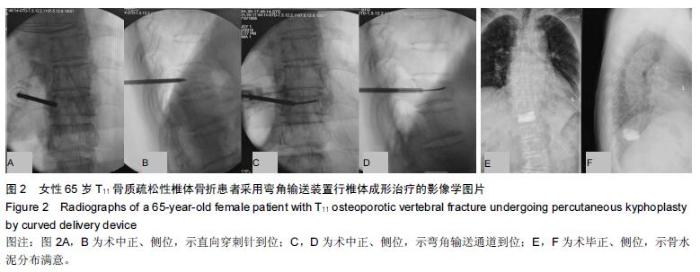
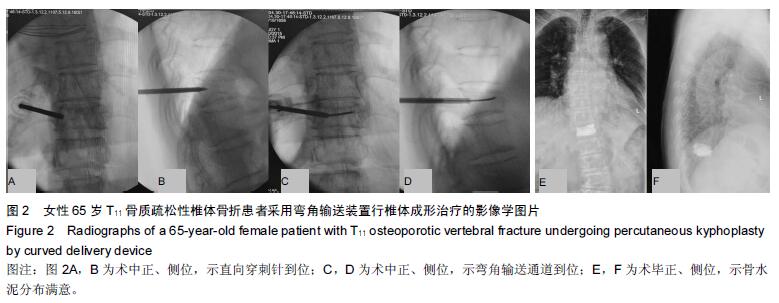
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (17): 2496-2502.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.17.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
Curved vertebroplasty device for thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures
Xiong Sen, Mao Ke-ya, Han Zhen-chuan, Zhang Ya-bin, Wang Xu-xuan, Li Xiu-can
- Department of Orthopedics, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China
-
Received:2016-03-13Online:2016-04-22Published:2016-04-22 -
Contact:Mao Ke-ya, M.D., Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China -
About author:Mao Ke-ya, M.D., Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 51372276
Cite this article
Xiong Sen, Mao Ke-ya, Han Zhen-chuan, Zhang Ya-bin, Wang Xu-xuan, Li Xiu-can. Curved vertebroplasty device for thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(17): 2496-2502.
share this article
| [1] Galibert P, Deramond H, Rosat P, et al. Preliminary note on the treatment of vertebral angioma by percutaneous acrylic vertebroplasty.Neurochirurgie.1987;33:166-167. [2] Wang JC, Liu ZD, Yang JD, et al. Improved percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.Chin J Orthop Traum. 2012; 14(3):216-219. [3] Burton AW,Hamid B.Kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2008;12(1):22-27. [4] Rapadeo A. General management of vertebralfractures. Bone. 1996;18:191-196. [5] Division of Mental Health.Field trial WHOQOL-100:The 100 questions With response scales WHO, GeneVa, 1995. [6] Alvarez L,Perez-Higueras A,Granizo J,et al.Predictors of outcomes of percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporoticvertebral fractures. Spine.2005;30:87-92. [7] Hoh BL,Rabinov JD,Pryor JC,et al.Balloon kyphoplasty for vertebral compression fracture using a unilateral balloon tamp via a unipedicular approach: technique note. Pain Phys. 2004,7:111-114. [8] Kin AK,Jensen ME,Dion JE,et al.Unilateral transpedicular percutaneous vertebroplasty: initial experience. Radiology. 2002;22(2): 737-741. [9] Murphy KJ, Lin DD, Khan AA, et al. Multilevel vertebroplasty via a single pedicular approach using a curved 13-gauge needle: technical note. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2002;53(5): 293-295. [10] Knavel EM,Rad AE,Thielen KR,et al. Clinical outcomes withhemivertebral filling during percutaneous vertebroplasty. AJNR Am J Neororadiol. 2009;30(3): 496-499. [11] Theocharopoulos N, Perisinakis K, Damilakis J,et al. Occupational exposure from common fluoroscopic projection used in orthopaedic surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85:1698-1703. [12] Liebschner MAK,Rosenberg WS,Keaveny TM.Effects of bone cement volume and distribution on vertebral stiffness after vertebroplasty. Spine. 2001;26:1547-1554. [13] Chen BL,Li YQ,Xie DH,et al.Effects of unipedicular and bipedicular kyphoplasties on stiffness and biomechanical balance of the compression-fractured vertebral bodies. Chin J Orthop Trauma. 2011;13(3): 251-255. [14] Belkoff SM, Mathis JM, Fenton DC,et al. An exvivo biomechanical evaluation of an inflatable bonetamp used in the treatment of compression fracture. Spine.2001; 26(14):151-156. [15] Brugieres P, Gaston A, Heran F, et al.Percutaneous biopsies of the thoracic spine under CT guidance: transcostovertebral approach. Compur Assist Tomogr. 1990;14(3):446-448. [16] Boszczyk BM, Bierschneider M, Hauck S, et al. Transcostovertebral kyphoplasty of the mid and high thoracic spine. Eur Spine J. 2005;14(10):992-999. [17] Ryu KS,Park CK,Kim MK,et al.Single balloon kyphoplasty using far lateral extrapedicular approach: technical note and preliminary results. Spinal Disord Tech. 2007;20(5):392-398. [18] Ryu KS,Huh HY,Jun SC,et al.Single-balloon kyphoplasty in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures:far-lateral extrapedicular approach. Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2009;45(2):122-126. [19] Wang S,Wang Q,Kang J,et al.An imaging anatomical study on percutaneous kyphoplasty for lumbar via a unilateral transverse process-pedicle approach. Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2014;39(9):701-706. [20] Baumann C,FuchsH,Jürgen K,et al.Complications in Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Associated with Puncture or Cement Leakage. Cardiovasc Inter Rad. 2007;30(2): 161-168. [21] Heo DH,Cho YJ.Segmental artery injury following percutaneous vertebroplasty using ertrapedicular approach. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2011;49(2): 131-133. [22] Puri AS,Colen RR,Reddy AS,et al. Lumbar artery pseudoaneurysm after percutaneous vertebroplasty:a unique vascular complication. J Neurosurg Spine. 