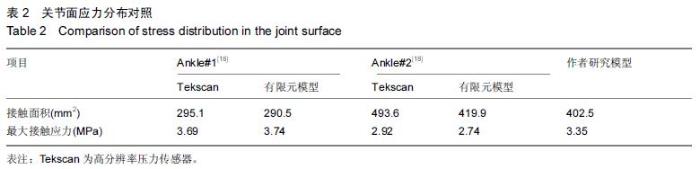
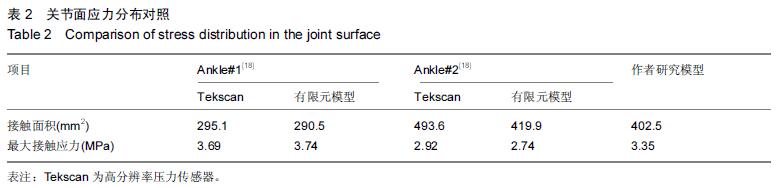
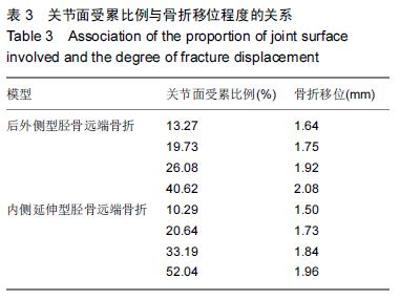
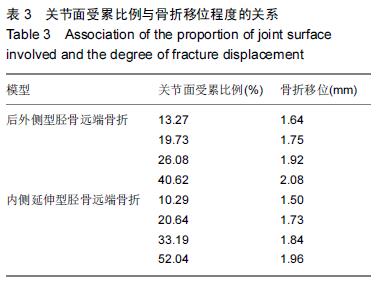
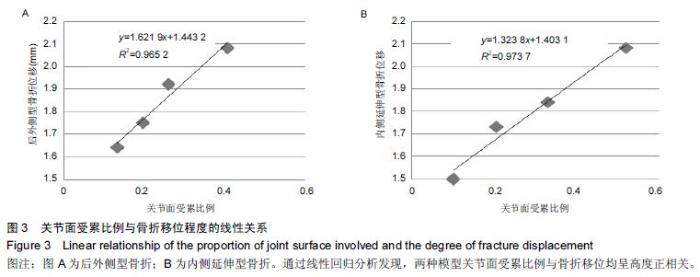
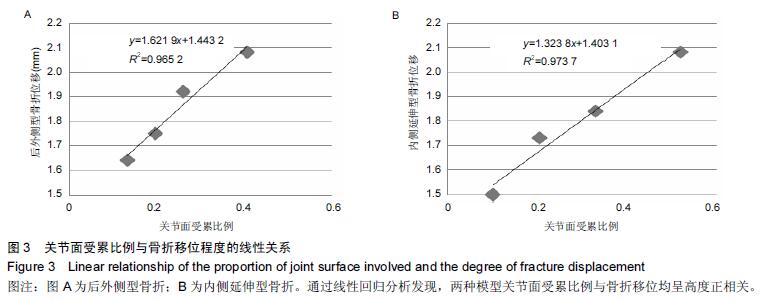
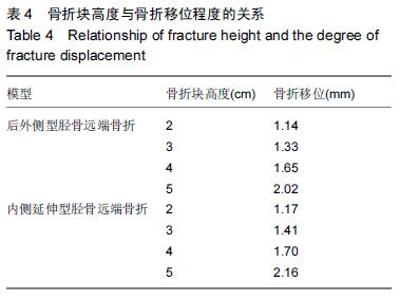
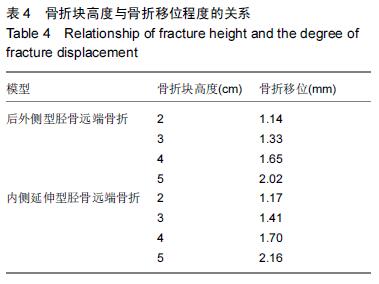
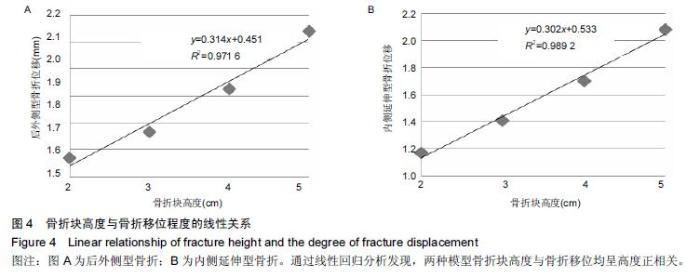
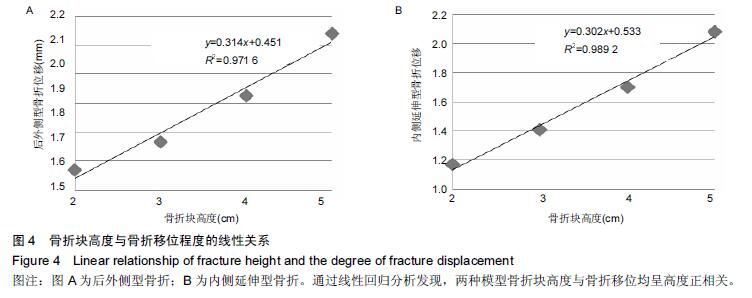
| [1] 姜文辉,董伊隆,张程,等. 成人胫腓骨下端连接的解剖及其临床意义[J]. 解剖学报,2013,44(2):249-252. [2] 张程,张力成,姜文辉,等. 人踝关节深层胫距后韧带远端止点的解剖[J]. 解剖学报,2013, 44(2):245-248. [3] 马腾,徐国浩,朱亮亮,等. 踝关节骨折伴下胫腓联合分离和三角韧带损伤的治疗及临床意义[J].吉林医学, 2013, 34(31):6536-6537. [4] 段德宇,杨述华,王洪,等. 踝关节软骨损伤关节镜术后的综合康复治疗[J]. 临床急诊杂志,2013,14(10):465-467. [5] 戴海飞,余斌,张凯瑞,等. 踝关节周围韧带损伤对距骨稳定性影响的有限元分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2012, 27(2):121-124. [6] 张秋霞,张林,王国祥,等. 功能性不稳踝关节位置觉和肌肉力觉特征[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2012,31(1):9-13. [7] Weil NL,Termaat MF,Rubinstein SM,et al. WARRIOR-trial-is routine radiography following the 2-week initial follow-up in trauma patients with wrist and ankle fractures necessary:study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2015;16(1):600. [8] 张浩,马南,朱建民. 腕关节有限元模型的建立及应用进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2012,16(52):9813-9817. [9] 孙卫东,温建民. 足部有限元建模方法应用现状[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(13):2457-2461. [10] 黄宇文.有限元分析在口腔生物力学中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(13):2423-2426. [11] 陈纪宝,奚春阳,焦力刚,等. 有限元分析在腰椎生物力学应用中的研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16 (26): 4908-4912. [12] 牛晓东,卢莉蓉.医学有限元仿真实验的研究[J]. 中国现代教育装备,2013,11(19):84-86. [13] 郭鹏超,王成伟.踝关节三维有限元生物力学研究的临床转化[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(31):5056-5061. [14] Schwartz D,Guleyupoglu B,Koya B,et al. Development of a computationally efficient full human body finite element model. Traffic Inj Prev. 2015;16(1):S49-56. [15] Zach L,Kun?ická L,R??i?ka P,et al. Design,analysis and verification of a knee