Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (25): 4629-4636.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.25.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Combination of cryopreserved hydroxyapatite/bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells repairs rabbit radial defects
Xing Zhi-yuan1, 2, Zhang Ji-bo2, Kong Ling-ju2, Liu Jian-sheng2, Zheng De-yu2
- 1 Department of Orthopedics, Municipal Central Hospital of Panjin, Panjin 124000, Liaoning Province, China
2 Department of Anatomy, Liaoning Medical University, Jinzhou 121001, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2013-02-18Revised:2013-05-17Online:2013-06-18Published:2013-06-18 -
Contact:Zheng De-yu, M.D., Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Anatomy, Liaoning Medical University, Jinzhou 121001, Liaoning Province, China zdy4673349@163.com -
About author:Xing Zhi-yuan★, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Municipal Central Hospital of Panjin, Panjin 124000, Liaoning Province, China; Department of Anatomy, Liaoning Medical University, Jinzhou 121001, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the Educational Bureau of Liaoning Province, No. L2011144
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xing Zhi-yuan, Zhang Ji-bo, Kong Ling-ju, Liu Jian-sheng, Zheng De-yu. Combination of cryopreserved hydroxyapatite/bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells repairs rabbit radial defects[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(25): 4629-4636.
share this article

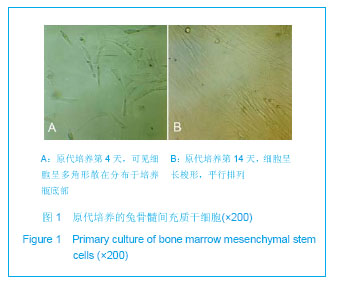
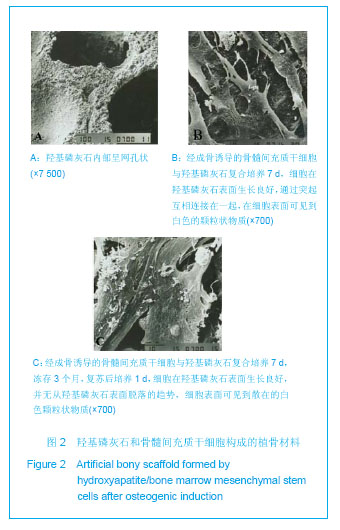
细胞传代后生长速度较原代培养快,约8 d能达到80%融合。流式细胞仪检测结果显示:培养的第3代兔骨髓间充质干细胞均一表达CD44、CD90及CD105,阳性率分别为94.23%,86.23%及96.24%;而CD34、CD45呈阴性,阳性率分别为1.36%及1.45%,结合他人文献可以认为实验获得的细胞主要为间充质干细胞。 2.3 羟基磷灰石复合成骨诱导后骨髓间充质干细胞构成的复合植骨材料 见图2。成骨诱导的骨髓间充质干细胞与多孔羟基磷灰石共培养7 d后,扫描电镜可见骨髓间充质干细胞在多孔羟基磷灰石表面伸出了突起,相互接触,彼此连接成片,有的细胞已经伸入到羟基磷灰石的孔隙内。在部分骨髓间充质干细胞之间有丝状纤维连接,在细胞表面也可见到有大小不等的白色钙质颗粒,见图2B。复合植骨材料冻存复苏后,多孔羟基磷灰石的表面及孔隙内骨髓间充质干细胞状态与冻存前并没有明显区别,细胞也没有从羟基磷灰石表面脱落的趋势,见图2C。"
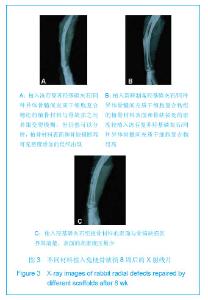
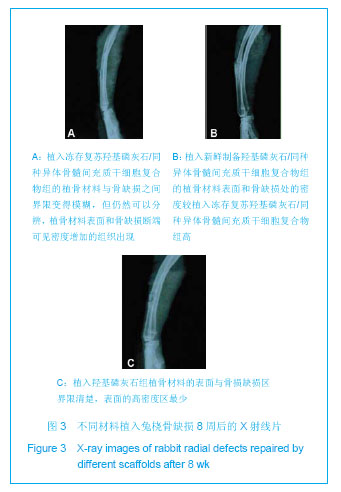
2.4 复合材料原位成骨结果 术后所有动物全身状况良好,正常进食。切口无红肿及渗出液,部分动物术区周围有一定程度肿胀,虽未进行特殊处理这些肿胀也逐渐自行消退。无动物死亡,所有动物均计入实验统计。 大体观察:术后8周,冻存复合材料组植骨材料两端均有骨痂生长,断端仍然清晰可见,桡骨及支架材料周围软组织未见充血、变性及坏死表现;其中冻存复合材料组和新鲜复合材料组的支架材料均无移位;羟基磷灰石组有部分标本支架材料可轻微活动。术后12周,冻存复合材料组和新鲜复合材料组植骨材料完全被骨样组织包裹,并形成连续性骨痂,塑形较好;羟基磷灰石组支架材料与自体骨间界限模糊,结合处被骨痂包绕,在某些植骨材料的表面多为纤维样组织包裹。 X射线观察:术后8周,冻存复合材料组和新鲜复合材料组复合植骨材料与自体骨两端交错,可见少量骨痂,断端可见;羟基磷灰石组几乎未见骨痂,断端清晰,见图3。术后12周,冻存复合材料组和新鲜复合材料组可见支架材料与自体骨融合,材料的密度与正常骨相似,有连续性骨痂通过断端,皮质骨形成,髓腔通畅,塑形良好;羟基磷灰石组断端变模糊,骨痂量少,塑形欠佳,仍可见部分支架,见图4。"

组织学观察:术后所有时间点在材料周围均未发现明显的炎性细胞浸润情况。术后8周,冻存复合材料组和新鲜复合材料组复合植骨材料开始降解,在材料边缘有大量类骨质形成,材料内部可见新生的骨岛形成,偶可见小血管,新骨形成增多;而羟基磷灰石组的复合材料内很少见到骨岛形成,仅在材料的边缘形成一薄层的骨组织,大部分为纤维结缔组织,见图5。术后12周,冻存复合材料组和新鲜复合材料组支架材料与自体骨之间可见大量新生骨组织,有规则骨小梁通过,局部可见有少量皮质骨形成,内部可见小血管;羟基磷灰石组支架材料与自体骨间也见新生骨组织,但较少且骨质薄,中间的空隙多数为纤维结缔组织相连,近骨断端侧有骨小梁形成,但尚没有与羟基磷灰石表面组织形成有效连接、贯通,见图6。"

