Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (15): 2387-2393.doi: 10.12307/2022.596
Previous Articles Next Articles
Levels of histone modification in promoter of NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing protein 3 in synovial fibroblasts of osteoarthritis
Wang Jian, Gu Sanjun, Liu Yu, Zhao Kai, Li Haifeng
- Department of Joint Surgery, Wuxi Ninth Hospital Affiliated to Soochow University/Wuxi Ninth People’s Hospital/Wuxi Orthopedic Hospital, Wuxi 214000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2021-06-02Revised:2021-06-04Accepted:2021-07-24Online:2022-05-28Published:2022-01-06 -
Contact:Li Haifeng, Associate chief physician, Department of Joint Surgery, Wuxi Ninth Hospital Affiliated to Soochow University/Wuxi Ninth People’s Hospital/Wuxi Orthopedic Hospital, Wuxi 214000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Wang Jian, Master, Department of Joint Surgery, Wuxi Ninth Hospital Affiliated to Soochow University/Wuxi Ninth People’s Hospital/Wuxi Orthopedic Hospital, Wuxi 214000, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the Project of Wuxi Municipal Science and Technology Department, No. N20202041 (to LY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Jian, Gu Sanjun, Liu Yu, Zhao Kai, Li Haifeng. Levels of histone modification in promoter of NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing protein 3 in synovial fibroblasts of osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(15): 2387-2393.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
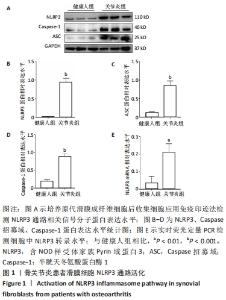
2.1 骨关节炎患者滑膜细胞NLRP3通路过度激活 为了明确骨关节炎患者滑膜细胞中NLRP3通路相关分子的表达水平,通过对临床手术获得的骨关节炎患者滑膜组织及非骨关节炎患者滑膜组织进行原代细胞培养,提取滑膜成纤维细胞样细胞中蛋白及RNA,通过免疫印迹及荧光定量PCR实验检测NLRP3、Caspase招募域和Casepase-1表达水平。结果发现,与非骨关节炎患者滑膜成纤维细胞样细胞相比,骨关节炎患者滑膜成纤维细胞样细胞中NLRP3、Caspase招募域、Caspase-1蛋白表达水平均显著增高(n=3,P < 0.001),见图1A-D。为进一步验证,通过实时荧光定量PCR实验检测NLRP3表达水平,发现骨关节炎患者滑膜成纤维细胞样细胞中NLRP3转录水平较非骨关节炎患者增高(0.03±0.02 vs. 0.21±0.03,n=4,P < 0.01),见图1E。结果提示,骨关节炎患者滑膜成纤维细胞样细胞中存在NLRP3过度激活。"
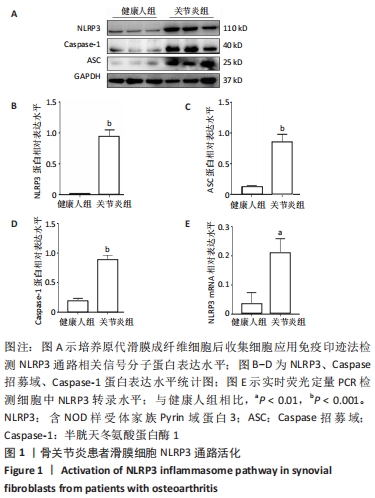
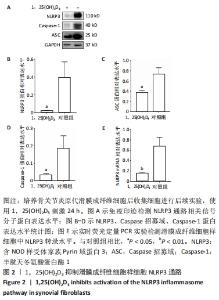
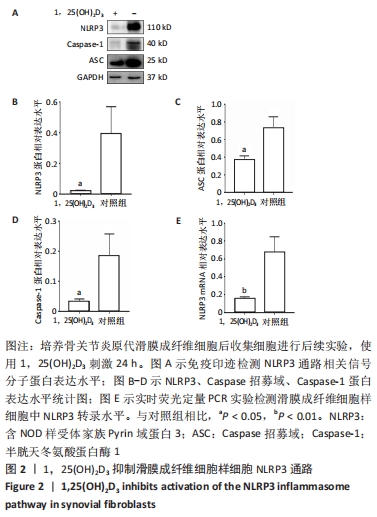
2.2 1,25(OH)2D3处理可以抑制骨关节炎患者滑膜成纤维细胞样细胞中NLRP3信号通路 研究显示,1,25(OH)2D3缺乏是导致骨关节炎的重要危险因素,有研究显示1,25(OH)2D3可以抑制类风湿性关节炎患者滑膜成纤维细胞样细胞中NLRP3信号通路活化[23],但是1,25(OH)2D3是否可以抑制骨关节炎患者滑膜成纤维细胞样细胞中NLRP3的表达水平尚不明确。为了探索1,25(OH)2D3在其中的作用,通过原代培养获得骨关节炎患者滑膜成纤维细胞样细胞,并使用终浓度为10-7 mol/L的1,25(OH)2D3刺激滑膜成纤维细胞样细胞,24 h后提取蛋白及RNA检测NLRP3相关通路分子的改变。结果显示,与对照组相比,1,25(OH)2D3处理可以抑制滑膜成纤维细胞样细胞中NLRP3、Caspase招募域及Caspase-1的蛋白表达水平(n=3,P < 0.05),见图2A-D;同时1,25(OH)2D3可明显抑制NLRP3分子的转录表达(0.03±0.01 vs. 0.18±0.04,n=3,P < 0.01),见图2E。"
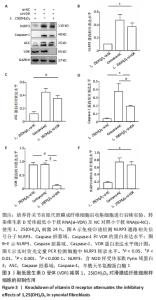
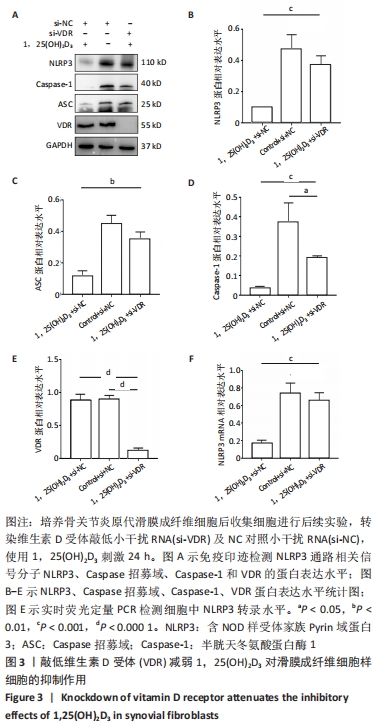
2.3 1,25(OH)2D3抑制滑膜成纤维细胞样细胞中NLRP3信号通路依赖于维生素D受体分子 1,25(OH)2D3调控下游靶点主要是通过与维生素D受体结合后发挥转录调控作用[24]。为了进一步探索1,25(OH)2D3调控NLRP3通路是否依赖于维生素D受体,通过使用小干扰RNA敲低滑膜成纤维细胞样细胞中维生素D受体的水平。通过免疫印迹检测NLRP3、Caspase招募域及Caspase-1的表达水平,结果发现,敲低滑膜成纤维细胞样细胞内维生素D受体的表达后,1,25(OH)2D3处理无法抑制滑膜成纤维细胞样细胞内NLRP3、Caspase招募域及Caspase-1分子的蛋白表达水平,这提示1,25(OH)2D3抑制滑膜成纤维细胞样细胞中NLRP3信号通路依赖于维生素D受体分子。为了进一步明确1,25(OH)2D3抑制NLRP3转录表达是否依赖于维生素D受体,通过实时荧光定量PCR实验发现,转染敲低维生素D受体之后,可以减少滑膜成纤维细胞样细胞内维生素D受体的表达水平,但是1,25(OH)2D3处理对滑膜成纤维细胞样细胞的维生素D受体表达似乎没有明显影响。 