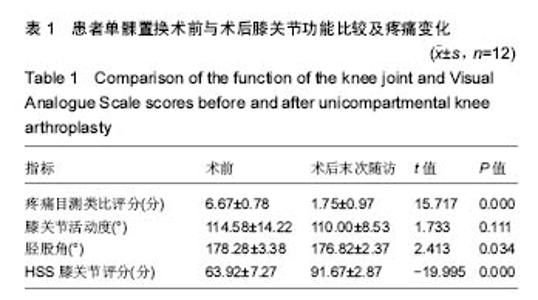
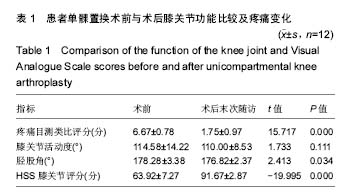
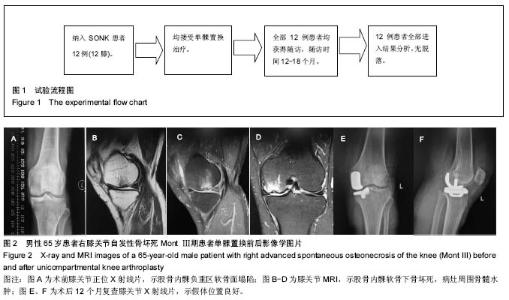
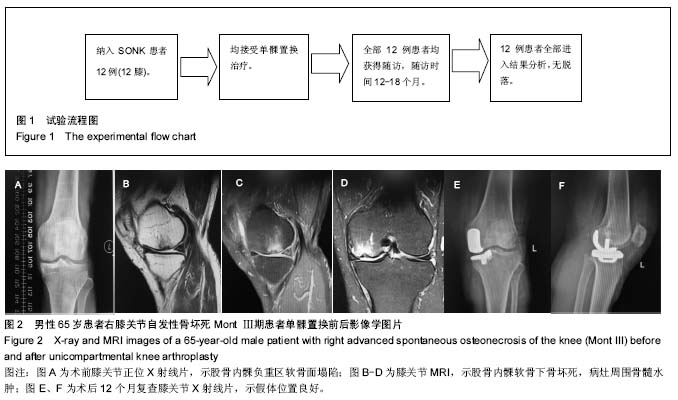
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (35): 5577-5582.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.35.001
Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty used for advanced spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee
Feng En-hui, Mai Xiu-jun, Huang Yong-ming, Cao Zhen-wu, Chen Kang-yao, Su Hai-tao
- Department of Orthopedics, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China
-
Online:2017-12-18Published:2018-01-02 -
Contact:Huang Yong-ming, M.D., Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Feng En-hui, Master, Physician, Department of Orthopedics, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81273781
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Feng En-hui, Mai Xiu-jun, Huang Yong-ming, Cao Zhen-wu, Chen Kang-yao, Su Hai-tao. Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty used for advanced spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(35): 5577-5582.
share this article
| [1] Filip AM, Van den Broeck SB. Spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee (SONK). JBR-BTR. 2014;97(4):268.[2] Ahlback S, Bauer GC, Bohne WH. Spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee. Arthritis Rheum. 1968;11(6):705-733.[3] Chambers C, Craig JG, Zvirbulis R, et al. Spontaneous osteonecrosis of knee after arthroscopy is not necessarily related to the procedure. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2015;44(6):E184-E189.[4] Berruto M, Ferrua P, Uboldi F, et al. Can a biomimetic osteochondral scaffold be a reliable alternative to prosthetic surgery in treating late-stage SPONK? Knee. 2016;23(6): 936-941.[5] Bruni D, Iacono F, Raspugli G, et al. Is unicompartmental arthroplasty an acceptable option for spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012; 470(5):1442-1451.[6] Heyse TJ, Khefacha A, Fuchs-Winkelmann S, et al. UKA after spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee: a retrospective analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131(5):613-617.[7] 李子荣. 骨坏死[M]. 北京:人民卫生出版社,2012:260-268.[8] Horikawa A, Miyakoshi N, Shimada Y, et al. Spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee: a retrospective analysis by using MRI and DEXA. Open Orthop J. 2016;10:532-538.[9] Mont MA, Marker DR, Zywiel MG, et al. Osteonecrosis of the knee and related conditions. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2011; 19(8):482-494.[10] 郭万首. 单髁关节置换术影像学评价[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2015,9(5):640-643.[11] Katz JN, Barrett J, Mahomed NN, et al. Association between hospital and surgeon procedure volume and the outcomes of total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86-A(9): 1909-1916.[12] Insall JN, Ranawat CS, Aglietti P, et al. A comparison of four models of total knee-replacement prostheses. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1976;58(6):754-765.[13] 杨伟铭,曹学伟. 膝关节自发性骨坏死的研究进展[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2017,25(2):79-82.[14] 刘新光,郭万首. 膝关节自发性骨坏死的病因学研究进展[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2016,9(6):536-540.[15] Lafforgue P, Daumen-Legre V, Clairet D, et al. Insufficiency fractures of the medial femoral condyle. Rev Rhum Engl Ed. 1996;63(4):262-269.[16] Sokoloff RM, Farooki S, Resnick D. Spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee associated with ipsilateral tibial plateau stress fracture: report of two patients and review of the literature. Skeletal Radiol. 2001;30(1):53-56.[17] Narvaez JA, Narvaez J, De Lama E, et al. Spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee associated with tibial plateau and femoral condyle insufficiency stress fracture. Eur Radiol. 2003;13(8):1843-1848.[18] Uchio Y, Ochi M, Adachi N, et al. Intraosseous hypertension and venous congestion in osteonecrosis of the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;(384):217-223.