骨转子间骨折高发年龄是70-90岁,其中80-90岁最多,见图1。结果还显示,在不种骨折类型中,不同年龄层的性别分布差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表1。股骨颈骨折>50岁时女性患者数多于男性;其他年龄段男性患者数均多于女性。股骨转子间骨折>60岁以上的女性患者数多于男性;其他年龄段男性患者数均多于女性。 "
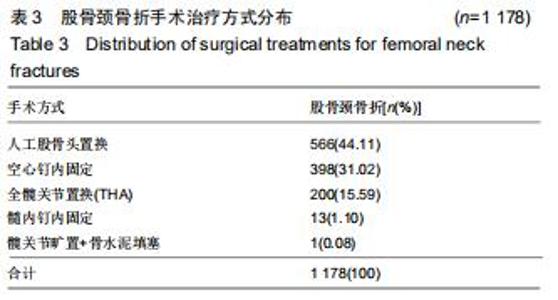
2.6 治疗情况分布 髋部骨折所有患者中,选择非手术治疗的有234例患者,占病例总数的9.99%,选择手术治疗的有2 108例患者,占病例总数的90.01%。股骨颈骨折有 1 178例(1 178/1 283,91.82%)患者选择不同的手术方式治疗,其中进行人工股骨头置换的患者最多,占44.11%;其次为空心钉内固定术,占31.02%。见表3。股骨转子间骨折的患者中有930例(930/1059,87.82%)患者选择手术治疗,最常见的治疗方式为髓内固定,包括股骨近端防旋髓内钉(Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation,PFNA)、INTERTAN髓内钉、Zimmer中立钉(Zimmer natural nail,ZNN)、γ-III(Gamma 3 nail)型髓内钉内固定,占92.04%。其中PFNA内固定术最常用,占股骨转子间骨折手术患者总数的66.29%。见表4。 "
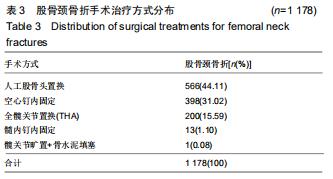
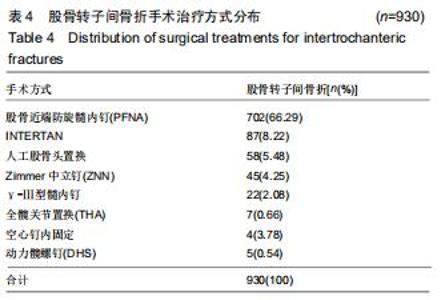
2.6 治疗情况分布 髋部骨折所有患者中,选择非手术治疗的有234例患者,占病例总数的9.99%,选择手术治疗的有2 108例患者,占病例总数的90.01%。股骨颈骨折有 1 178例(1 178/1 283,91.82%)患者选择不同的手术方式治疗,其中进行人工股骨头置换的患者最多,占44.11%;其次为空心钉内固定术,占31.02%。见表3。股骨转子间骨折的患者中有930例(930/1059,87.82%)患者选择手术治疗,最常见的治疗方式为髓内固定,包括股骨近端防旋髓内钉(Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation,PFNA)、INTERTAN髓内钉、Zimmer中立钉(Zimmer natural nail,ZNN)、γ-III(Gamma 3 nail)型髓内钉内固定,占92.04%。其中PFNA内固定术最常用,占股骨转子间骨折手术患者总数的66.29%。见表4。 "
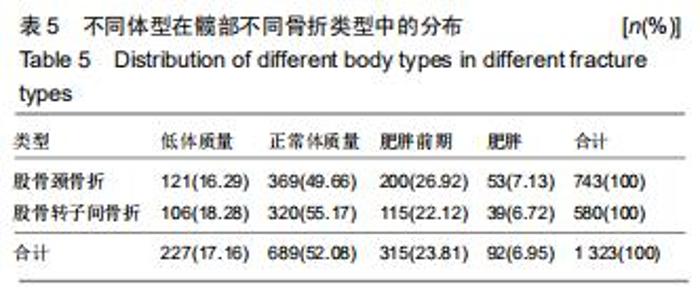
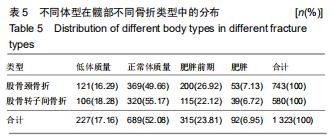