与1,25(OH)2D3组相比,维生素D受体敲低后1,25(OH)2D3抑制骨关节炎患者滑膜成纤维细胞样细胞中NLRP3表达作用明显减弱(n=3,P < 0.001);与对照组相比,维生素D受体敲低后,1,25(OH)2D3的抑制作用两者之间差异无显著性意义(n=3,P=0.1478),提示1,25(OH)2D3的抑制作用可能主要依赖于维生素D受体。同时,检测Caspase招募域分子,发现维生素D受体敲除也可以减弱1,25(OH)2D3的抑制作用(n=3,P < 0.001);检测Caspase-1分子也获得了同样的结论(n=3,P < 0.01);与对照组相比,1,25(OH)2D3抑制Caspase-1的作用,两者之间差异无显著性意义(n=3,P=0.0887)。见图3A-E。 通过实时荧光定量PCR实验结果发现,与si-NC组相比,敲低维生素D受体表达后1,25(OH)2D3抑制滑膜成纤维细胞样细胞NLRP3转录表达的作用减弱(n=3,P < 0.001),且与对照组之间无明显差异(n=3,P=0.2587),见图3F。综合上述结果,可以初步明确1,25(OH)2D3主要通过与维生素D受体结合后抑制NLRP3转录表达及下游信号通路的活化。"
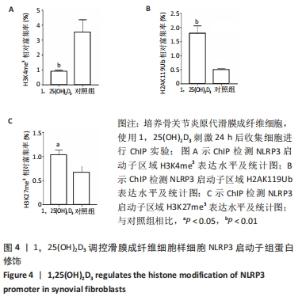
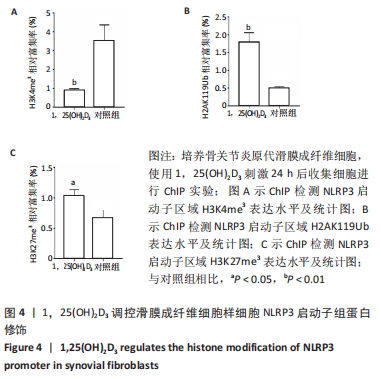
2.4 1,25(OH)2D3抑制滑膜成纤维细胞样细胞中NLRP3启动子激活性组蛋白修饰,促进抑制性组蛋白修饰 研究显示1,25(OH)2D3可影响影响下游靶基因的组蛋白修饰参与转录调控[25],为了进一步明确1,25(OH)2D3抑制NLRP3转录表达是否依赖于这一过程。对上述滑膜成纤维细胞样细胞刺激后,通过染色质免疫共沉淀检测NLRP3启动子区域的组蛋白H3K27三甲基化(H3K27me3)、H2AK119单泛素化(H2AK119Ub)及H3K4三甲基化(H3K4me3)。结果发现,1,25(OH)2D3刺激可以抑制NLRP3启动子区域H3K4me3的表达水平(n=3,P < 0.01),见图4A,H3K4me3修饰可以使染色质松散,激活转录表达。同时发现1,25(OH)2D3刺激可提高NLRP3启动子区域H3K27me3和H2AK119Ub的表达水平(n=3,P < 0.05,P < 0.001),见图4B,C,H2K37me3及H2AK119Ub修饰可以压缩染色质,抑制转录。上述结果提示1,25(OH)2D3抑制NLRP3转录可能是由于其抑制了NLRP3启动子区域激活性组蛋白修饰水平,并提高了抑制性组蛋白修饰的水平。"
| [1] CORYELL PR, DIEKMAN BO, LOESER RF. Mechanisms and therapeutic implications of cellular senescence in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021;17(1):47-57. [2] CHEN L, ZHENG JJY, LI G, et al. Pathogenesis and clinical management of obesity-related knee osteoarthritis: Impact of mechanical loading. J Orthop Translat. 2020;24:66-75. [3] MASON D, ENGLUND M, WATT FE. Prevention of posttraumatic osteoarthritis at the time of injury: Where are we now, and where are we going? J Orthop Res. 2021;39(6):1152-1163. [4] RAMASAMY B, MAGNE F, TRIPATHY SK, et al. Association of Gut Microbiome and Vitamin D Deficiency in Knee Osteoarthritis Patients: A Pilot Study. Nutrients. 2021;13(4):1272. [5] KULKARNI P, MARTSON A, VIDYA R, et al. Pathophysiological landscape of osteoarthritis. Adv Clin Chem. 2021;100:37-90. [6] WANG R, XU B. TGF-beta1-modified MSC-derived exosomal miR-135b attenuates cartilage injury via promoting M2 synovial macrophage polarization by targeting MAPK6. Cell Tissue Res. 2021;384(1):113-127. [7] CHU L, LIU X, HE Z, et al. Articular Cartilage Degradation and Aberrant Subchondral Bone Remodeling in Patients with Osteoarthritis and Osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res. 2020; 35(3):505-515. [8] HAN D, FANG Y, TAN X, et al. The emerging role of fibroblast-like synoviocytes-mediated synovitis in osteoarthritis: An update. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(17): 9518-9532. [9] ZHANG H, CAI D, BAI X. Macrophages regulate the progression of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020; 28(5):555-561. [10] HU W, CHEN Y, DOU C, et al. Microenvironment in subchondral bone: predominant regulator for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;80(4):413-422. [11] QIAO L, LI Y, SUN S. Insulin Exacerbates Inflammation in Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes. Inflammation. 