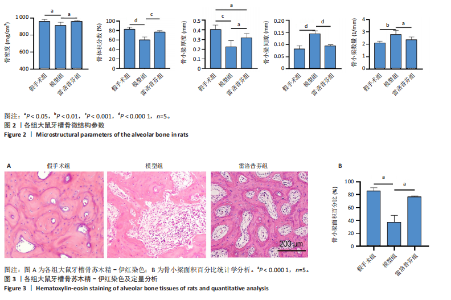
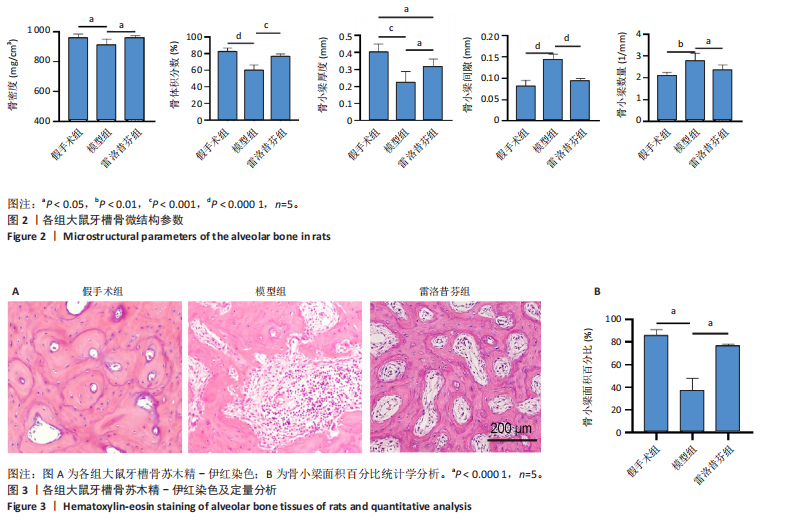
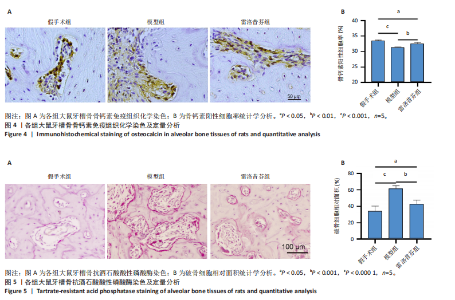
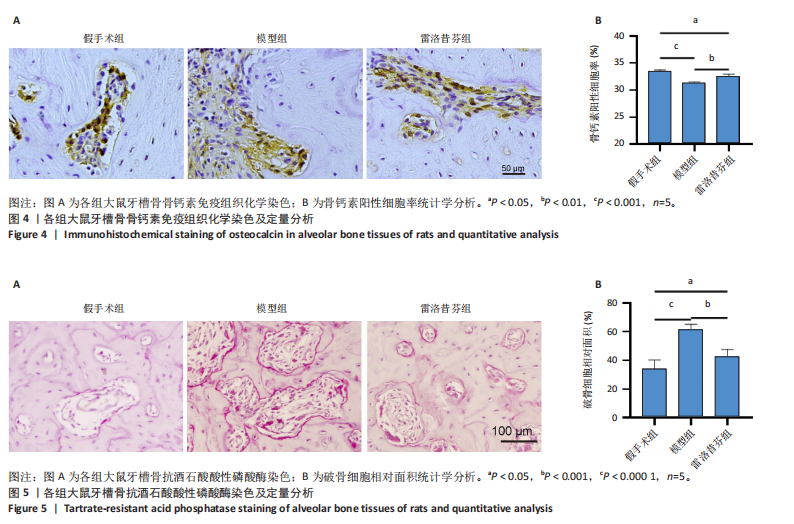
[1] GAO Y, CHEN N, FU Z, et al. Progress of Wnt Signaling Pathway in Osteoporosis. Biomolecules. 2023;13(3):483.
