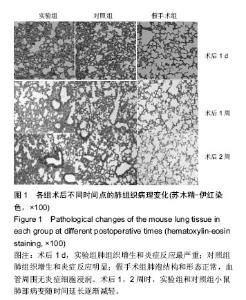
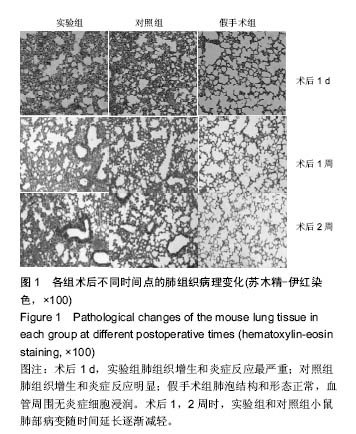
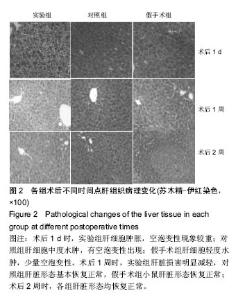
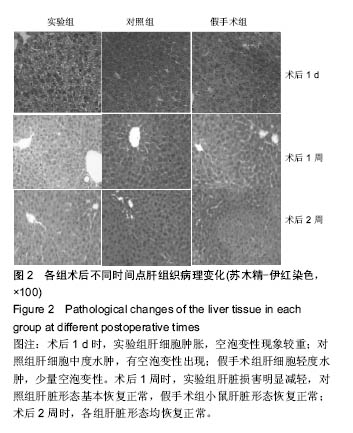
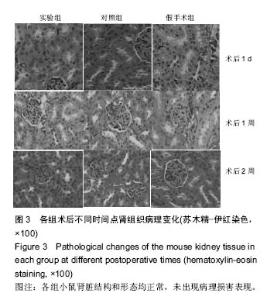
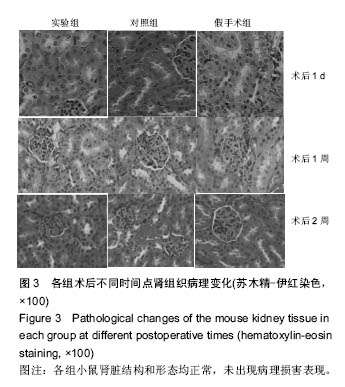
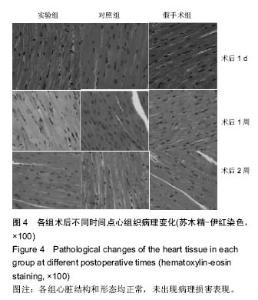
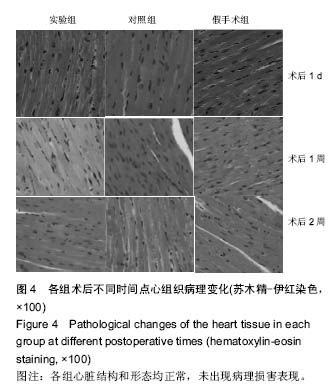
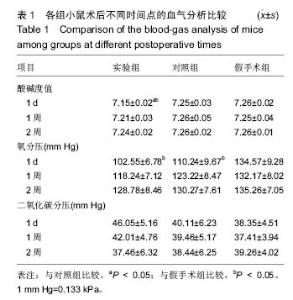
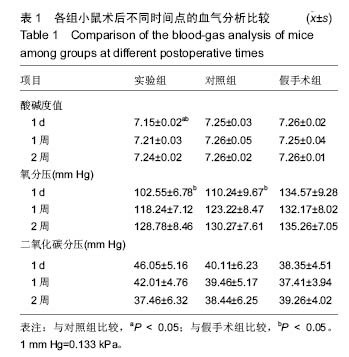
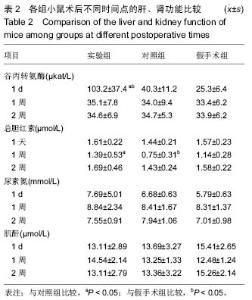
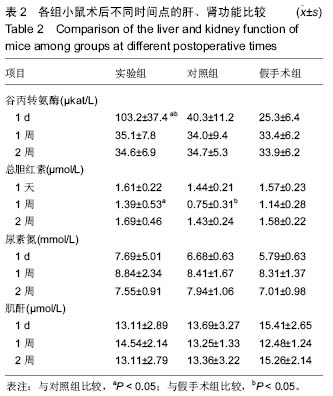
| [1]Hu Y,Wu B,Jin Q,et al.Facile synthesis of 5nm NaYF4:Yb/Er nanoparticles for targeted upconversion imaging of cancer cells.Talanta.2016;152:504-512.[2]单爽,吴昊,谭明乾,等.稀土上转换荧光纳米材料的制备与生物应用[J].生物化学与生物物理进展, 2013,40(10): 925-934.[3]刘涛,孙丽宁,刘政,等.稀土上转换发光纳米材料的应用[J].化学进展,2012,24(2):304-317.[4]林敏,赵英,董宇卿,等.稀土上转换发光纳米材料的制备及生物医学应用研究进展[J].中国材料进展, 2012,31(1): 36-43.[5]Gnanasammandhan MK,Idris NM,Bansal A,et al. Near-IR photoactivation using mesoporous silica-coated NaYF4:Yb,Er/Tm upconversionnanoparticles.Nat Protoc. 2016;11(4): 688-713.[6]张亭亭.基于稀土上转换纳米材料的纳米荧光探针的合成及其应用研究[D].山东师范大学,2014.[7]Wei R,Wei Z,Sun L,et al.Nile Red Derivative-Modified Nanostructure forUpconversion Luminescence Sensing and Intracellular Detection of Fe(3+) and MR Imaging.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(1): 400-410. [8]He F,Li C,Zhang X,et al.Optimization of upconversion luminescence of Nd(3+)-sensitized BaGdF5-based nanostructures and their application in dual-modalityimaging and drug delivery.Dalton Trans. 2016;45(4):1708-1716.[9]Li R,Ji Z,Dong J,et al.Enhancing the imaging and biosafety of upconversionnanoparticles through phosphonate coating.ACS Nano.2015;9(3):3293-3306.[10]Wang Y,Deng R,Xie X,et al.Nonlinear spectral and lifetime management inupconversion nanoparticles by controlling energy distribution.Nanoscale. 2016;8(12): 6666-6673.[11]葛雪莹,袁荃.稀土上转换纳米材料的生物医学应用[J].武汉大学学报(理学版),2015, 61(1):10-20.[12]张瑞锐,高源,唐波.稀土掺杂氟化物纳米材料的上转换发光特征及其生物应用[J].分析科学学报, 2010,26(3): 353-357.[13]刘波,胡丹,刘玉萍,等.