2020;43(3):916-936. [12] YOSHITOMI H. Regulation of Immune Responses and Chronic Inflammation by Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1395. [13] ZHANG G, GU M, XU Y, et al. A comprehensive analysis on the effects of 1,25(OH)2D3 on primary chondrocytes cultured from patients with osteoarthritis. Gene. 2020;730:144322. [14] AMINI KADIJANI A, BAGHERIFARD A, MOHAMMADI F, et al. Association of Serum Vitamin D with Serum Cytokine Profile in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis. Cartilage. 2021:19476035211010309. [15] SUN HQ, YAN D, WANG QN, et al. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 attenuates disease severity and induces synoviocyte apoptosis in a concentration-dependent manner in rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis by inactivating the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. J Bone Miner Metabol. 2019;37(3):430-440. [16] GU X, GU B, LV X, et al. 1, 25-dihydroxy-vitamin D3 with tumor necrosis factor-alpha protects against rheumatoid arthritis by promoting p53 acetylation-mediated apoptosis via Sirt1 in synoviocytes. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7(10):e2423. [17] FENG X, LV C, WANG F, et al. Modulatory effect of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on IL1 beta -induced RANKL, OPG, TNF alpha , and IL-6 expression in human rheumatoid synoviocyte MH7A. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013;2013:160123. [18] DANKERS W, GONZALEZ-LEAL C, DAVELAAR N, et al. 1,25(OH)2D3 and dexamethasone additively suppress synovial fibroblast activation by CCR6(+) T helper memory cells and enhance the effect of tumor necrosis factor alpha blockade. Arthrit Res Ther. 2018;20(1):212. [19] QIN Q, LIU H, SHOU J, et al. The inhibitor effect of RKIP on inflammasome activation and inflammasome-dependent diseases. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021; 18(4):992-1004. [20] AN S, HU H, LI Y, et al. Pyroptosis Plays a Role in Osteoarthritis. Aging Dis. 2020; 11(5):1146-1157. [21] ZHAO LR, XING RL, WANG PM, et al. NLRP1 and NLRP3 inflammasomes mediate LPS/ATPinduced pyroptosis in knee osteoarthritis. Mol Me Rep. 2018;17(4):5463-5469. [22] ZU Y, MU Y, LI Q, et al. Icariin alleviates osteoarthritis by inhibiting NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):307. [23] XIN L, CHE B, ZHAI B, et al. 1,25-Dihydroxy Vitamin D3 Attenuates the Oxidative Stress-Mediated Inflammation Induced by PM2.5via the p38/NF-kappaB/NLRP3 Pathway. Inflammation. 2019;42(2):702-713. [24] CARLBERG C. Vitamin D Signaling in the Context of Innate Immunity: Focus on Human Monocytes. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2211. [25] ZHANG H, KHOA LTP, MAO F, et al. MLL1 Inhibition and Vitamin D Signaling Cooperate to Facilitate the Expanded Pluripotency State. Cell Rep. 2019;29(9): 2659-2671.e2656. [26] ZHANG Z, HUANG C, JIANG Q, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of osteoarthritis in China (2019 edition). Ann Trans Med. 2020;8(19):1213. [27] DE LANGE-BROKAAR BJ, IOAN-FACSINAY A, VAN OSCH GJ, et al. Synovial inflammation, immune cells and their cytokines in osteoarthritis: a review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(12):1484-1499. [28] LIU S, CAO C, ZHANG Y, et al. PI3K/Akt inhibitor partly decreases TNF-alpha-induced activation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in osteoarthritis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):425. [29] ROEMER FW, GUERMAZI A, HUNTER DJ, et al. The association of meniscal damage with joint effusion in persons without radiographic osteoarthritis: the Framingham and MOST osteoarthritis studies. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2009; 17(6):748-753. [30] BENITO MJ, VEALE DJ, FITZGERALD O, et al. Synovial tissue inflammation in early and late osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64(9):1263-1267. [31] YANG CR, SHIH KS, LIOU JP, et al. Denbinobin upregulates miR-146a expression and attenuates IL-1beta-induced upregulation of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expressions in osteoarthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. J Mol Med. 2014;92(11):1147-1158. [32] CARLBERG C, MUNOZ A. An update on vitamin D signaling and cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020.S1044-579X(20)30114-0. [33] MALLUCHE HH, HENRY H, MEYER-SABELLAK W, et al. Effects and interactions of 24R,25(OH)2D3 and 1,25(OH)2D3 on bone. Am J Physiol. 1980;238(5):E494-498. [34] KELLEY N, JELTEMA D, DUAN Y, et al. The NLRP3 Inflammasome: An Overview of Mechanisms of Activation and Regulation. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(13):3328. [35] RATHINAM VA, FITZGERALD KA. Inflammasome Complexes: Emerging Mechanisms and Effector Functions. Cell. 2016;165(4):792-800. [36] SUTTERWALA FS, HAASKEN S, CASSEL SL. Mechanism of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2014;1319(1):82-95. [37] CAO R, MA Y, LI S, et al. 1,25(OH)2 D3 alleviates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis via inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation. J Leukoc Biol. 2020;108(1):283-295. [38] TULK SE, LIAO KC, MURUVE DA, et al. Vitamin D(3) metabolites enhance the NLRP3-dependent secretion of IL-1beta from human THP-1 monocytic cells. J Cell Biochem. 2015;116(5):711-720. [39] POLI G, FABI C, BELLET MM, et al. Epigenetic Mechanisms of Inflammasome Regulation. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(16):5758. [40] LECOEUR H, PRINA E, ROSAZZA T, et al. Targeting Macrophage Histone H3 Modification as a Leishmania Strategy to Dampen the NF-kappaB/NLRP3-Mediated Inflammatory Response. Cell Rep. 2020;30(6):1870-1882.e1874. [41] LECOEUR H, ROSAZZA T, KOKOU K, et al. Leishmania amazonensis Subverts the Transcription Factor Landscape in Dendritic Cells to Avoid Inflammasome Activation and Stall Maturation. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1098. [42] UCKELMANN M, SIXMA TK. Histone ubiquitination in the DNA damage response. DNA Rep. 2017;56:92-101. [43] CHAN HL, MOREY L. Emerging Roles for Polycomb-Group Proteins in Stem Cells and Cancer. Trends Biochem Sci. 2019;44(8):688-700. [44] BARBOUR H, DAOU S, HENDZEL M, et al. Polycomb group-mediated histone H2A monoubiquitination in epigenome regulation and nuclear processes. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):5947. [45] FU B, WANG H, WANG J, et al. Epigenetic regulation of BMP2 by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 through DNA methylation and histone modification. PloS One. 2013;8(4):e61423. |
