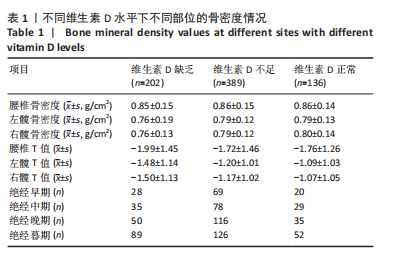
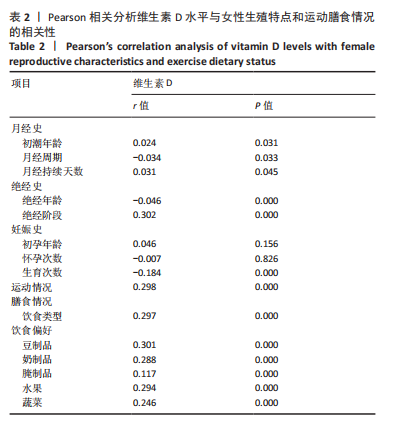
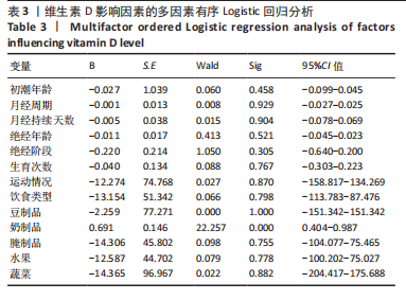
[1] 王永炫,李梅,章振林,等.《原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2022)》要点解读[J].协和医学杂志,2023,14(6):1203-1207.
[2] 许晓宇,安小春.绝经后骨质疏松发生机制的研究进展[J].滨州医学院学报,2023,46(1):77-80.
[3] 黄秀红,翟素平.原发性骨质疏松患者血清25-羟维生素D表达与骨密度的关系研究[J].临床医学工程,2021,28(12):1737-1738.
[4] MOGIRE RM, MOROVAT A, MURIUKI JM, et al. Prevalence and predictors of vitamin D deficiency in young African children. BMC Med. 2021;19(1):115.
[5] BRUYÈRE O, SLOMIAN J, BEAUDART C, et al. Prevalence of vitamin D inadequacy in European women aged over 80 years. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2014;59(1):78-82.
[6] MISRA M, PACAUD D, PETRYK A, et al.Drug and Therapeutics Committee of the Lawson Wilkins Pediatric Endocrine Society. Vitamin D deficiency in children and its management: review of current knowledge and recommendations. Pediatrics. 2008;122(2):398-417.
[7] LI B, JIANG C, ZHAN X. Combined Therapy of Yishen Zhuanggu Decoction and Caltrate D600 Alleviates Postmenopausal Osteoporosis by Targeting FoxO3a and Activating the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022;2022:7732508.
[8] RAI AD, SHERPA ML, SINGH A, et al.Bone Alkaline Phosphatase and Urine Hydroxyproline Assay in Pre and Postmenopausal Women in the State of Sikkim and its Correlation with Bone Mineral Density. J Midlife Health. 2021;12(4):304-309.
[9] HSU SL, CHOU WY, HSU CC, et al. Shockwave Therapy Modulates the Expression of BMP2 for Prevention of Bone and Cartilage Loss in the Lower Limbs of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis Rat Model. Biomedicines. 2020;8(12):614.
[10] ADAS-OKUMA MG, MAEDA SS, GAZZOTTI MR, et al. COPD as an independent risk factor for osteoporosis and fractures. Osteoporos Int. 2020;31(4):687-697.
[11] CATALANO A, BELLONE F, SANTORO D, et al. Vitamin D Boosts Alendronate Tail Effect on Bone Mineral Density in Postmenopausal Women with Osteoporosis. Nutrients. 2021;13(6):1878.
[12] MA R, WU M, LI Y, et al. The use of bone turnover markers for monitoring the treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal females undergoing total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):195.
[13] RECKER R, LAPPE J, DAVIES K,et al.Characterization of perimenopausal bone loss: a prospective study. J Bone Miner Res. 2000;15(10): 1965-1973.
[14] 黄琪仁.钙、维生素D与原发性骨质疏松症[J].中国实用妇科与产科杂志,2014,30(5):336-340.
[15] 刘斌,董芬,任晓岚,等.甘肃省20岁~80岁和绝经后女性骨质疏松症患病影响因素分析[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(5):656-663.
[16] HEIDARI B, HOSSEINI R, JAVADIAN Y, et al. Factors affecting bone mineral density in postmenopausal women. Arch Osteoporos. 2015; 10:15.
[17] VAN CROMPHAUT SJ, RUMMENS K, STOCKMANS I, et al. Intestinal calcium transporter genes are upregulated by estrogens and the reproductive cycle through vitamin D receptor-independent mechanisms. J Bone Miner Res. 2003;18(10):1725-1736.
[18] LIEL Y, SHANY S, SMIRNOFF P, et al.Estrogen increases 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D receptors expression and bioresponse in the rat duodenal mucosa. Endocrinology. 1999;140(1):280-285.
[19] 朱玲龑,冉利梅,聂四平,等.677例围绝经期女性维生素D3水平及其影响因素[J].贵州医科大学学报,2017,42(11):1321-1326.
[20] TANABE S, YANO S, MISHIMA S, et al.Physical inactivity and vitamin D deficiency in hospitalized elderlies. J Bone Miner Metab. 2019;37(5): 928-934.
[21] 张静,匡晓梅,罗小婉.中山市绝经后妇女骨质疏松症患病状况调查分析[J].临床医学工程,2023,30(5):717-718.
[22] 李得利,吕珊珊,杜伟锋.541例围绝经期和绝经后妇女骨质疏松状况及影响因素分析[J].中国妇幼保健,2022,37(24):4691-4694.
[23] PENG J, DONG Z, HUI Z, et al. Bone Sclerostin and Dickkopf-related protein-1 are positively correlated with bone mineral density, bone microarchitecture, and bone strength in postmenopausal osteoporosis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):480.
[24] 陈艳林.运动对绝经后妇女骨质疏松的影响及相关因素调查[J].中国妇幼保健,2022,37(18):3434-3437.
[25] 卢登攀,刘芳.绝经后妇女骨质疏松症饮食危险因素研究进展[J].中国预防医学杂志,2018, 19(6):458-462.
[26] 吴立兵,谭凡,万华兵.鄂西北地区正常人群骨质疏松危险因素的相关研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2016,22(1):107-110.
[27] 杨秀琳.生活方式调整预防老年绝经后骨质疏松的研究进展[J].中国老年学杂志,2016,36(24):6312-6314.
[28] 王素萍.骨质疏松与盐摄入[J].国外医学(医学地理分册),2001, 22(3):120-122.
[29] 杨俊贤,李青南.高钠摄入与骨质疏松的关系[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2017,10(3):306-310.
[30] VAFA M, SOLTANI S, ZAYERI F, et al. The relationship between sodium intake and some bone minerals and osteoporosis risk assessment instrument in postmenopausal women. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2016;30:377.
[31] HUERTAS JR, RODRÍGUEZ LARA A, GONZÁLEZ ACEVEDO O, et al.[Milk and dairy products as vehicle for calcium and vitamin D: role of calcium enriched milks]. Nutr Hosp. 2019;36(4):962-973.
[32] 文海昭,梁绛槟,王立,等.北京市老年人骨质疏松的危险因素[J].中国老年学杂志,2022,42(6):1484-1486. |