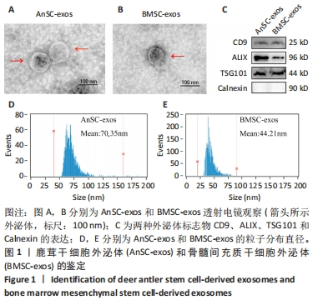
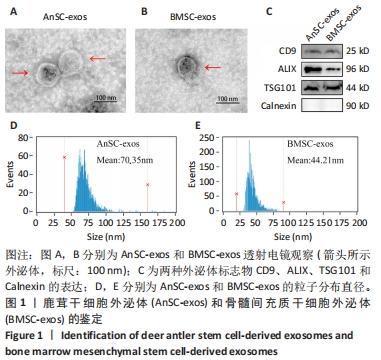
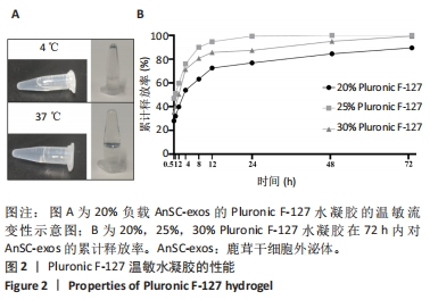
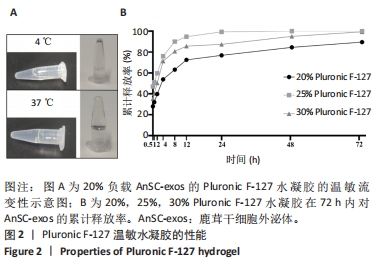
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (34): 7344-7352.doi: 10.12307/2025.491
Previous Articles Next Articles
Deer antler stem cell exosome composite hydrogel promotes the repair of burned skin
Zhao Jianwei, Li Xunsheng, Lyu Jinpeng, Zhou Jue, Jiang Yidi, Yue Zhigang, Sun Hongmei
- Institute of Special Animal and Plant Sciences, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Changchun 130000, Jilin Province, China
-
Received:2024-07-16Accepted:2024-09-07Online:2025-12-08Published:2025-01-17 -
Contact:Sun Hongmei, PhD, Associate researcher, Master’s supervisor, Institute of Special Animal and Plant Sciences, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Changchun 130000, Jilin Province, China -
About author:Zhao Jianwei, Master candidate, Institute of Special Animal and Plant Sciences, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Changchun 130000, Jilin Province, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province, No. YDZJ202401459ZYTS (to SHM); Science and Technology Innovation Project of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, No. CAAS-ASTIP-2021-ISAPS (to SHM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhao Jianwei, Li Xunsheng, Lyu Jinpeng, Zhou Jue, Jiang Yidi, Yue Zhigang, Sun Hongmei. Deer antler stem cell exosome composite hydrogel promotes the repair of burned skin[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7344-7352.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
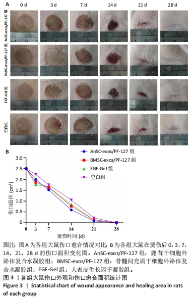
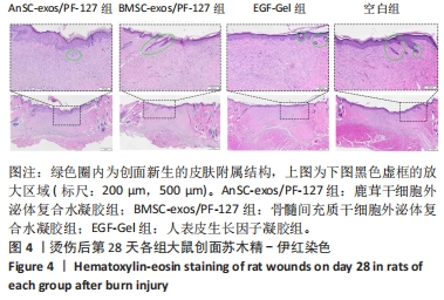
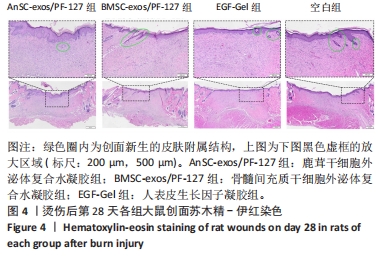