上转换发光纳米材料在生物成像中应用的研究进展[J].科学通报,2013,58(7):517-523.[14]Yao C,Wei C,Huang Z,et al.Phosphorylated Peptide Functionalization of Lanthanide Upconversion Nanoparticles for Tuning Nanomaterial-Cell Interactions.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(11): 6935-6943. [15]He M,Pang X,Liu X.Monodisperse Dual-Functional UpconversionNanoparticlesEnabled Near-Infrared Organolead Halide Perovskite Solar Cells.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl.2016;55(13):4280-4284. [16]Jo EJ,Mun H,Kim MG.Homogeneous Immunosensor Based on Luminescence Resonance Energy Transfer for Glycated Hemoglobin Detection Using UpconversionNanoparticles.Anal Chem. 2016;88(5): 2742-2746.[17]郑晓鹏,田甘,谷战军.荧光上转换纳米材料在光动力学治疗癌症中的应用[J].中国肿瘤临床,2014,41(1):27-31.[18]刘通.新型稀土氧化物纳米材料的合成、发光性质与应用[D].吉林大学,2013.[19]田婧,罗华锋.稀土上转换纳米发光材料研究进展[J].化学教育,2014,35(20):1-4.[20]Wang A,Jin W,Chen E,et al.Drug delivery function of carboxymethyl-β-cyclodextrin modified upconversion nanoparticles for adamantine phthalocyanine and their NIR-triggered cancer treatment.Dalton Trans. 2016; 45(9):3853-3862. [21]Wang H,Han RL,Yang LM,et al.Design and Synthesis of Core-Shell-ShellUpconversion Nanoparticles for NIR-Induced Drug Release, Photodynamic Therapy, and Cell Imaging.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016; 8(7):4416-4423. [22]He M,Li Z,Ge Y,et al.Portable Upconversion Nanoparticles-Based Paper Device for Field Testing of Drug Abuse.Anal Chem.2016;88(3):1530-1534. [23]Wu X,Zhang Y,Takle K,et al.Dye-Sensitized Core/Active Shell UpconversionNanoparticles for Optogenetics and Bioimaging Applications.ACS Nano. 2016;10(1):1060-1066. [24]Wang D,Xue B,Kong X,et al.808 nm driven Nd3+-sensitized upconversionnanostructures for photodynamic therapy and simultaneous fluorescenceimaging.Nanoscale.2015;7(1):190-197. [25]Wang A,Jin W,Chen E,et al.Drug delivery function of carboxymethyl-β-cyclodextrin modified upconversion nanoparticles for adamantine phthalocyanine and their NIR-triggered cancer treatment.Dalton Trans. 