Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (3): 329-334.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.03.001
Cocktail therapy reduces hidden blood loss after total knee arthroplasty
Shi Li-jun1, Gao Fu-qiang2, Sun Wei2, Wang Wei-guo2, Cheng Li-ming2, Guo Wan-shou2
- 1China-Japan Friendship Medical School, Peking University Health Science Center, Beijing 100029, China; 2Orthopedic Department, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China
-
Revised:2016-12-20Online:2017-01-28Published:2017-03-14 -
Contact:Sun Wei, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Orthopedic Department, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China -
About author:Shi Li-jun, Studying for master’s degree, China-Japan Friendship Medical School, Peking University Health Science Center, Beijing 100029, China Shi Li-jun and Gao Fu-qiang contributed equally to this paper. -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81372013; a grant from China-Japan Friendship Hospital, No. 2014-4-QN-29; the Young Technology Talent Program of China-Japan Friendship Hospital, No. 2014-QNYC-A-06
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Shi Li-jun, Gao Fu-qiang, Sun Wei, Wang Wei-guo, Cheng Li-ming, Guo Wan-shou. Cocktail therapy reduces hidden blood loss after total knee arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 329-334.
share this article
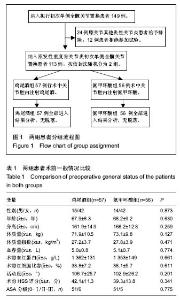
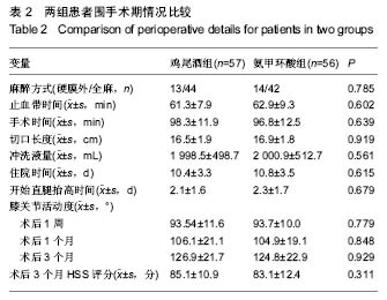
2.1 参与者数量分析 从2013年7月至2015年10月,作者对149例就诊于中日友好医院需要行初次全膝关节置换的住院患者进行筛选和评估,选择符合标准的患者进入试验研究。24例患者符合排除标准不能进入试验,主要是膝关节其他炎性关节炎患者如类风湿性关节炎、创伤性骨关节炎患者,此外还有12例患者拒绝参加本次试验。因此,在进行随机化分组后,共有113例患者参与本试验,其中57例患者术中使用鸡尾酒,56例患者单纯使用氨甲环酸。分组流程图见图1。 2.2 基线资料比较 通过比较分析,术前2组患者性别、年龄、身高、体质量、体质量指数、HSS评分、膝关节活动度、血容量、ASA分级、血红蛋白和红细胞比容等一般情况和临床表现差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),具有可比性(表1)。"

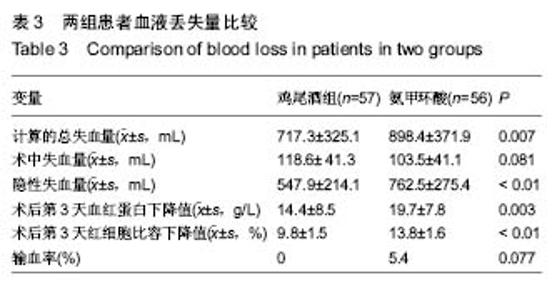
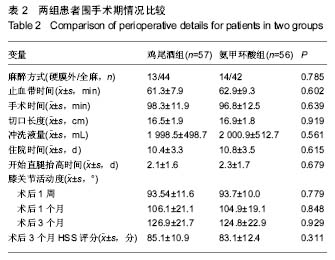
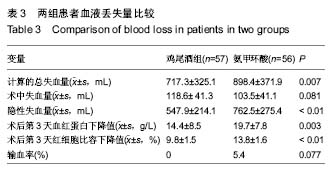
2.4 失血量分析 通过比较分析,与氨甲环酸组患者相比,鸡尾酒组患者术后第3天的血红蛋白下降值、红细胞比容下降值、隐性失血量以及计算得出的总失血量均较少 (P < 0.05);2组患者术中失血量差异无显著性意义(P=0.081);术后鸡尾酒组患者比氨甲环酸组患者输血量更低,但是2组患者输血率差异无显著性意义(P=0.077);在氨甲环酸组患者中,有3例患者需要输注2 U的浓缩红细胞,见表3。 2.5 不良事件 术后观察患者生命体征、患肢疼痛肿胀症状、有无呼吸困难和胸痛症状以及伤口局部愈合情况。2组患者均无切口感染、血压骤升、症状性的肺栓塞和下肢深静脉血栓形成等情况出现,未见氨甲环酸相关不良反应。"
| [1] Sadigursky D, Andion D, Boureau P,et al. Effect of tranexamic acid on bleeding control in total knee arthroplasty. Acta Ortop Bras. 2016; 24(3):131-136.[2] Volquind D, Zardo RA, Winkler BC,et al. Use of tranexamic acid in primary total knee replacement: effects on perioperative blood loss. Braz J Anesthesiol. 2016; 66(3):254-258.[3] Zhaohui L, Wanshou G, Qidong Z, et al. Topical hemostatic procedures control blood loss in bilateral cemented single-stage total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Sci. 2014; 19:948.[4] Su EP, Su S. Strategies for reducing peri-operative blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2016; 98-B (1 Suppl A): 98-100.[5] Murphy M, Stanworth S, Yazer M. Transfusion practice and safety: current status and possibilities for improvement.Vox Sang.2011; 100:46-59. [6] Hemlata SS, Verma A. Adverse events related to blood transfusion. Indian J Anaesth. 2014; 58(5): 543-551.[7] Lemaire R. Strategies for blood management in orthopaedic and trauma surgery. J Bone Joint Surg (Br). 2008; 90:1128.[8] Pitta M, Zawadsky M, Verstraete R, et al. Intravenous administration of tranexamic acid effectively reduces blood loss in primary total knee arthroplasty in a 610-patient consecutive case series. Transfusion. 2016; 56(2):466-471.[9] Xie J, Ma J, Yao H, et al. Multiple Boluses of Intravenous Tranexamic Acid to Reduce Hidden Blood Loss After Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty Without Tourniquet: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J Arthroplasty. 2016.[10] Wang H, Shen B, Zeng Y. Blood Loss and Transfusion After Topical Tranexamic Acid Administration in Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2015; 38(11):e1007-1016.[11] Wang G, Wang D, Wang B, et al. Efficacy and safety evaluation of intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty operation with temporarily drainage close. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015; 8(8):14328-14334.[12] Gasparini G, Papaleo P, Pola P, et al. Local infusion of norepinephrine reduces blood losses and need of transfusion in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2006; 30:253.[13] Goyal N, Chen DB, Harris IA, et al. Clinical and financial benefits of intra-articular tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2016; 24(1):3-6.[14] Yang ZG, Chen WP, Wu LD. Effectiveness and safety of tranexamic acid in reducing blood loss in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012: 94:1153.[15] Huang GP, Jia XF, Xiang Z, et al. Tranexamic Acid Reduces Hidden Blood Loss in Patients Undergoing Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Comparative Study and Meta-Analysis. Med Sci Monit. 2016; 22:797-802.[16] He P, Zhang Z, Li Y,et al. Efficacy and Safety of Tranexamic Acid in Bilateral Total Knee Replacement: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Med Sci Monit. 2015; 21:3634-3642.[17] Yang Y, Lv YM, Ding PJ, et al. The reduction in blood loss with intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid in unilateral total knee arthroplasty without operative drains: a randomized controlled trial. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015; 25:135.[18] Gross JB. Estimating allowable blood loss: corrected for dilution. Anesthesiology. 1983; 58:277.[19] Nadler SB, Hidalgo JH, Bloch T. Prediction of blood volume in normal human adults. Surgery. 1962; 51:224. [20] Sehat KR, Evans RL, Newman JH. Hidden blood loss following hip and knee arthroplasty correct management of blood loss should take hidden loss into account. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004; 86:561.[21] Stulberg BN, Zadzilka JD. Blood management issues using blood management strategies. J Arthroplasty. 2007; 22 (4 Suppl 1): 95-98.[22] Wu YG, Zeng Y, Shen B, et al. Combination of erythropoietin and tranexamic acid in bilateral simultaneous total hip arthroplasty: a randomised, controlled trial. Hip Int. 2016.[23] Moore EE, Moore HB, Gonzalez E, et al. Rationale for the selective administration of tranexamic acid to inhibit fibrinolysis in the severely injured patient. Transfusion. 2016; 56 Suppl 2: S110-114.[24] Aslam KS, Niazi AK, Nabi O. Efficacy of tranexamic acid in reducing blood loss in total knee replacements. J Pak Med Assoc. 2015; 65(11 Suppl 3):S210-214.[25] Tai TW, Lin CJ, Jou IM, et al. Tourniquet use in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011; 19:1121.[26] Hourlier H, Fennema P. Chemoprophylaxis without intra-articular wound drainage can replace autotransfusion in primary TKA. Orthopedics. 2011; 34:154.[27] Dunn CJ, Goa KL. Tranexamic acid: a review of its use in surgery and other indications. Drugs. 1999; 57:1005.[28] Mannucci PM. Hemostatic drugs. N Engl J Med. 1998; 339:245.[29] Larson J, Lewis DH, Liljedhal S-O, et al. Early biomechanical and hemodynamic changes after operation in a bloodless field. Eur Surg Res. 1977; 9:311.[30] Yun-Choi HS, Park KM, Pyo MK. Epinephrine induced platelet aggregation in rat platelet-rich plasma. Thromb Res. 2000; 100:511.[31] Zhang QD, Guo WS, Zhang Q, et al. Comparison between closed suction drainage and nondrainage in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2011; 26:1265.[32] Ecthason J, Petz L, Keeler E, et al. The cost effectiveness of preoperative autologous donations. N Engl J Med. 1995; 332: 719.[33] Tan J, Chen H, Liu Q, et al. Meta-analysis of the effectiveness and safety of using tranexamic acid in primary unilateral total knee arthroplasty. J Surg Res. 2013; 184:880.[34] Aggarwal AK, Singh N, Sudesh P. Topical vs Intravenous Tranexamic Acid in Reducing Blood Loss After Bilateral Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Prospective Study. J Arthroplasty. 2015.[35] Chimento GF, Huff T, Ochsner JJ, et al. An evaluation of the use of topical tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2013; 28:74.[36] Georgiadis AG, Muh SJ, Silverton CD, et al. A prospective double-blind placebo controlled trial of topical tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2013; 28:78.