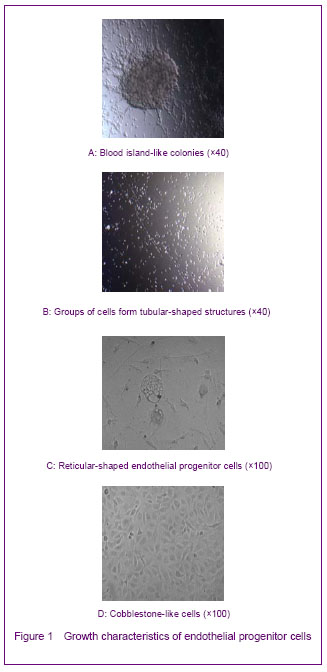
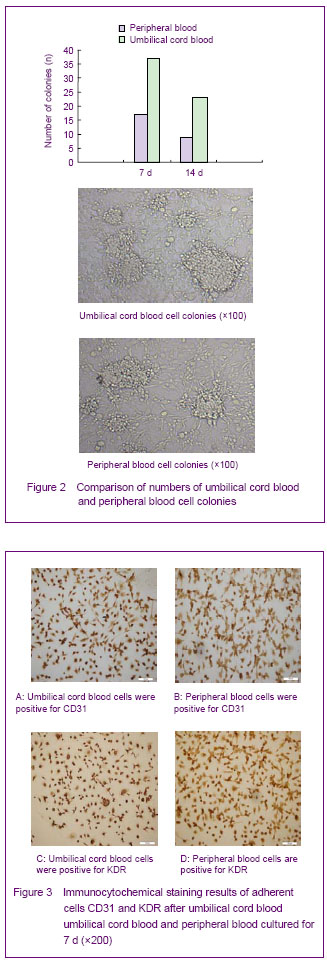
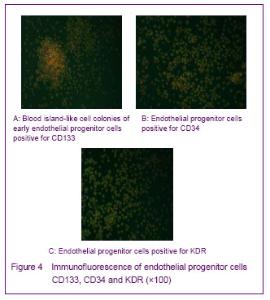
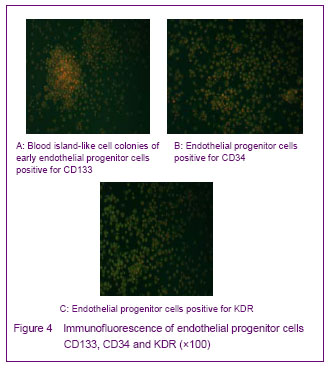
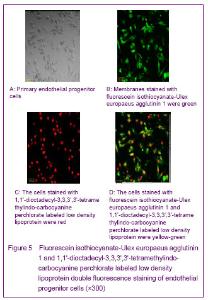
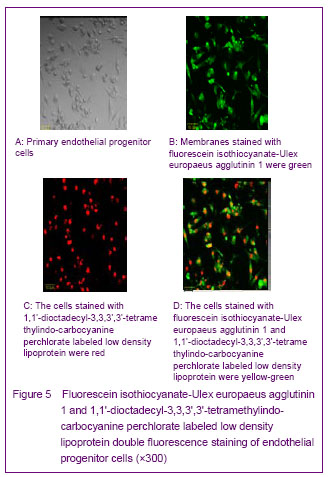
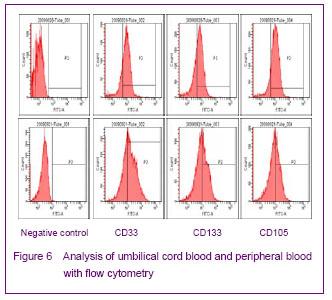
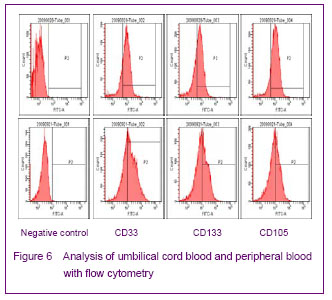
| [1] Yip HK, Chang LT, Chang WN, et al. Level and value of circulating endothelial progenitor cells in patients after acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2008;39(1):69-74.[2] He TR, Leslie AS, Harrington S, et al. Transplantation of circulating endothelial progenitor cells restores endothelial function of denuded rabbit carotid arteries transplantation. Stroke. 2004;35(10):2378-2384.[3] Patrick AU, Laurence MD, Dan GD, et al. Differential in vivo potential of endothelial progenitor cells from human umbilical cord blood and adult peripheral blood to form functional long-lasting vessels. Blood. 2008;111(3):1302-1305.[4] Thored P, Wood J, Arvidsson A, et al. Long-term neuroblast migration along blood vessels in an area with transient angiogenesis and increased vascularization after stroke. Stroke. 2007;38(11):3032-3039.[5] Urao N, Inomata H, Razvi M, et al. Role of nox22based NADPH oxidase in bone marrow and progenitor cell function involved in neovascularization induced by hindlimb ischemia. Circ Res. 2008;103:212-220.[6] Asahara T, Murohara T, Sullivan A, et al. Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis. Science.1997;275:964-967.[7] Risau W, Flamme I. Vasculogenesis. Ann Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1995;11:73-91.[8] Tilling L, Chowienczyk P, Clapp B. Progenitors in motion: mechanisms of mobilization of endothelial progenitor cells. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2009;68(4):484-492.[9] Fei XH, Ye HH, Ruan LM, et al. Gender differences in adult circulating endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) and effect of estradiol on arousing of EPCs in vitro. Zhonghua Bingli Shengli Zazhi. 2012;28(3):393-397.[10] Ge XB, Hu HJ, Deng FS, et al. SDF-1 combined with peripheral blood endothelial progenitor cells transplantation for the treatment of hindlimb ischemia in nude mice. Zhonghua Putong Waike Zazhi. 2011;26(7):584-588.