[2] 何海洋,杨嘉玲,雷迅.绝经后女性骨质疏松症患病率及影响因素的Meta 分析[J].中国全科医学,2024,27(11):1370-1379.
[3] 谢丽华,柴昊,叶云金,等.续苓健骨颗粒治疗肾虚血瘀型绝经后骨质疏松症的疗效及转录机制研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2022, 28(4):558-561,600.
[4] WU D, CLINE-SMITH A, SHASHKOVA E, et al. T-Cell Mediated Inflammation in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Front Immunol. 2021; 12:687551.
[5] 代庆刚,房兵,张鹏,等.不同去势时间大鼠牙槽骨微结构变化的Micro-CT 研究[J].上海口腔医学,2014,23(6):641-645.
[6] DAI QG, ZHANG P, WU YQ, et al. Ovariectomy induces osteoporosis in the maxillary alveolar bone: an in vivo micro-CT and histomorphometric analysis in rats. Oral Dis. 2014;20(5):514-520.
[7] CHANG HJ, LEE SJ, YONG TH, et al. Deep Learning Hybrid Method to Automatically Diagnose Periodontal Bone Loss and Stage Periodontitis. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):7531.
[8] ARCEO-MENDOZA RM, CAMACHO PM. Postmenopausal Osteoporosis: Latest Guidelines. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2021;50(2):167-178.
[9] NOSHADI N, BONYADIAN A, ZARIAN S, et al. The effect of raloxifene supplementation on blood pressure and Apo-lipoproteins in postmenopausal women: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2024;175:106912.
[10] MOHD-DOM T, AYOB R, MOHD-NUR A, et al. Cost analysis of periodontitis management in public sector specialist dental clinics. BMC Oral Health. 2014;14:56.
[11] MOHD DOM TN, AYOB R, ABD MUTTALIB K, et al. National Economic Burden Associated with Management of Periodontitis in Malaysia. Int J Dent. 2016;2016:1891074.
[12] KIM J, MUNSTER PN. Estrogens and breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2025; 36(2):134-148.
[13] BARZAMAN K, KARAMI J, ZAREI Z, et al. Breast cancer: Biology, biomarkers, and treatments. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;84:106535.
[14] GALLANT MA, BROWN DM, HAMMOND M, et al. Bone cell-independent benefits of raloxifene on the skeleton: a novel mechanism for improving bone material properties. Bone. 2014;61:191-200.
[15] LIU Q, MA L, CHEN F, et al. Raloxifene-driven benzothiophene derivatives: Discovery, structural refinement, and biological evaluation as potent PPARγ modulators based on drug repurposing. Eur J Med Chem. 2024;269:116325.
[16] MOSHI MR, NICOLOPOULOS K, STRINGER D, et al. The Clinical Effectiveness of Denosumab (Prolia®) for the Treatment of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women, Compared to Bisphosphonates, Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERM), and Placebo: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Calcif Tissue Int. 2023;112(6):631-646.
[17] HAO X, WANG Y, HOU MJ, et al. Raloxifene Prevents Chemically-Induced Ferroptotic Neuronal Death In Vitro and In Vivo. Mol Neurobiol. 2025;62(3):3934-3955.
[18] BERMAN AG, DAMRATH JG, HATCH J, et al. Effects of Raloxifene and tibial loading on bone mass and mechanics in male and female mice. Connect Tissue Res. 2022;63(1):3-15.
[19] MOTLANI G, MOTLANI V, ACHARYA N, et al. Novel Advances in the Role of Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators in Hormonal Replacement Therapy: A Paradigm Shift. Cureus. 2023;15(11):e49079.
[20] 李剑平,刘培.雷洛昔芬对骨质疏松性颌骨骨折大鼠骨折愈合及 OPG/RANKL/RANK 系统的影响[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2021, 19(3):213-216.
[21] 杨正祥,李航,李鲲.雷洛昔芬对牙周炎合并系统性绝经后骨质疏松症小鼠模型局部牙槽骨破坏的影响[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2020,18(5):407-411.