[37] Zhao-Yu C, Yan G, Wei C, et al. Reduced blood loss after intra-articular tranexamic acid injection during total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of the literature. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014; 22:3181.[38] Cid J, Lozano M. Tranexamic acid reduces allogeneic red cell transfusions in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty: results of a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Transfusion. 2005; 45:1302.[39] Li ZJ, Fu X, Xing D, et al. Is tranexamic acid effective and safe in spinal surgery? A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur Spine J. 2013; 22:1950.[40] Tanaka N, Sakahashi H, Sato E, et al. Timing of the administration of tranexamic acid for maximum reduction in blood loss in arthroplasty of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001; 83:702.[41] Sasanuma H, Sekiya H, Takatoku K, et al. Efficient strategy for controlling postoperative hemorrhage in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2011; 19:921. |
| [1] | Wang Jianping, Zhang Xiaohui, Yu Jinwei, Wei Shaoliang, Zhang Xinmin, Xu Xingxin, Qu Haijun. Application of knee joint motion analysis in machanism based on three-dimensional image registration and coordinate transformation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-5. |
| [2] | Zhuang Zhikun, Wu Rongkai, Lin Hanghui, Gong Zhibing, Zhang Qianjin, Wei Qiushi, Zhang Qingwen, Wu Zhaoke. Application of stable and enhanced lined hip joint system in total hip arthroplasty in elderly patients with femoral neck fractures complicated with hemiplegia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1429-1433. |
| [3] | Li Canhui, Wu Zhengjie, Zeng Yanhui, He Yinghao, Situ Xiaopeng, Du Xuelian, Hong Shi, He Jiaxiong. Advantage and disadvantage of robot-assisted sacroiliac screw placement and traditional fluoroscopy in orthopedic surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1434-1438. |
| [4] | Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [5] | Zhang Jichao, Dong Yuefu, Mou Zhifang, Zhang Zhen, Li Bingyan, Xu Xiangjun, Li Jiayi, Ren Meng, Dong Wanpeng. Finite element analysis of biomechanical changes in the osteoarthritis knee joint in different gait flexion angles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1357-1361. |
| [6] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [7] | Wu Bingshuang, Wang Zhi, Tang Yi, Tang Xiaoyu, Li Qi. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: from enthesis to tendon-to-bone healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1293-1298. |
| [8] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [9] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [10] | Yang Kuangyang, Wang Changbing. MRI evaluation of graft maturity and knee function after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with autogenous bone-patellar tendon-bone and quadriceps tendon [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 963-968. |
| [11] | Liu Dongcheng, Zhao Jijun, Zhou Zihong, Wu Zhaofeng, Yu Yinghao, Chen Yuhao, Feng Dehong. Comparison of different reference methods for force line correction in open wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 827-831. |
| [12] | Shao Yangyang, Zhang Junxia, Jiang Meijiao, Liu Zelong, Gao Kun, Yu Shuhan. Kinematics characteristics of lower limb joints of young men running wearing knee pads [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 832-837. |
| [13] | Huang Hao, Hong Song, Wa Qingde. Finite element analysis of the effect of femoral component rotation on patellofemoral joint contact pressure in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 848-852. |
| [14] | Yuan Jing, Sun Xiaohu, Chen Hui, Qiao Yongjie, Wang Lixin. Digital measurement and analysis of the distal femur in adults with secondary knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 881-885. |
| [15] | Zhou Jianguo, Liu Shiwei, Yuan Changhong, Bi Shengrong, Yang Guoping, Hu Weiquan, Liu Hui, Qian Rui. Total knee arthroplasty with posterior cruciate ligament retaining prosthesis in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis with knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 892-897. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||