[19] Lecouvet FE, Malghem J, Maldague BE, et al. MR imaging of epiphyseal lesions of the knee: current concepts, challenges, and controversies. Radiol Clin North Am. 2005;43(4):655-672.[20] Pape D, Seil R, Kohn D, et al. Imaging of early stages of osteonecrosis of the knee. Orthop Clin North Am. 2004; 35(3):293-303.[21] Takeda M, Higuchi H, Kimura M, et al. Spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee: histopathological differences between early and progressive cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90(3):324-329.[22] Koshino T. The treatment of spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee by high tibial osteotomy with and without bone-grafting or drilling of the lesion. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982;64(1):47-58.[23] 石清坡. 外科与保守治疗对继发性膝关节骨坏死的远期疗效对比分析[J]. 临床医药文献电子杂志,2014,1(13):1525-1526.[24] 郝军,高文香,邹春雨,等. 中西医结合治疗膝关节骨坏死21例[J]. 中医药导报,2014,20(3):97-99.[25] 张嘉良,魏凌峰,赵传喜,等. 膝关节单髁置换术用于青年晚期膝关节自发性骨坏死治疗中的疗效及患者功能分析[J]. 齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2016,37(34):4304-4305.[26] Aglietti P, Insall JN, Buzzi R, et al. Idiopathic osteonecrosis of the knee. Aetiology, prognosis and treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1983;65(5):588-597.[27] 马路遥,郭万首,程立明. 单髁关节置换术后膝关节运动学研究现状[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2015,8(1):97-100.[28] 张启栋,郭万首,刘朝晖,等. 单髁与全膝关节置换术治疗高龄患者的配对病例对照研究[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2017, 11(1):4-8.[29] Lunebourg A, Parratte S, Galland A, et al. Is isolated insert exchange a valuable choice for polyethylene wear in metal-backed unicompartmental knee arthroplasty? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(10):3280-3286.[30] Fabre-Aubrespy M, Ollivier M, Pesenti S, et al. Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in patients older than 75 results in better clinical outcomes and similar survivorship compared to total knee arthroplasty. A matched controlled study. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(12):2668-2671.[31] Malcherczyk D, Figiel J, Hahnlein U, et al. MRI following UKA: The component-bone interface. Acta Orthop Belg. 2015; 81(1):84-89.[32] van der List JP, Chawla H, Villa JC, et al. Early functional outcome after lateral UKA is sensitive to postoperative lower limb alignment. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017; 25(3):687-693.[33] Staats K, Merle C, Schmidt-Braekling T, et al. Is the revision of a primary TKA really as easy and safe as the revision of a primary UKA? Ann Transl Med. 2016;4(24):532.[34] Ko YB, Gujarathi MR, Oh KJ. Outcome of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: a systematic review of comparative studies between fixed and mobile bearings focusing on complications. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2015;27(3):141-148.[35] Ollivier M, Parratte S, Argenson JN. Results and outcomes of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am. 2013;44(3):287-300.[36] Ollivier M, Parratte S, Lunebourg A, et al. The John Insall Award: no functional benefit after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty performed with patient-specific instrumentation: A Randomized Trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(1):60-68.[37] 马童, 涂意辉,薛华明,等. 牛津假体单髁置换术治疗膝关节自发性骨坏死初步研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24 (7):660-662[38] Xue H, Tu Y, Ma T, et al. Up to twelve year follow-up of the Oxford phase three unicompartmental knee replacement in China: seven hundred and eight knees from an independent centre. Int Orthop. 2017;41(8):1571-1577.[39] Ma T, Tu Y, Xue H, et al. Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty for spontaneous osteonecrosis. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2017;25(1):2309499017690328. [40] Pandit H, Hamilton TW, Jenkins C, et al. The clinical outcome of minimally invasive Phase 3 Oxford unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: a 15-year follow-up of 1000 UKAs. Bone Joint J. 2015;97-B(11):1493-1500. [41] Zhang Q, Guo W, Liu Z, et al. Minimally invasive unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in treatment of osteonecrosis versus osteoarthritis: a matched-pair comparison. Acta Orthop Belg. 2015;81(2):333-339.