Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (2): 216-221.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0009
Previous Articles Next Articles
In vivo and in vitro hemostatic effects of composite collagen sponge
- Beijing Institute of Traumatology and Orthopaedics, Beijing 100035, China
-
Received:2017-08-22Online:2018-01-18Published:2018-01-18 -
Contact:Sun Lei, M.D., Researcher, Beijing Institute of Traumatology and Orthopaedics, Beijing 100035, China -
About author:Jin Shao-feng, Technician, Beijing Institute of Traumatology and Orthopaedics, Beijing 100035, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jin Shao-feng, Qi Hui, Shu Xiong, Jie Yong-sheng, Zheng Rui, Chen Lei, Sun Lei .
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
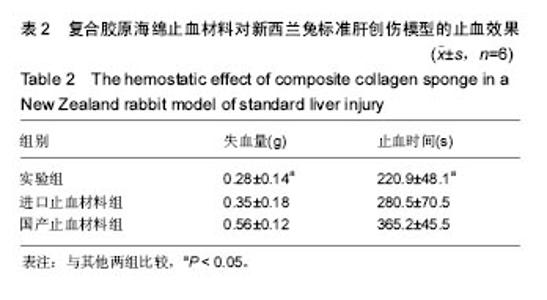
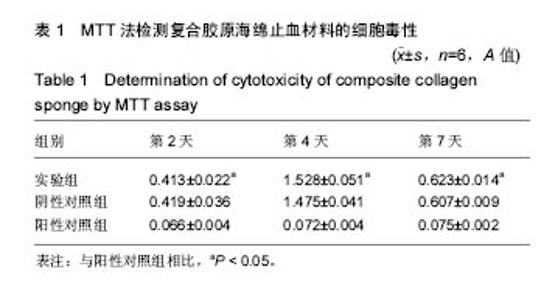
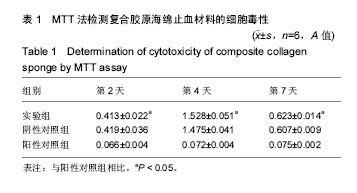
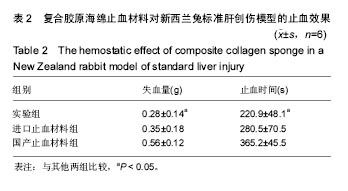
2.3 复合胶原海绵止血材料的体外凝血活性测定 与进口材止血料和国产止血材料相比较,复合胶原海绵止血材料的体外凝血指数显著下降(23.145±1.145,38.126± 2.278,18.285±2.146,P < 0.05),体外凝血活性测定表明复合胶原海绵止血材料的凝血效果显著提高。 2.4 复合胶原海绵止血材料的体内止血效果 在新西兰兔标准肝创伤模型中采用失血量(g)和止血时间(s)作为考察指标,结果见表2所示:与进口止血材料组和国产止血材料组相比较,实验组失血量(g)和止血时间(s)均显著性地减小 (P < 0.05),这个与体外凝血指数测试的结果相吻合;与进口止血材料组和国产止血材料组相比较,实验组失血量分别减少了25%和100%,止血时间则分别缩短了27%和65.9%,其差异均达到显著水平(P < 0.05)。动物活体实验结果表明,复合胶原海绵止血材料不但明显缩短了肝缺损的止血时间,同时也明显减少了失血量,具有应用于临床止血的潜力。"
| [1]Broekema FI,van Oeveren W,Boerendonk A,et al.Hemostatic action of polyurethane foam with 55% polyethylene glycol compared to collagen and gelatin.Biomed Mater Eng.2016; 27(2-3):149-159. [2]Yang JC.Causes of Death in Patients with Trauma Emergency Surgery.Chin Foreign Med Res.2016. [3]Gerdin M,Roy N,Khajanchi M,et al.Validation of a novel prediction model for early mortality in adult trauma patients in three public university hospitals in urban India.BMC Emerg Med.2016;16:15.[4]Santos Tde S,Abuna RP,Almeida AL,et al.Effect of collagen sponge and fibrin glue on bone repair.J Appl Oral Sci.2015; 23(6):623-628. [5]Mahesh L,Kurtzman GM,Shukla S.Regeneration in Periodontics: Collagen-A Review of Its Properties and Applications in Dentistry.Compend Contin Educ Dent.2015; 36(5):358-363.[6]Wang Y,Ni H.Fibronectin maintains the balance between hemostasis and thrombosis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73(17): 3265-3277. [7]Six KR,Devloo R,Van Aelst B,et al.A Microfluidic Flow Chamber Model for Platelet Transfusion and Hemostasis Measures Platelet Deposition and Fibrin Formation in Real-time.J Vis Exp. 2017;(120). doi: 10.3791/55351.[8]Fiorica C,Palumbo FS,Pitarresi G,et al.Hyaluronic acid and beta cyclodextrins films for the release of corneal epithelial cells and dexamethasone.Carbohydr Polym. 2017;166: 281-290. [9]Fan J,Yang J.Preparation and characterization of a chitosan/galactosylated hyaluronic acid/heparin scaffold for hepatic tissue engineering.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2017; 28(6):569-581. [10]do Nascimento MHM,Ferreira M,Malmonge SM,et al.Evaluation of cell interaction with polymeric biomaterials based on hyaluronic acid and chitosan.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2017;28(5):68.[11]Li H,Cheng W,Liu K,et al.Reinforced collagen with oxidized microcrystalline cellulose shows improved hemostatic effects. Carbohydr Polym.2017;165:30-38.[12]Fernandez RS, Lee A.Effects of methods used to achieve hemostasis on radial artery occlusion following percutaneous coronary procedures: a systematic review.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep.2017;15(3):738-764. [13]Smith RB,Coughlin A.Thyroidectomy Hemostasis.Otolaryngol Clin North Am.2016;49(3):727-748. [14]Kirsch WM,Hudson SM,Crofton A.Composition, preparation, and use of chitosan shards for biomedical applications. Dataroom Biotechnology,2016. [15]Li J,Wei CP,Wang FM,et al.Preparation and Performance Research of Hemostatic Powder of Chitosan Mixed with Scutellaria baicalensis.Mater Sci Forum.2016;852:1277-1281.[16]Zhu S,Lu Y,Sinno T,et al.Dynamics of Thrombin Generation and Flux from Clots during Whole Human Blood Flow over Collagen/Tissue Factor Surfaces.J Biol Chem. 2016;291(44): 23027-23035. [17]Ivanciu L,Stalker TJ.Spatiotemporal regulation of coagulation and platelet activation during the hemostatic response in vivo.J Thromb Haemost.2015;13(11):1949-1959. [18]Cheng X,Shao Z,Li C,et al.Isolation, Characterization and Evaluation of Collagen from Jellyfish Rhopilema esculentum Kishinouye for Use in Hemostatic Applications. PloS One. 2017;12(1): e0169731.