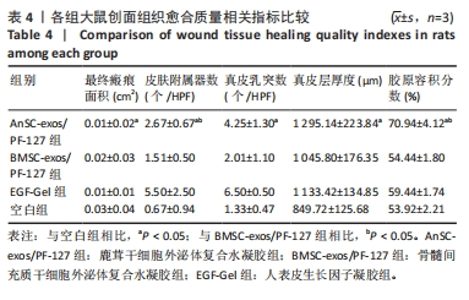
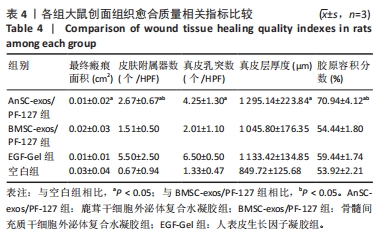
2.3 实验动物数量分析 选用10周龄SPF级雄性SD大鼠24只,体质量250-300 g,进行皮肤深Ⅲ度烫伤模型的制备。模型制备过程中无大鼠死亡。造模成功的24只大鼠随机分为4组,每组6只,随即进行给药实验。 2.4 伤口形态外观和愈合速度评估 观察创面的愈合过程(图3A)可以发现,烫伤后7 d可见伤口处有结痂形成,14 d左右结痂脱落,痂下为深红色的肉芽组织,21 d时给药组的皮肤伤口明显缩小,但颜色仍旧为深红色,而空白组伤口皮肤变白,大体观察皮肤微微凸起,28 d时给药组伤口愈合,而空白组间有大小不一的瘢痕生成。烫伤后28 d,鹿茸干细胞外泌体复合水凝胶组伤口已趋近于周围正常皮肤,大体观察到有毛发生长,而空白组有大面积瘢痕生成。对比伤口面积的统计图(图3B)可知:鹿茸干细胞外泌体复合水凝胶组、骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体复合水凝胶组、人表皮生长因子凝胶组伤口在烫伤后24 d基本闭合,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),而空白组伤口在28 d时闭合。"

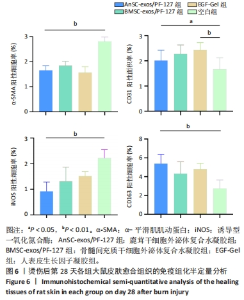
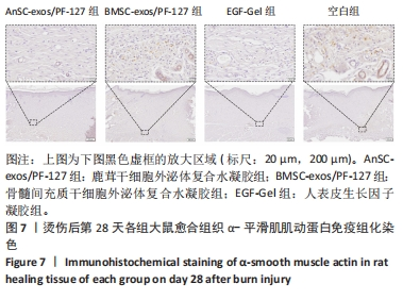
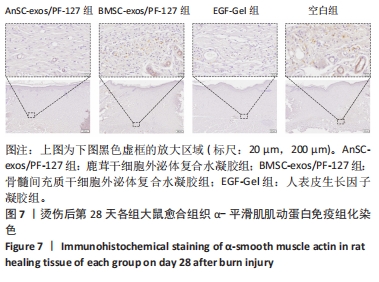
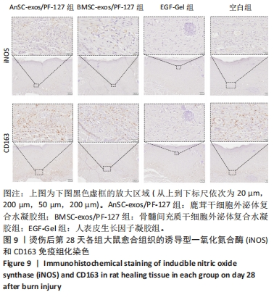
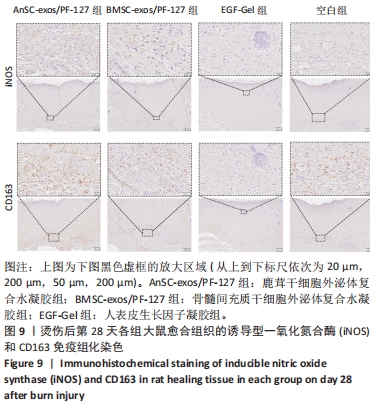
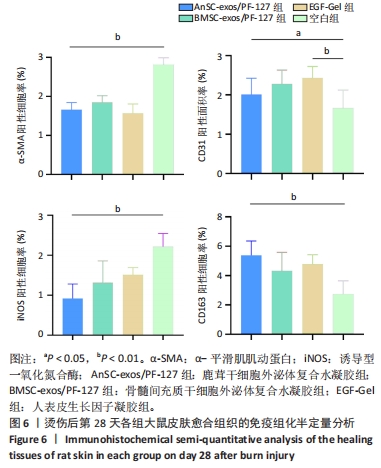
2.6 愈合组织的免疫组化分析 鹿茸干细胞外泌体复合水凝胶组α-平滑肌肌动蛋白阳性细胞率显著低于空白组(P < 0.01),与骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体复合水凝胶组和人表皮生长因子凝胶组并无显著差异(图6,7)。与空白组相比,给药各组均有大量棕色环状的新生小血管生成(图8),鹿茸干细胞外泌体复合水凝胶组的CD31阳性面积率显著高于空白组(P < 0.05),另外人表皮生长因子凝胶组的CD31阳性面积率也显著高于空白组(P < 0.01)(图6)。与空白组相比,鹿茸干细胞外泌体复合水凝胶组的诱导型一氧化氮合酶阳性细胞率显著降低(P < 0.01),CD163阳性细胞率显著升高(P < 0.01)(图6,图9)。"
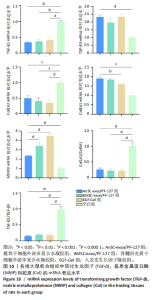
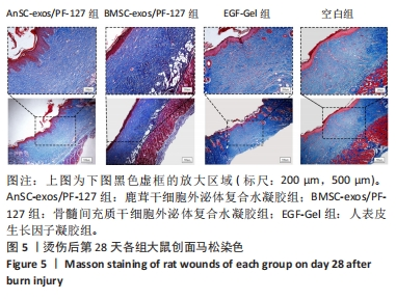
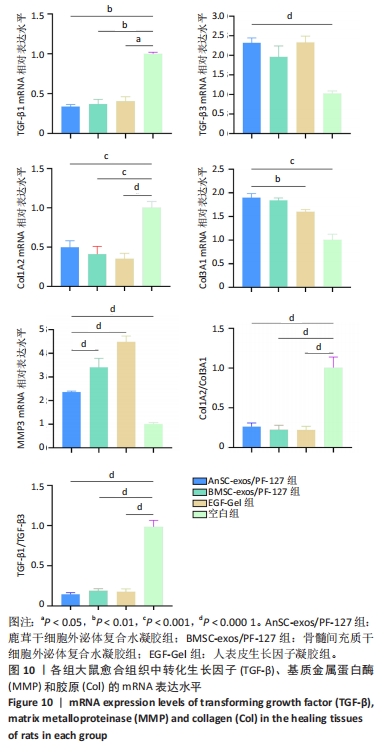
2.7 创面愈合组织中转化生长因子、基质金属蛋白酶和胶原的mRNA表达水平 由图10可见:在烫伤后第28天,鹿茸干细胞外泌体复合水凝胶组愈合组织中转化生长因子β1基因的表达水平显著低于空白组(P < 0.01),而转化生长因子β3基因的表达水平显著高于空白组(P < 0.000 1);相比于空白组,给药各组的Ⅲ型胶原蛋白α1基因的表达水平显著升高,而Ⅰ型胶原蛋白α2基因的表达水平显著降低。鹿茸干细胞外泌体复合水凝胶组的Ⅰ型胶原蛋白α2/Ⅲ型胶原蛋白α1比值显著低于空白组(P < 0.000 1);鹿茸干细胞外泌体复合水凝胶组基质金属蛋白酶3基因的表达水平显著高于空白组(P < 0.000 1);所有组均未检测到基质金属蛋白酶1基因的表达,推测第28天时基质金属蛋白酶1基因在皮肤伤口中不表达。"