| [1] | Zhang Jichao, Dong Yuefu, Mou Zhifang, Zhang Zhen, Li Bingyan, Xu Xiangjun, Li Jiayi, Ren Meng, Dong Wanpeng. Finite element analysis of biomechanical changes in the osteoarthritis knee joint in different gait flexion angles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1357-1361. |
| [2] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [3] | Wang Baojuan, Zheng Shuguang, Zhang Qi, Li Tianyang. Miao medicine fumigation can delay extracellular matrix destruction in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1180-1186. |
| [4] | Xiang Xinjian, Liu Fang, Wu Liangliang, Jia Daping, Tao Yue, Zhao Zhengnan, Zhao Yu. High-dose vitamin C promotes the survival of autologous fat transplantation in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1242-1246. |
| [5] | Liu Dongcheng, Zhao Jijun, Zhou Zihong, Wu Zhaofeng, Yu Yinghao, Chen Yuhao, Feng Dehong. Comparison of different reference methods for force line correction in open wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 827-831. |
| [6] | Zhou Jianguo, Liu Shiwei, Yuan Changhong, Bi Shengrong, Yang Guoping, Hu Weiquan, Liu Hui, Qian Rui. Total knee arthroplasty with posterior cruciate ligament retaining prosthesis in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis with knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 892-897. |
| [7] | He Junjun, Huang Zeling, Hong Zhenqiang. Interventional effect of Yanghe Decoction on synovial inflammation in a rabbit model of early knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 694-699. |
| [8] | Lin Xuchen, Zhu Hainian, Wang Zengshun, Qi Tengmin, Liu Limin, Suonan Angxiu. Effect of xanthohumol on inflammatory factors and articular cartilage in a mouse mode of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 676-681. |
| [9] | Liu Yiyi, Qiu Junqiang, Yi Longyan, Zhou Cailiang. Effect of resistance training on interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein in middle-age and elderly people: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 804-812. |
| [10] | Xu Lei, Han Xiaoqiang, Zhang Jintao, Sun Haibiao. Hyaluronic acid around articular chondrocytes: production, transformation and function characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 768-773. |
| [11] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [12] | Liu Shaohua, Zhou Guanming, Chen Xicong, Xiao Keming, Cai Jian, Liu Xiaofang. Changes in kinematic parameters after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty and high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 390-396. |
| [13] | Wang Chong, Zhang Meiying, Zhou Jian, Lao Kecheng. Early gait changes after total hip arthroplasty through direct anterior approach and posterolateral approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 359-364. |
| [14] | Zhang Jian, Lin Jianping, Zhou Gang, Fang Yehan, Wang Benchao, Wu Yongchang. Semi-quantitative MRI evaluation of cartilage degeneration in early knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 425-429. |
| [15] | Guan Hong, Zhang Hongbo, Shao Yan, Guo Dong, Zhang Haiyan, Cai Daozhang. PDZ domain containing 1 deficiency promotes chondrocyte senescence in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 182-189. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||