| [1] Sundararaj GD,Amritanand R,Venkatesh K,et al.The use of titanium mesh cages in the reconstruction of anterior column defects in active spinal infections: can we rest the crest? Asian Spine J.2011;5(3):155-161.[2] Richardson RM,Rapoport A,Oreopoulos DG,et al.Unusual fractures associated with osteoporosis in premenopausal women.Can Med Assoc J. 1978;119(5):473-476. [3] Rader EP,Cederna PS,McClellan WT.Effect of cleft palate repair on the susceptibility to contraction-induced injury of single permeabilized muscle fibers from congenitally-clefted goat palates.Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2008;45(2): 113-120. [4] Einhorn TA,Gundberg CM,Devlin VJ,et al.Fracture healing and osteocalcin metabolism in vitamin K deficiency.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1988; (237):219-225.[5] Smartt JmJr,Karmacharya J,Gannon FH,et al.Repair of the immature and mature craniofacial skelet on with a carbonated calcium phosphate capacity.Plast Reconstr Surg.2005; 115(6): 1642-1650.[6] 顾祖超,李起鸿,赵玉峰,等.自自体骨髓基质细胞复合支架材料修复兔尺骨干节段骨缺损的实验研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2004, 6(6):651-656.[7] Morigi M,Introna M,Imberti B,et al.Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells accelerate recovery of acute renal injury and prolong survival in mice.Stem Cells.2008;26(8): 2075-2082. [8] Nina VJ,Assef MA,Rodrigues RR,et al.Reconstruction of the chest wall with external metal brace: alternative technique in poststernotomy mediastinitis. Rev Bras Cir Cardiovasc.2008; 23(4):507-511.[9] Hannouche D.Tissue engineering for the repair of cartilage defects. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot.2008;94(8 Suppl):383-393. [10] 王伯春.组织工程化骨低温保存研究现状及展望[J].制冷与空调, 2008,22(4):22-27. [11] Khanna-Jain R,Mannerström B,Vuorinen A,et al.Osteogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells on B-tricalcium phosphate/poly (l-lactic acid/caprolactone) three-dimensional scaffolds.J Tissue Eng. 2012;3(1):2041.[12] Dyondi D,Webster TJ,Banerjee R.A nanoparticulate injectable hydrogel as a tissue engineering scaffold for multiple growth factor delivery for bone regeneration.Int J Nanomedicine.2013; 8: 47-59.[13] Kulakov AA,Goldshtein DV,Grigoryan AS,et al.Clinical study of the efficiency of combined cell transplant on the basis of multipotent mesenchymal stromal adipose tissue cells in patients with pronounced deficit of the maxillary and mandibulary bone tissue.Bull Exp Biol Med.2008;146(4):522-525.[14] Choi SH,Jin SE,Lee MK,et al.Novel cationic solid lipid nanoparticles enhanced p53 gene transfer to lung cancer cells.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2008;68(3):545-554.[15] Au A,Boehm CA,Mayes AM,et al.Formation of osteogenic colonies on well-defined adhesion peptides by freshly isolated human marrow cells.Biomaterials.2007;28: 1847-1861.[16] Si HP,Lu ZH,Lin YL.Transfect bone marrow stromal cells with pcDNA3.1-VEGF to construct tissue engineered bone in defect repair. Chin Med J (Engl). 2012;125(5):906-911.[17] Janebodin K,Horst OV,Ieronimakis N,et al.Isolation and characterization of neural crest-derived stem cells from dental pulp of neonatal mice. PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27526.[18] Hamada Y,Fujitani W,Kawaguchi N.et al.The preparation of PLLA/calcium phosphate hybrid composite and its evaluation of biocompatibility. Dent Mater J.2012;31(6):1087-1096.