2.10 体质量指数分布 体质量指数的计算公式为体质量/身高2(kg/m2)[7]。髋部骨折患者中有1 323例获取到有效体质量指数值,平均为(22.20±3.72) kg/m2。其中,有743例股骨颈骨折,平均体质量指数为(22.39±3.67) kg/m2;有580例股骨转子间骨折,平均体质量指数为(21.95±3.77) kg/m2,两者差异有显著性意义(Z=-2.361,P=0.018),股骨转子间骨折患者整体偏瘦。国人依据体质量指数值不同,分为低体质量(体质量指数<18.5 kg/m2),正常体质量(18.5 kg/m2≤体质量指数<24.0 kg/m2),肥胖前期(24.0 kg/m2≤体质量指数< 28.0 kg/m2),肥胖(体质量指数≥28.0 kg/m2)4组[7]。股骨颈和股骨转子间骨折的不同体型分布差异具有显著性意义 (χ2=9.606,P=0.022),见表5。髋部骨折患者大多分布于正常体质量组,占52.08%。 "
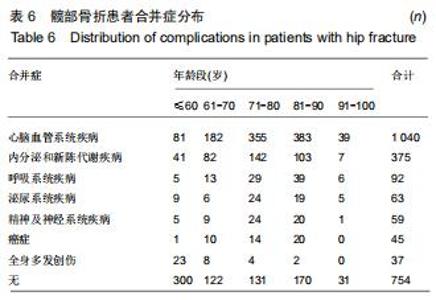
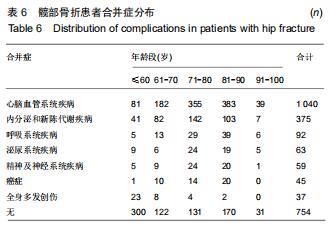
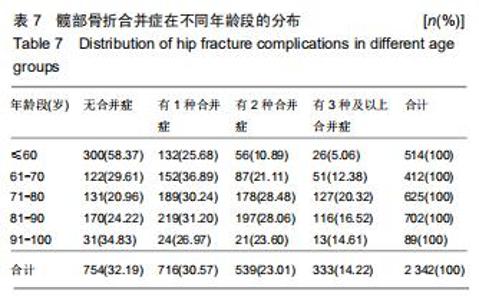
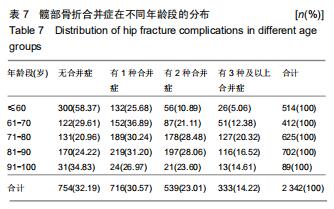
2.11 合并症分布 逐一查阅患者病历资料,将其合并症分类为心血管疾病、呼吸系统疾病、精神及神经系统疾病、泌尿系统疾病、内分泌和新陈代谢疾病、癌症及全身多发创伤等。其中合并最多的疾病为心脑血管系统疾病,占患者总数的44.41%;其次为内分泌和新陈代谢疾病,占患者总数的16.01%;第3位是呼吸系统疾病,占3.93%。同时随着年龄增长,无合并症患者占比不断下降,有至少一种合并症的患者占比不断升高;合并全身多发创伤的患者数量逐渐减少,合并其他疾病的患者数量增加。见表6。髋部骨折患者中,至少有一种合并症的患者达到67.81%,71-80岁年龄段患者有至少一种合并症的比例最高,占该年龄段患者总数的79.04%。有1种合并症的患者中,61-70岁组患者居多;有2种合并症的患者中,71-90岁组患者居多;有3种合并症的患者中,71-80岁组患者居多。见表7。 "
2.11 合并症分布 逐一查阅患者病历资料,将其合并症分类为心血管疾病、呼吸系统疾病、精神及神经系统疾病、泌尿系统疾病、内分泌和新陈代谢疾病、癌症及全身多发创伤等。其中合并最多的疾病为心脑血管系统疾病,占患者总数的44.41%;其次为内分泌和新陈代谢疾病,占患者总数的16.01%;第3位是呼吸系统疾病,占3.93%。同时随着年龄增长,无合并症患者占比不断下降,有至少一种合并症的患者占比不断升高;合并全身多发创伤的患者数量逐渐减少,合并其他疾病的患者数量增加。见表6。髋部骨折患者中,至少有一种合并症的患者达到67.81%,71-80岁年龄段患者有至少一种合并症的比例最高,占该年龄段患者总数的79.04%。有1种合并症的患者中,61-70岁组患者居多;有2种合并症的患者中,71-90岁组患者居多;有3种合并症的患者中,71-80岁组患者居多。见表7。 "
|
[1] 刁喜财,胡奕山,林璜,等.汕头地区1437例髋部骨折流行病学特点[J].广东医学,2017,38(z2):112-114.