[42] Wang L, Lin WJ, Chen K, et al.Analysis of clinical effect of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in treating spontaneousosteonecrosis of the knee. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2015;28(4):357-362. [43] Guo WS, Zhang QD, Liu ZH, et al.Minimally invasive unicompartmental knee arthroplasty for spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee. Orthop Surg. 2015;7(2):119-124. [44] Choy WS, Kim KJ, Lee SK, et al. Medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in patients with spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee. Clin Orthop Surg. 2011;3(4):279-284.[45] Servien E, Verdonk PC, Lustig S, et al. Medial unicompartimental knee arthroplasty for osteonecrosis or osteoarthritis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2008; 16(11):1038-1042. [46] Tírico LEP, Early SA, McCauley JC, et al. Fresh osteochondral allograft transplantation for spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee: a case series. Orthop J Sports Med. 2017;5(10):2325967117730540.[47] Yasuda T, Ota S, Fujita S, et al. Association between medial meniscus extrusion and spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee. Int J Rheum Dis. 2017. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.. |
| [1] | Wang Jianping, Zhang Xiaohui, Yu Jinwei, Wei Shaoliang, Zhang Xinmin, Xu Xingxin, Qu Haijun. Application of knee joint motion analysis in machanism based on three-dimensional image registration and coordinate transformation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-5. |
| [2] | Zhuang Zhikun, Wu Rongkai, Lin Hanghui, Gong Zhibing, Zhang Qianjin, Wei Qiushi, Zhang Qingwen, Wu Zhaoke. Application of stable and enhanced lined hip joint system in total hip arthroplasty in elderly patients with femoral neck fractures complicated with hemiplegia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1429-1433. |
| [3] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [4] | Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [5] | Li Huo, Wang Peng, Gao Jianming, Jiang Haoran, Lu Xiaobo, Peng Jiang. Relationship between revascularization and internal microstructure changes in osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1323-1328. |
| [6] | Zhang Jichao, Dong Yuefu, Mou Zhifang, Zhang Zhen, Li Bingyan, Xu Xiangjun, Li Jiayi, Ren Meng, Dong Wanpeng. Finite element analysis of biomechanical changes in the osteoarthritis knee joint in different gait flexion angles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1357-1361. |
| [7] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [8] | Wang Baojuan, Zheng Shuguang, Zhang Qi, Li Tianyang. Miao medicine fumigation can delay extracellular matrix destruction in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1180-1186. |
| [9] | Wu Bingshuang, Wang Zhi, Tang Yi, Tang Xiaoyu, Li Qi. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: from enthesis to tendon-to-bone healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1293-1298. |
| [10] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [11] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [12] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [13] | Liu Dongcheng, Zhao Jijun, Zhou Zihong, Wu Zhaofeng, Yu Yinghao, Chen Yuhao, Feng Dehong. Comparison of different reference methods for force line correction in open wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 827-831. |
| [14] | Shao Yangyang, Zhang Junxia, Jiang Meijiao, Liu Zelong, Gao Kun, Yu Shuhan. Kinematics characteristics of lower limb joints of young men running wearing knee pads [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 832-837. |
| [15] | Huang Hao, Hong Song, Wa Qingde. Finite element analysis of the effect of femoral component rotation on patellofemoral joint contact pressure in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 848-852. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||