[19] Nudelman F,Pieterse K,George A,et al.The role of collagen in bone apatite formation in the presence of hydroxyapatite nucleation inhibitors. Nat Mater. 2010;9(12):1004-1009. [20] Tilley S,Bolland BJ,Partridge K,et al.Taking tissue-engineering principles into theater: augmentation of impacted allograft with human bone marrow stromal cells. Regen Med. 2006;1(5): 685-692.[21] Inanç B,Arslan YE,Seker S,et al.Periodontal ligament cellular structures engineered with electrospun poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) nanofibrous membrane scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res A.2009;90(1):186-195.[22] Balloni S,Calvi EM,Damiani F,et al. Effects of titanium surface roughness on mesenchymal stem cell commitment and differentiation signaling. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009; 24(4):627-635.[23] Rezwana K,ChenQZ,Blaker JJ,et al.Biodegradable and bioactive porous polymer/inorganic scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.Biomaterials.2006;27(18):3413-3431.[24] Vallet-Regi M, Gonzalez-Calbet JM. “ Calcium phosphates as substitution of bone tissues.Prog Sol State Chem.2004; 32(1-2): 1-31.[25] Lavery K,Swain P,Falb D,et al.BMP-2/4 and BMP-6/7 differentially utilize cell surface receptors to induce osteoblastic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells.J Biol Chem. 2008;283(30): 20948-20958.[26] James AW,Levi B,Nelson ER,et al.Deleterious effects of freezing on osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stromal cells in vitro and in vivo.Stem Cells Dev.2011;20(3):427-439. [27] Thevenot P,Nair A,Dey J,et al.Method to analyze three- dimensional cell distribution and infiltration in degradable scaffolds.Tissue Eng Part C Methods.2008;14(4): 319-331.[28] Polge C.The freezing of mammalian embryos:perspectives and possibilities.Ciba Found Symp.1977;(52):3-18.[29] Wen Y,Li B,Dang RS,et al.Dier Junyi Daxue Xuebao.2007; 23(6):26-31.温昱,李彬,党瑞山,等.犬骨髓多能成体祖细胞的体外培养、鉴定及向平滑肌样细胞的诱导分化[J].第二军医大学学报,2007, 23(06):26-31.[30] Zhang J,Liu L,Gao Z,et al.Novel approach to engineer implantable nasal alar cartilage employing marrow precursor cell sheet and biodegradable scaffold. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009;67(2):257-264.[31] Beainy F,El Amm C,Abousleimane Y,et al.Biomechanical effects of cranioplasty for defects using autogenous calvarial bone. J Craniofac Surg. 2012;23(2):e152-155.[32] Khadka A,Hu J. Autogenous grafts for condylar reconstruction in treatment of TMJ ankylosis: current concepts and considerations for the future.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2012; 41(1):94-102. [33] Poppe P,Wysieński L,Synarski K,et al.Generating autogenous cartilage on the basis of subperichondrial grafts of demineralized bone matrix with local stimulation by growth factors.Ortop Traumatol Rehabil.2001;3(2):190-193.[34] Takigami H,Kumagai K,Latson L,et al.Bone formation following OP-1 implantation is improved by addition of autogenous bone marrow cells in a canine femur defect model. J Orthop Res.2007;25(10):1333-1342.[35] Dubreuil P,Abribat T,Broxup B,et al.Long-term growth hormone-releasing factor administration on growth hormone, insulin-like growth factor-I concentrations, and bone healing in the Beagle.Can J Vet Res. 1996;60(1):7-13.