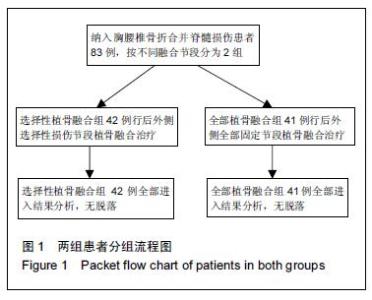
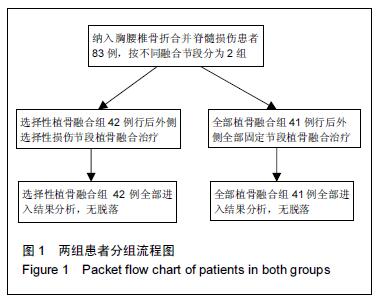
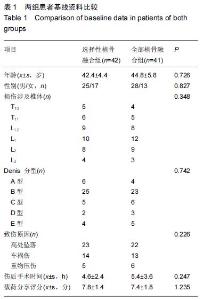
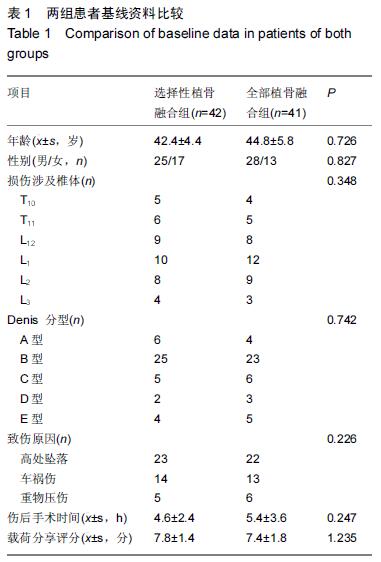
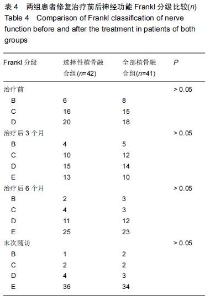
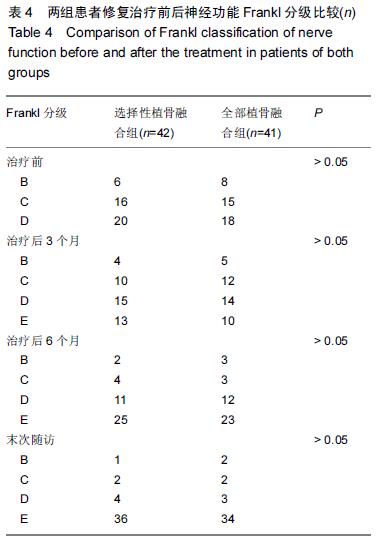
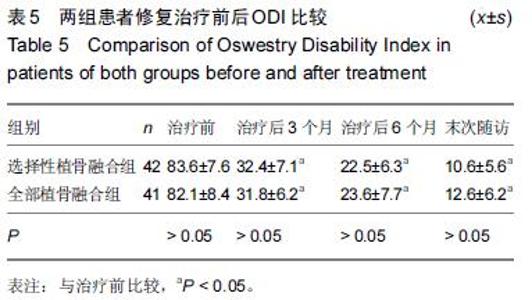
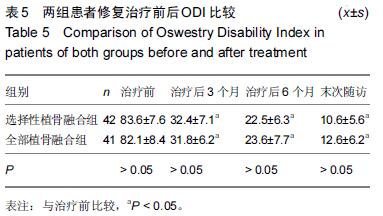
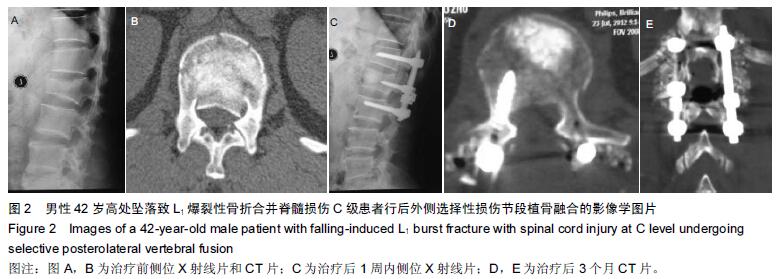
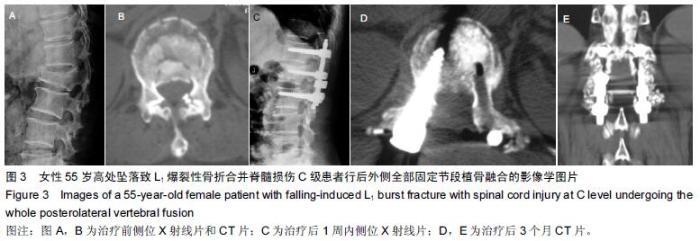
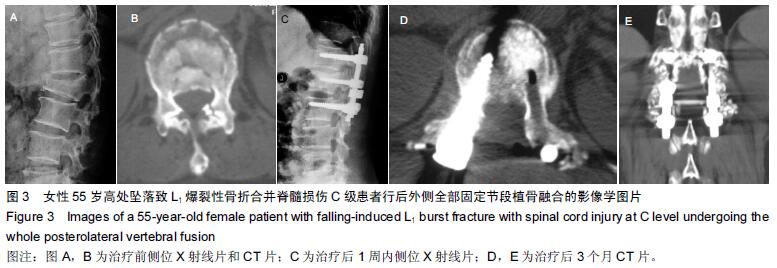
| [1] Dai LY, Jiang LS, Jiang SD.Posterior short-segment fixation with or without fusion for thoracolumbar burst fractures. a five to seven-year prospective randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2009;91(5):1033-1041. [2] Machino M,Yukawa Y,Ito K,et al.The complement of the load-sharing classification for the thoracolumbar injury classificationsystem in managing thoracolumbar burst fractures.J Orthop Sci.2013:18(1):81-86. [3] 张文武,申勇,姚晓光,等.后路长节段椎弓根螺钉固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的疗效评价[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(6): 487-492. [4] 张伟,胡文斌,张建湘.后路短节段固定联合植骨治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折的Meta分析[J].颈腰痛杂志, 2015,36(2): 144-149. [5] 张绍文,李盛华,樊成虎.后路开放手术治疗胸腰椎骨折研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2014,35(4):238-240. [6] Yang JY,Lee JK,Song HS.The impact of adjacent segment degeneration on the clinical outcome after lumbar spinal fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(5): 503-507. [7] 何磊,戍利民,董健文,等.后外侧融合与不融合在经伤椎固定治疗无脊髓损伤胸腰椎骨折中的疗效比较[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2013,15(6):499-504. [8] Weiner X,El Saman A,Ruger F,et al.Impact of surgical strategy on quality of life and radiological outcome in traumatic fractures of the thoracolumbar spine.Z Orthop Unfall.2013;151(3):264-271. [9] Kim YM, Kim DS,Choi ES,et al.Nonfusion method in thoracolumbar and lumbar spinal fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(2):170-176. [10] Tian NF,Wu YS,Zhang XL,et al.Fusion versus nonfusion for surgically treated