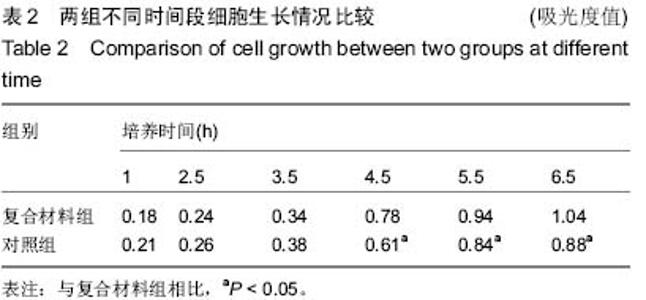
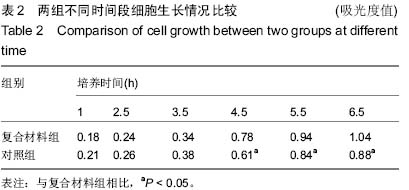
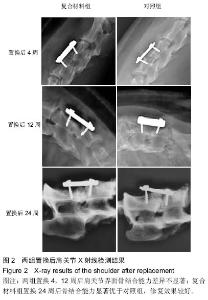
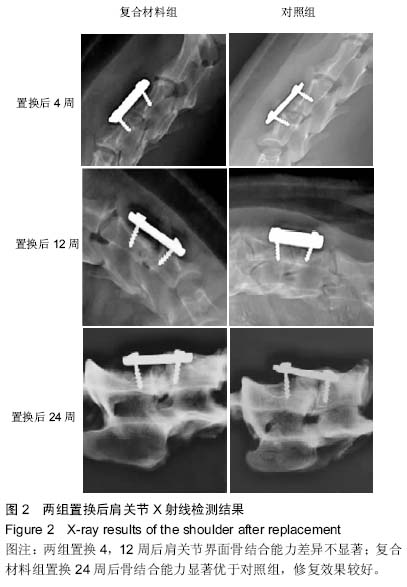
| [1] 孟纯阳,安洪,蒋电明,等.新型纳米骨重建和修复材料基磷灰石/聚酰胺体内植入的生物相容性及安全性[J].中国临床康复,2004, 8(29):6330-6333.
[2] 李鸿,李玉宝,严永刚,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66多孔材料制备和生物安全性初步评价[J].生物医学工程杂志,2008,25(5): 1126-1129.
[3] 相子民,应大君,吴雪晖,等.自制异体骨腰椎间融合器的力学测评[J].第三军医大学学报,2007,29(12):1237-1239.
[4] Ito Z, Matsuyama Y, Sakai Y, et al. Bone union rate with autologous iliac bone versus local bone graft in posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(21): E1101-E1105.
[5] 殷小平,夏忠斌,游建友,等.血管内支架成形术治疗颅内动脉狭窄性短暂性脑缺血发作的疗效观察[J].临床神经病学杂志,2011, 24(3):188-190.
[6] Watanabe K, Yamazaki A, Morita O, et al. Clinical outcomes of posterior lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar foraminal stenosis: preoperative diagnosis and surgical strategy. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2011;24(3):137-141.
[7] Bansal S, Chauhan V, Sharma S, et al. Evaluation of hydroxyapatite and beta-tricalcium phosphate mixed with bone marrow aspirate as a bone graft substitute for posterolateral spinal fusion.Indian J Orthop. 2009;43(3): 234-239.
[8] 王高举,王清,王松,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66复合生物活性人工椎体在骨质疏松性胸腰椎爆裂骨折前路手术中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(38): 7579- 7582.
[9] 何斌,蒋电明,欧云生,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66人工椎体置入与椎体重建[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(47):8889-8892.
[10] 嵇伟平,韩培,蒋垚.纳米骨植入材料表面结构及作用机制研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2007,28(2):125-127.
[11] 贾德民,古菊,周扬波,等.新型改性纳米碳酸钙对天然橡胶的补强作用[J].华南理工大学学报:自然科学版,2004,32(3): 94-97.
[12] 孙水升,李春忠,张玲,等.纳米二氧化硅颗粒表面设计及其填充聚氯乙烯复合材料的性能[J].高校化学工程学报,2006,5(20): 798-804.
[13] 李颖华,曹丽云,黄剑峰,等.生物医用纳米羟基磷灰石的性质及其制备[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(41): 8143-8146.
[14] 王海斌,赫淑清,赵冬梅,等.羧甲基壳聚糖/纳米羟基磷灰石复合支架材料的制备及生物安全性[J].复合材料学报,2008, 25(6):88-92.