[36] Tezer M,Erturer RE,Ozturk C,et al.Conservative treatment of fractures of the thoracolumbar spine.Int Orthop.2005;29(2): 78-82. [37] Lee C,Lashari S.Pseudofracture of the neck of femur secondary to osteomalacia. J Bone Joint Surg Br.2007;89(7): 956-958.[38] Tazi N,Zhang Z,Messaddeq Y,et al.Hydroxyapatite bioactivated bacterial cellulose promotes osteoblast growth and the formation of bone nodules.AMB Express.2012;2(1): 61-69.[39] Barron MJ,Goldman J,Tsai CJ,et al.Perfusion flow enhances osteogenic gene expression and the infiltration of osteoblasts and endothelial cells into three-dimensional calcium phosphate scaffolds.Int J Biomater.2012; 2012:915620. [40] Chen YC,Lin RZ,Qi H,et al.Functional Human Vascular Network Generated in Photocrosslinkable Gelatin Methacrylate Hydrogels.Adv Funct Mater.2012; 22(10):2027-2039.[41] Chen M,Le DQ,Hein S,et al.Fabrication and characterization of a rapid prototyped tissue engineering scaffold with embedded multicomponent matrix for controlled drug release. Int J Nanomedicine.2012;7:4285-4297.[42] Zeng XB,Hu H,Xie LQ,et al.Magnetic responsive hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds construction for bone defect reparation.Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:3365-3378.[43] Shimakura Y,Yamzaki Y,Uchinuma E.Experimental study on bone formation potential of cryopreserved human bone marrow mesenchymal cell/hydroxyapatite complex in the presence of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2.J Craniofac Surg.2003;14(1):108-116.[44] Zhang R,Ma PX.Poly(alpha-hydroxyl acids)/hydroxyapatite porous composites for bone-tissue engineering. I. Preparation and morphology. J Biomed Mater Res.1999;44(4):446-455.[45] James AW,Levi B,Nelson ER,et al.Deleterious effects of freezing on osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stromal cells in vitro and in vivo.Stem Cells Dev.2011;20(3): 427-439.[46] Chua KN,Chai C,Lee PC,et al.Functional nanofiber scaffolds with different spacers modulate adhesion and expansion of cryopreserved umbilical cord blood hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells.Exp Hematol.2007;35(5): 771-781.[47] Strick R,Strissel PL,Gavrilov K,et al.Cation-chromatin binding as shown by ion microscopy is essential for the structural integrity of chromosomes. J Cell Biol.2001;155(6):899-910.[48] Zhang YH,Qin SJ,Zheng DY,et al.Jinzhou Yixueyuan Xuebao. 2004;22(1):36-41.张玉华,秦书俭,郑德宇,等.基因转染BMSC与BGC的体外生物相容性的实验研究[J].锦州医学院学报,2004,22(1):36-41.[49] Qin SJ,Liu X,Zheng DY,et al.Zhongguo Linchuang Kangfu. 2004;8(20):356-362.秦书俭,刘学,郑德宇,等.外源性人骨形态发生蛋白-2基因在兔骨髓基质细胞中的稳定表达及其诱导成骨作用[J].中国临床康复, 2004,8(20):356-362.[50] Zhou ZH,Macnab SJ,Jakana J,et al.Identification of the sites of interaction between the scaffold and outer shell in herpes simplex virus-1 capsids by difference electron imaging.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.1998;95(6):2778-2783.[51] Jancár J,Slovíková A,Amler E,et al.Mechanical response of porous scaffolds for cartilage engineering.Physiol Res.2007; 56 Suppl 1:S17-25.