[11] Ahrens I, Domeij H, Topcic D, et al. Successful in vitro expansion and differentiation of cord blood derived CD34+ cells into early endothelial progenitor cells reveals highly differential gene expression. PloS ONE. 2011;6(8): 23210.[12] Wyler von Ballmoos M, Yang Z, Völzmann J, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells induce a phenotype shift in differentiated endothelial cells towards PDGF/ PDGFβ axis-mediated angiogenesis. PloS ONE. 2010;5(11):e14107.[13] Zhang LJ, Liu WX, Chen YD, et al. Proliferation, migration and apoptosis activities of endothelial progenitor cells in acute coronary syndrome. Chin Med J (Engl). 2010; 123(19):2655-2661.[14] Rehman J, Li J, Orschell CM, et al. Peripheral blood endothelial progenitor cells\are derived from monocyte/macrophages and secrete angiogenic growth factors. Circulation. 2003;107:1164-1169.[15] Gehling UM, Ergun S, Schumacher U, et al. In vitro differentiation of endothelial cells from AC1332positive p rogenitor cells. Blood. 2000;95:3106-3112.[16] Hirschi KK,Ingram DA ,Yoder MC. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2008,28:1584.[17] Hristov M, Weber C. Endothelial progenitor cells: characterization,pathophysiology, and possible clinical relevance. J Cell Mol Med. 2004;8:498-508.[18] Choi K, Kennedy M, Kazarov A, et al. A common precursor for hematopoietic and endothelial cells. Development. 1998;125:725-732.[19] Yin AH, Miraglia S, Zanjani ED, et al. AC133, a novel marker for human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Blood. 1997;90:5002-5012.[20] Peichev M, Naiyer AJ, Pereira D, et al. Expression of VEGFR-2 and AC133 by circulating human CD34(+) cells identifies a population of functional endothelial precursors. Blood. 2000;95:952-958.[21] Hur J, Yoon CH, Kim HS, et al. Characteristic of two types of endothelial progenitor cells and their different contributions to neovasculogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004;24:288-293.[22] Yao G, Liu ZH, Zheng C, et al. Evaluation of renal vascular lesions using circulating endothelial cell in patients with lupus nephritis. Rheumatology(Oxford). 2008;47:432-436. [23] Bagley RG, Rouleau C, St Martin T, et al. Human endothelial precursor cells express tumor endothelial marker 1/endosialin/CD248. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008;7: 2536-2546. |