[15] 陈琦,王大平,刘建全.纳米羟基磷灰石-聚乳酸复合材料制备及生物相容性研究[J].国际骨科杂志,2010,31(6):349-351.
[16] 张凯,王大平,刘建全.仿生增强型纳米羟基磷灰石-聚乳酸复合支架研究现状[J].国际骨科杂志,2010,31(6):352-357.
[17] 强小虎,张杰.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚乳酸复合材料的性能测试[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(5):911-913.
[18] Neuendorf RE, Saiz E, Tomsia AP, et al. Adhesion between biodegradable polymers and hudroxyapatite: relevance to synthetic bone-like materials and tissue engineering scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2008,4(5):1288-1296.
[19] Niu X,Fan Y,Liu X,et al. Repair of bone defect in femoral condyle using microencapsulated chitosan, nanohydroxyapatite/collagen and poly (L-lactide)-based microsphere scaffold delivery system. Artif Organs. 2011; 35(7):1525-1594.
[20] Kruyt MC,de Bruijn JD,Yuan H,et al. Optimization of bone tissue engingeering in goats: a preoperative seeding method using cryopreserved cells and localized bone formation in calcium phosphatescaffolds. Transplantation. 2004;77(3):359-365.
[21] 张凯,王大平,朱伟民,等.骨髓间充质干细胞与纳米羟基磷灰石支架材料题外相容性研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2011, 29(2):213-217.
[22] Phipps MC, Clem WC, Catledge SA, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell responses to bone-mimetic electrospun matrices composed of poly caprolactone, collagenⅠand nanoparticulate hydroxyapatite. PLoS One. 2011;6(2): e16813.
[23] 戚孟春,邓久鹏,董伟,等.骨髓间充质干细胞与支架材料nHA/PA66复合培养生物活性研究[J].口腔医学研究,2011, 26(6):805-808.
[24] 代震宇,李军,赵增辉,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚氨基酸符合材料生物安全性评价[J].第三军医大学学报,2010,32(21):2294- 2298.
[25] 李鸿,李玉宝.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66多孔材料制备和生物安全性初步评价[J].生物医学工程杂志,2008,25(5): 1126- 1129.
[26] Nandi SK, Kundu B, Ghosh SK, et al. Efficacy of nano-hydroxyapatite prepared by an aqueous solution combustion technique in healing bone defects of goat. J Vet Sci. 2008;9(2):183-191.
[27] Xu Q, Lu HY, Zhang JC, et al. Tissue engineering scaffold material of porous nanohydroxyapatite/polyamide 66. Int J Nanomed. 2010;5:331-335.
[28] Smith IO, McCabe LR, Baumann MJ. MC3T3-E1 osteoblast attachment and proliferation on porous hydroxyapatite scaffolds fabricated with nanophase powder. Int J Nanomed. 2006;1(2):189-194.
[29] 谢红军,王银龙,周健,等.纳米羟基磷灰石复合骨髓基质细胞修复兔股骨缺损的实验研究[J].口腔医学,2008,28(3):154-156.
[30] Steinbrech DS, Mehrara BJ, Rowe NM, et al. Gene expression of TGF-beta, TGF-beta receptor, and extracellular matrix proteins during membranous bone healing in rats. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000;105(6): 2028- 2038.
[31] 胡波,杨述华,肖德明,等.血管内皮生长因子复合纳米羟基磷灰石人工骨修复兔桡骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008,12(32):6209-6212.
[32] 刘阳,朱立新,王庆波,等.可注射性n-HA/CS-BMSCs复合物修复兔股骨缺损的实验研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2010, 28(4):421-429.
[33] 蒋电明,权正学,欧云生.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66复合生物活性人工椎体在胸腰椎爆裂骨折中的应用[J].中华创伤杂志, 2006,12:884-887.
[34] 蒋电明,权正学,黄伟.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66复合生物活性人工椎板的初步临床应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2007, 5:441-444.
[35] 代震宇,李军,蒋电明.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚氨基酸复合材料生物安全性评价[J].第三军医大学学报,2010,21:2294-2299.
[36] 许勇,朱立新,田京.纳米羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖复合材料与兔骨髓间充质干细胞的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009,13(8):1423-1426.
[37] 黄谦,吴涛,梁杰.全骨髓培养法和密度梯度离心法分离hBMSCs的比较研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2009,23(11): 1360-1364. |