| [1] YANG J, TIAN G, LIU J, et al. Epidemiology and clinical characteristics of burns in mainland China from 2009 to 2018. Burns Trauma. 2022; 10:tkac039. [2] 张成,彭源,罗小强,等.3067例住院烧伤患儿流行病学调查及其感染的病原学特征分析[J].中华烧伤杂志,2021,37(6):538-545. [3] ZHANG W, KE CH, GUO HH, et al. Antler stem cells and their potential in wound healing and bone regeneration. World J Stem Cells. 2021; 13(8):1049-1057. [4] DONG Z, COATES D. Bioactive Molecular Discovery Using Deer Antlers as a Model of Mammalian Regeneration. J Proteome Res. 2021;20(5): 2167-2181. [5] 孙红梅,赵海平,李春义,等.鹿茸皮肤完全再生机理的研究进展[J].特产研究,2021,43(1):64-72. [6] 郭倩倩.鹿茸再生初始阶段伤口愈合分子调控机制的研究[D].北京:中国农业科学院,2022. [7] HE Y, FISCHER D, HASAN I, et al. Sika deer antler as a novel model to investigate dental implant healing: A pilot experimental study. PLoS One. 2018;13(7):e0200957. [8] GUO Q, LIU Z, ZHENG J, et al. Substances for regenerative wound healing during antler renewal stimulated scar-less restoration of rat cutaneous wounds. Cell Tissue Res. 2021;386(1):99-116. [9] QIN T, ZHANG G, ZHENG Y, et al. A population of stem cells with strong regenerative potential discovered in deer antlers. Science. 2023; 379(6634):840-847. [10] WANG D, BERG D, BA H, et al. Deer antler stem cells are a novel type of cells that sustain full regeneration of a mammalian organ-deer antler. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(6):443. [11] LIU Q, LI J, CHANG J, et al. The characteristics and medical applications of antler stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):225. [12] ZHANG G, WANG D, REN J, et al. Antler stem cell-derived exosomes promote regenerative wound healing via fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transition inhibition. J Biol Eng. 2023;17(1):67. [13] KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020;367(6478):eaau6977. [14] WANG Y, LIN Q, ZHANG H, et al. M2 macrophage-derived exosomes promote diabetic fracture healing by acting as an immunomodulator. Bioact Mater. 