joint oncological prosthesis finite element model. Comput Biol Med. 2014;54: 53-60. [16] Boraiah S,Gardner MJ,Hel fet DL,et al. Higassociation of posterior malleolus fractures with spiral distal tibial fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466:1692-1698. [17] Macko VW,Matthews L,Zwirkoski P,et al. The joint-contact area of the ankle. Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991;73:347-351. [18] Anderson DD,Goldsworthy JK,Li W,et al. Physical validation of a patient-specific contact finite element model of the ankle. J Biomech. 2007;40(8):1662-1669. [19] 林志斌.陈旧性踝关节扭伤临床研究进展[J].亚太传统医药,2014,10(22):33-34. [20] 文军.足踝部关节在体运动度数字化三维测量新方法的建立及其初步应用研究[D].南方医科大学,2012. [21] 徐菲.足踝有限元模型在踝关节失稳中的应用[J]. 北京生物医学工程,2014,3:322-326. [22] 陶凯.人体足踝系统建模与相关力学问题研究[D].上海交通大学,2010. [23] 戴海飞,余斌,张凯瑞,等.踝关节周围韧带损伤对距骨稳定性影响的有限元分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2012, 27(2):121-124. [24] 吴恺,杨茂伟,都承斐.人体足踝部有限元模型的建立及有效性分析[J].中国骨与关节外科,2012,5(4):352-356. [25] 冯洋,王冬梅,刘安民,等. 足踝步态模拟机设计与运动特性分析[J]. 机械设计与制造,2014,52(8):5-7. [26] Liu Q,Zhao G,Yu B,et al. Effects of inferior tibiofibular syndesmosis injury and screw stabilization on motion of the ankle:a finite element study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014. [27] Jay Elliot B,Gundapaneni D,Goswami T. Finite element analysis of stress and wear characterization in total ankle replacements. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2014;34:134-145. [28] 牛文鑫,丁祖泉.三种三维有限元建模方法在跟骨模型建立中的应用和比较[J]. 医用生物力学,2007,22(4):345-350. [29] Huiskes R. On the modeling of long bones in structural analyses. J Biomech. 1982;15:65-69. [30] 唐自银,王伟亮,唐厚学,等.不同大小后踝骨折手术治疗临床疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,28(2):125-127. [31] 方玮,马兆龙,杨文贵,等. 阻挡钉结合交锁髓内钉治疗胫骨远端骨折的生物力学研究[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2014,29(4):359-361. [32] Macko VW,Matthews L,Zwirkoski P,et al. The joint-contact area of the ankle.Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991; 73:347-351. |