[52] Park KH,Kim H,Moon S,et al.Bone morphogenic protein-2 (BMP-2) loaded nanoparticles mixed with human mesenchymal stem cell in fibrin hydrogel for bone tissue engineering.J Biosci Bioeng.2009;108(6):530-537. [53] Yin HY,Cui L,Liu GP,et al.Zhongguo Meirong Zazhi.2009; 18(4):479-483.尹宏宇,崔磊,刘广鹏,等.深低温保存组织工程化骨的实验研究[J].中国美容杂志,2009,18(4):479-483.[54] Lan X,Ge BF,Liu XM.Chuangshang Waike Zazhi.2007;9(4): 301-305.蓝旭,葛宝丰,刘雪梅.冻存保护剂对低温保存的组织工程骨修复骨缺损的影响[J].创伤外科杂志,2007,9(4):301-305.[55] Ma L,Makino Y,Yamaza H,et al.Cryopreserved dental pulp tissues of exfoliated deciduous teeth is a feasible stem cell resource for regenerative medicine. PLoS One.2012;7(12): e51777. [56] Kodonas K,Gogos C,Papadimitriou S,et al.Experimental formation of dentin-like structure in the root canal implant model using cryopreserved swine dental pulp progenitor cells.J Endod.2012;38(7):913-919.[57] Costa PF,Dias AF,Reis RL,et al.Cryopreservation of cell/scaffold tissue-engineered constructs.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2012;18(11):852-858. [58] Ginis I,Grinblat B,Shirvan MH.Evaluation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells after cryopreservation and hypothermic storage in clinically safe medium.Tissue Eng Part C Methods.2012;18(6):453-463. |
| [1] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [2] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [3] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [4] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [5] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [6] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [7] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [8] | Chen Junyi, Wang Ning, Peng Chengfei, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Bei Chaoyong. Decalcified bone matrix and lentivirus-mediated silencing of P75 neurotrophin receptor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| [9] | Liu Jiangfeng. Nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide 66 composite filling combined with locking plate in the treatment of fibrous dysplasia of femoral bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 542-547. |
| [10] | Li Li, Ma Li. Immobilization of lactase on magnetic chitosan microspheres and its effect on enzymatic properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 576-581. |
| [11] | Jiang Tao, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Ma Chuang, Wei Qin. Platelet-derived growth factor BB induces bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3937-3942. |
| [12] | He Lin, Wu Xi, He Song, Yang Sen. Hydrophilicity and cell adhesion of hydroxyapatite bioceramics after the coating of polydopamine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3540-3544. |
| [13] | Zhou Anqi, Tang Yufei, Wu Bingfeng, Xiang Lin. Designing of periosteum tissue engineering: combination of generality and individuality [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3551-3557. |
| [14] | Lang Limin, He Sheng, Jiang Zengyu, Hu Yiyi, Zhang Zhixing, Liang Minqian. Application progress of conductive composite materials in the field of tissue engineering treatment of myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3584-3590. |
| [15] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||