[22] DEMIRBAŞ AE, MOHSEN F, TOPAN C, et al. The Combined Therapy of Teriparatide and Raloxifene Improves Osseointegration of Dental Implants in the Osteoporotic Rabbit Model. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2024;(3):435-445.
[23] TAŃSKI W, KOSIOROWSKA J, SZYMAŃSKA-CHABOWSKA A. Osteoporosis - risk factors, pharmaceutical and non-pharmaceutical treatment. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021;25(9):3557-3566.
[24] 郭峰,李正南,刘晋平,等.六月龄大鼠去卵巢后建立骨质疏松症模型的可行性[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(24):4459-4462.
[25] 魏伟,吴希美,李元建.药理实验方法学[M].4版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2010:56-57.
[26] QIAN H, JIA J, YANG Y, et al. A Follicle-Stimulating Hormone Exacerbates the Progression of Periapical Inflammation Through Modulating the Cytokine Release in Periodontal Tissue. Inflammation. 2020;43(4): 1572-1585.
[27] CONDI FLF, FUCHS LFP, CARVALHO KC, et al. Treatment with Raloxifene Induces the Expression of Kisspeptin, Insulin, and Androgen Receptors in Bones of Castrated Adult Female Rats. Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2024;59(2):e228-e234.
[28] YUAN C, LIANG Y, ZHU K, et al. Clinical efficacy of denosumab, teriparatide, and oral bisphosphonates in the prevention of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):447.
[29] LIAO X, DENG J, DU L, et al. Effect of Raloxifene Treatment on Apolipoproteins and Lipoprotein(a) Concentrations in Postmenopausal Women: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Clin Ther. 2024;46(10):799-807.
[30] RIZZOLI R. Postmenopausal osteoporosis: Assessment and management. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;32(5):739-757.
[31] LAMA A, SANTORO A, CORRADO B, et al. Extracorporeal shock waves alone or combined with raloxifene promote bone formation and suppress resorption in ovariectomized rats. PLoS One. 2017;12(2): e0171276.
[32] 王丽随,范哲华,陈海英.雷洛昔芬联合仙灵骨葆对骨质疏松骨微结构和生物力学性能的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(11): 1429-1432.
[33] ICHIMARU R, TOMINARI T, YOSHINOUCHI S, et al. Raloxifene reduces the risk of local alveolar bone destruction in a mouse model of periodontitis combined with systemic postmenopausal osteoporosis. Arch Oral Biol. 2018;85:98-103.
[34] TANAKA M, EJIRI S, TOYOOKA E, et al. Effects of ovariectomy on trabecular structures of rat alveolar bone. J Periodontal Res. 2002; 37(2):161-165.
[35] MILLER SC, WRONSKI TJ. Long-term osteopenic changes in cancellous bone structure in ovariectomized rats. Anat Rec. 1993;236(3):433-441.
[36] POSRITONG S, HONG JM, ELENISTE PP, et al. Pyk2 deficiency potentiates osteoblast differentiation and mineralizing activity in response to estrogen or raloxifene. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2018;474:35-47.
[37] BROMMAGE R. New Targets and Emergent Therapies for Osteoporosis. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2020;262:451-473.
[38] ALVA-CHAVARRÍA D, SOTO-NÚÑEZ M, FLORES-SOTO E, et al. Hemostatic Effects of Raloxifene in Ovariectomized Rats. Life (Basel). 2023;13(7):1612.
[39] SHIN S, HONG N, RHEE Y. A randomized controlled trial of the effect of raloxifene plus cholecalciferol versus cholecalciferol alone on bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with osteopenia. JBMR Plus. 2024;8(7):ziae073.
[40] 马学智,马勇,郭杨.补肾健脾活血法治疗绝经后骨质疏松症疗效的Meta分析[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(4):527-535.
[41] JAYUSMAN PA, NASRUDDIN NS, BAHARIN B, et al. Overview on postmenopausal osteoporosis and periodontitis: The therapeutic potential of phytoestrogens against alveolar bone loss. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1120457.
|