thoracolumbar burst fractures:a meta-analysis. PLoS One.2013;8(5):e63995. [11] Wei FX,Liu SY,Liang CX,et al. Transpedicular fixation in management of thoracolumbar burst fractures: monosegmental fixation versus short-segment instrumentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(15): E714-720. [12] Lee GW, Jang SJ, Kim JD, et al. The efficacy of percutaneous long-segmental posterior fixation of unstable thoracolumbar fracture with partial neurologic deficit. Asian Spine J.2013;7(2):81-90. [13] Jiang SD, Wu QZ, Lan SH,et al. Reliability of the measurement of thoracolumbar burst fracture kyphosis with Cobb angle, Gardner angle, and sagittal index. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132(2): 221-225. [14] 曾忠友,张建乔,金才益,等.经伤椎置钉椎弓根螺钉系统固定治疗胸腰椎骨折2年以上随访结果[J].中国骨伤,2012, 25(2):128-132. [15] Yang M,Ding GZ,Xu ZJ.Surgical Outcome in Thoracolumbar Fractures Managed by Short-segment Pedicle Instrumentation. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2014;43(1):24-32. [16] Yang H,Shi JH,Ebraheim M, et al.Outcome of thoracolumbar burst fractures treated with indirect reduction and fixation without fusion.Eur Spine J. 2011;20(3):380-386. [17] Hwang JH, Modi HN, Yang JH, et, al.Short segment pedicle screw fixation for unstable T11-L2 fractures: with or without fusion? A three-year follow-up study. Acta Orthop Belg. 2009;75(6):822-827. [18] 翁习生,徐宏光.胸腰椎骨折整复内固定后是否应植骨融合[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2002,12(5):328. [19] 张英泽,李宝俊,张奇,等.胸腰椎骨折椎弓根内固定术后失败原因探讨[J].中华骨科杂志,2009,29(1):7-11. [20] Wei FX,Liu SY,Liang CX,et al.Transpedicular fixation in management of thoracolumbar burst fractures: monosegmental fixation versus short-segment instrumentation.Spine.2010;35(15):E714-E720. [21] 曾忠友.经伤椎固定胸腰椎骨折的治疗进展[J].脊柱外科杂志,2013,11(1):57-60. [22] Norton RP,Milne EL,Kaimrajh DN,et al.Biomechanical analysis of four- versus six-screw constructs for short-segment pedicle screw and rod instrumentation of unstable thoracolumbar fractures. Spine J. 2014;14(8): 1734-1739. |