2016; 45(9):3853-3862.[26]Yang D,Li C,Lin J.Multimodal cancer imaging using lanthanide-basedupconversion nanoparticles. Nanomedicine (Lond).2015;10(16):2573-2591. [27]高渊,曹天野,李富友.具有协同表面配体的水溶性稀土上转换发光纳米材料用于活体淋巴结显像[J].无机化学学报,2012,28(10):2043-2048.[28]周晶.稀土上转换发光纳米材料用于小动物成像研究[D].复旦大学,2012.[29]Li Y,Tang J,Pan DX,et al.A Versatile Imaging and Therapeutic Platform Based on Dual-Band Luminescent LanthanideNanoparticles toward Tumor Metastasis Inhibition.ACS Nano. 2016;10(2): 2766-2773. [30]曹天野.水溶性稀土上转换纳米材料用于小动物活体成像的研究[D].复旦大学,2013.[31]彭娟娟.光功能纳米材料的构建及其生物成像与肿瘤治疗应用研究[D].复旦大学,2013.[32]李章秀.上转换纳米材料制备及在生物小分子、离子检测中的应用[D].湖南大学,2012.[33]Wu S,Duan N,Li X,et al.Homogenous detection of fumonisin B(1) with a molecular beacon based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer between NaYF4: Yb, Ho upconversion nanoparticles and goldnanoparticles.Talanta.2013;116:611-618. [34]汪超.稀土上转换发光纳米材料在肿瘤治疗与生物影像检测方面的应用[D].苏州大学,2014.[35]Hu Y,Wu B,Jin Q,et al.Facile synthesis of 5nm NaYF4:Yb/Er nanoparticles for targeted upconversion imaging of cancercells.Talanta.2016;152:504-512. [36]Tian G,Zhang X,Gu Z,et al.Recent Advances in UpconversionNanoparticles-Based Multifunctional Nanocomposites for Combined CancerTherapy.Adv Mater. 2015;27(47):7692-712. [37]陈庆涛,陈凤华,刘桂霞,等.NaYF_4:Yb/Er-碳纳米管功能纳米材料的制备、表征及其在肿瘤细胞的靶向检测和治疗中的应用[J].中国科学:化学,2011,41(5):798-805.[38]Wang K,Ma J,He M,et al.Toxicity assessments of near-infraredupconversionluminescent LaF3:Yb,Er in early development of zebrafish embryos.Theranostics. 2013;3(4):258-266. [39]Zhou JC,Yang ZL,Dong W,et al.Bioimaging and toxicity assessments of near-infrared upconversion luminescent NaYF4:Yb,Tm nanocrystals. Biomaterials. 2011;32(34):9059-9067. [40]Cheng L,Yang K,Shao M,et al.In vivo pharmacokinetics, long-term biodistribution and toxicology study of functionalizedupconversionnanoparticlesin mice. Nanomedicine (Lond).2011;6(8):1327-1340.[41]张云娇.特异性表面结合肽调控稀土纳米材料自噬和毒性的研究[D].中国科学技术大学,2012. |