2011; 14(2):296-299. [23] Potet J, Weber-Donat G, Curis E, et al. Incidence of Pulmonary Cement Embolism after Real-Time CT Fluoroscopy-guided Vertebroplasty. Vasc Interv Radiol. 2013; 24:1853-1860. [24] Boger A,Heini P, Windolf M,et al.Adjacent vertebral failure after vertebroplasty: a biomechanical study of low-modulus PMMA cement. Eur Spine. 2007;16(12): 2118-2125. [25] Kinzl M,Benneker LM,Boger A,et al.The effect of standard and low- modulus cement augmentation on the stiffness,strength,and end plate pressure distribution in vertebroplasty.Eur Spine J. 2012;21:920-929. [26] Wang CY, Fan SW, Liu JH. Basivertebral foramen could be connected with intravertebral cleft: a potential risk factor of cement leakage in percutaneous kyphoplasty. Spine J. 2014;14:1551-1558. [27] Venmans A,Klazen CA,Lohle PN.Percutaneous vertebroplasty and pulmonary cement embolism: results from Vertos II.Am J Neuroradiol. 2010;31:1451-1453. [28] [Bohner M,Gasser B,Baroud G,et al.Theoretical and experimental model to describe the injection of a polymethylmethacrylate cement into a porous structure. Biomaterials. 2003;24(16):2721-2730. [29] 唐振华,桂红利,伍正华. 经横突椎弓根入路和经椎弓根入路单侧穿刺行椎体成形治疗OVCF的临床疗效分析[J].现代医药卫生,2014,30(12):1830-1831. [30] Chu W, Tsuei YC, Liao PH, et al. Decompressed percutaneous vertebroplasty: A secured bone cement delivery procedure for vertebral augmentation in osteoporotic compression fractures. J Injury. 2013;44(6): 813-818. [31] 李鹏.弯角椎体成形穿刺装置的研制及应用研究[D].军医进修学院,2012. [32] Srinivasan D, Than KD, Anthony C, et al. Wang.Radiation Safety and Spine Surgery: Systematic Review of Exposure Limits and Methods to Minimize Radiation Exposure World Neurosurg. 2014;82(6):1337-1343. [33] Kim SM, Kim JU, Lim JH, et al. Delayed complication of vertebroplasty: intradural penetration of previous PMMA leakage after trauma. Spine J. 2015; (15): 1146–1149. [34] Corcos G, Dbjay J, Mastier C, et al. Cement leakage in percutaneous vertebroplasty for spinal metastases: a retrospective evaluation of incidence and risk factors.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(5): E332-338. [35] Ha KY, Lee JS, Kim KW, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for vertebral compression fractures with and without intravertebral clefts. Bone Joint Surg (Br). 2006;88(5): 629-633. [36] Xing D,Ma JX,Ma XL,et al.A meta-analysis of balloon kyphoplasty compared to percutaneous vertebroplasty for treating osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Clin Neurosci. 2013;20(6):795-803. [37] Murphy KJ, Lin DD, Khan AA, et al. Multilevel vertebro-plasty via a single pedicular approach using a curved 13-gauge needle: technical note. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2002;53(5): 293-295. [38] Kaufmann TJ, Trout AT, Kallmes DF. The effects of cement volume on clinical outcomes of percutaneous vertebroplasty. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006;27(9): 1933-1937. [39] Lyster M,Symington K,Stalcup J,et al.Osseoplasty: Review and Analysis of 1081 Cases in the United States and Europe. Available at: http://www.osseon.com/wp- content/uploads/1081-Patient-Case-Study.pdf Soon WC,Mathew RK,Timothy J,et al.Comparison of vertebroplasty using directional versus straight needle.J Acta Radiol Open. 2015;4(3):2047981615569268. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [3] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [4] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [5] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [6] | Xu Yulin, Shen Shi, Zhuo Naiqiang, Yang Huilin, Yang Chao, Li Yang, Zhao Heng, Zhao Lu. Biomechanical comparison of three different plate fixation methods for acetabular posterior column fractures in standing and sitting positions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 826-830. |
| [7] | Cai Qunbin, Zou Xia, Hu Jiantao, Chen Xinmin, Zheng Liqin, Huang Peizhen, Lin Ziling, Jiang Ziwei. Relationship between tip-apex distance and stability of intertrochanteric femoral fractures with proximal femoral anti-rotation nail: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 831-836. |
| [8] | Song Chengjie, Chang Hengrui, Shi Mingxin, Meng Xianzhong. Research progress in biomechanical stability of lateral lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 923-928. |
| [9] | Xie Chongxin, Zhang Lei. Comparison of knee degeneration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with or without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 735-740. |
| [10] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [11] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [12] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [13] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [14] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [15] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||