[2] 张英泽. 临床创伤骨科流行病学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2009: 204-206.
[3] 马文辉, 张英泽.股骨颈骨折:问题及对策[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(9):1426-1433.
[4] 赵玉沛, 陈孝平. 外科学(下册)[M]. 3版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2015: 887-888.
[5] KARRES J, KIEVIET N, EERENBERG JP, et al. Predicting Early Mortality After Hip Fracture Surgery: The Hip Fracture Estimator of Mortality Amsterdam. J Orthop Trauma. 2018;32(1):27-33.
[6] 王雪婷. 山西省人口老龄化时空差异演变研究[D].大连:辽宁师范大学,2018.
[7] 程小游,钟新生.BMI分布规律及不同BMI人群体质水平研究[J].福建体育科技,2014,33(4):27-30.
[8] 贺丽英,孙蕴,要文娟,等.2010-2016年中国老年人骨质疏松症患病率Meta分析[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2016,22(12):1590-1596.
[9] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会.原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2017)[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2017,10(5):413-443.
[10] 居家宝,张培训.髋部骨折流行病学特点:单中心1397例分析[J].实用骨科杂志,2019,25(7):592-595.
[11] STERLING RS. Gender and Race/Ethnicity Differences in Hip Fracture Incidence, Morbidity, Mortality, and Function. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(7):1913-1918.
[12] 刘忠厚.骨矿与临床[M].北京:中国科学技术出版社,2006:5-30.
[13] 张如云. 新疆地区2454例老年骨折患者流行病学特征分析[D].石家庄市:河北医科大学,2014.
[14] 孙志颖,吴云峰.北京东高地地区859例体检人群的骨密度情况分析[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2010,19(22):2759-2760.
[15] 张健,蒋协远,黄晓文.1139例老年髋部骨折治疗及流行病学分析[J].中国医刊,2016,51(6):91-94.
[16] 马永方.大连市老年初发及再发髋部骨折单中心流行病学研究[D].大连:大连医科大学,2019.
[17] COLLINS KJ, EASTON JC, BELFIELD-SMITH H, et al. Effects of age on body temperature and blood pressure in cold environments. Clin Sci (Lond). 1985;69(4):465-470.
[18] 王影,傅秀珍,张广清.老年髋部骨折患者跌倒风险及自我效能的评估[J].广东医学,2013,34(7):1141-1143.
[19] 梁玉柱,郭洪刚.股骨转子间骨折179例流行病学调查:天津医科大学总医院2013至2015年就诊资料分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2018, 22(8):1167-1172.
[20] 翁蔚宗,李密,周启荣,等.髋部骨折流行病学分布特点:单中心2859例分析[J].第二军医大学学报,2017,38(04):415-420.
[21] 王翠娴. 老年髋部骨折术后下肢深静脉血栓形成的预防护理进展[J]. 继续医学教育,2018,32(2):113-115.
[22] 王浩然,聂中林,陈世远,等. 下腔静脉滤器治疗深静脉血栓临床效果的Meta分析[J]. 齐齐哈尔医学院学报, 2018,39(6):637-641.
[23] 王长海.呼和浩特地区老年髋部骨折流行病学调查及其相关研究[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2010.
[24] FU MC, BODDAPATI V, GAUSDEN EB, et al. Surgery for a fracture of the hip within 24 hours of admission is independently associated with reduced short-term post-operative complications. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-B(9):1216-1222.
[25] SOBOLEV B, GUY P, SHEEHAN KJ, et al. Mortality effects of timing alternatives for hip fracture surgery. CMAJ. 2018;190(31): E923-E932.
[26] 钟凯.中国女性体重指数与髋部骨折风险关系[D].长沙:湖南师范大学,2010. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [5] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [6] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [7] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [8] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [9] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [10] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [11] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [12] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [13] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [14] | Zhang Shangpu, Ju Xiaodong, Song Hengyi, Dong Zhi, Wang Chen, Sun Guodong. Arthroscopic suture bridge technique with suture anchor in the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1417-1422. |
| [15] | Liang Yan, Zhao Yongfei, Xu Shuai, Zhu Zhenqi, Wang Kaifeng, Liu Haiying, Mao Keya. Imaging evaluation of short-segment fixation and fusion for degenerative lumbar scoliosis assisted by highly selective nerve root block [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1423-1427. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||