[19]Pippi R,Santoro M,Cafolla A.The Use of a Chitosan-Derived Hemostatic Agent for Postextraction Bleeding Control in Patients on Antiplatelet Treatment.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;75(6):1118-1123.[20]Barba JD,Tranquilan-Aranilla C,Abad LV.Hemostatic potential of natural/synthetic polymer based hydrogels crosslinked by gamma radiation.Radiat Phys Chem.2016;118:111-113.[21]Diehn K,Dowling M,Raghavan SR,et al.Advanced functional biocompatible polymer putty used as a hemostatic agent for treating damaged tissue and cells.WIPO Patent Application WO,2014. [22]Wang FM,Wei CP,Lu J,et al.Preparation and Properties Characterization of Modified Chitosan Composited Hemostatic Materials.Mater Sci Forum.2016;852:1271-1276.[23]Lan G,Lu B,Wang T,et al.Chitosan/gelatin composite sponge is an absorbable surgical hemostatic agent.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2015;136:1026-1034. [24]Son SR,Sarkar SK,Nguyen-Thuy BL,et al.Platelet-rich plasma encapsulation in hyaluronic acid/gelatin-BCP hydrogel for growth factor delivery in BCP sponge scaffold for bone regeneration.J Biomater Appl.2015;29(7):988-1002. [25]Zhou Q,Zhang Y,Lin D,et al.The relationships of meteorological factors and nutrient levels with phytoplankton biomass in a shallow eutrophic lake dominated by cyanobacteria, Lake Dianchi from 1991 to 2013.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int.2016;23(15):15616-15626. [26]Jaikumar D,Baskaran B,Vaidyanathan VG.Effect of chromium(III) gallate complex on stabilization of collagen.Int J Biol Macromol.2017;96:429-435. [27]Duan L,Yuan J,Yang X, et al.Interaction study of collagen and sericin in blending solution.Int J Biol Macromol.2016;93(Pt A): 468-475. [28]Nicolás M,Peña E,Malvè M,et al. Mathematical modeling of the fibrosis process in the implantation of inferior vena cava filters.J Theor Biol.2015;387:228-240.[29]Norouzi M,Shabani I,Ahvaz HH,et al. PLGA/gelatin hybrid nanofibrous scaffolds encapsulating EGF for skin regeneration.J Biomed Mater Res A.2015;103(7):2225-2235. [30]Huang W,Wang Y,Chen Y,et al.Strong and Rapidly Self-Healing Hydrogels: Potential Hemostatic Materials.Adv Healthc Mater.2016;5(21):2813-2822. [31]Tan H, Wu B, Li C, et al. Collagen cryogel cross-linked by naturally derived dialdehyde carboxymethyl cellulose. Carbohydr Polym.2015;129:17-24.[32]Sun L, Li B, Jiang D, et al. Nile tilapia skin collagen sponge modified with chemical cross-linkers as a biomedical hemostatic material. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2017; 159:89-96. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Shen Jinbo, Zhang Lin. Micro-injury of the Achilles tendon caused by acute exhaustive exercise in rats: ultrastructural changes and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1190-1195. |
| [3] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [4] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [5] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [6] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [7] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [8] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [9] | Liu Liu, Zhou Qingzhu, Gong Zhuo, Liu Boyan, Yang Bin, Zhao Xian. Characteristics and manufacturing techniques of collagen/inorganic materials for constructing tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 607-613. |
| [10] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [11] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [12] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [13] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [14] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [15] | Xu Xiaoming, Chen Yan, Song Qian, Yuan Lu, Gu Jiaming, Zhang Lijuan, Geng Jie, Dong Jian. Human placenta derived mesenchymal stem cell gel promotes the healing of radiation skin damage in SD rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3976-3980. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||