2023;28:273-283. [15] WANG Y, ZHANG Y, LI T, et al. Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Exosomes Promote Keratinocytes and Fibroblasts Embedded in Collagen/Platelet-Rich Plasma Scaffold and Accelerate Wound Healing. Adv Mater. 2023;35(40):e2303642. [16] YE H, WANG F, XU G, et al. Advancements in engineered exosomes for wound repair: current research and future perspectives. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1301362. [17] SUN Y, ZHANG S, SHEN Y, et al. Therapeutic application of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in skin wound healing. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;12:1428793. [18] WEI JT, HE T, SHEN K, et al. Adipose stem cell-derived exosomes in the treatment of wound healing in preclinical animal models: a meta-analysis. Burns Trauma. 2024;12:tkae025. [19] GOH M, DU M, PENG WR, et al. Advancing burn wound treatment: exploring hydrogel as a transdermal drug delivery system. Drug Deliv. 2024;31(1):2300945. [20] XU Y, HU J, BI D, et al. A bioactive xyloglucan polysaccharide hydrogel mechanically enhanced by Pluronic F127 micelles for promoting chronic wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;277(Pt 2):134102. [21] HASSAN MA, BASHA AA, ERAKY M, et al. Advancements in silk fibroin and silk sericin-based biomaterial applications for cancer therapy and wound dressing formulation: A comprehensive review. Int J Pharm. 2024;662:124494. [22] SHARUN K, BANU SA, MAMACHAN M, et al. Pluronic F127 composite hydrogel for the repair of contraction suppressed full-thickness skin wounds in a rabbit model. Curr Res Transl Med. 2024;72(4):103458. [23] LI C, LITTLEJOHN RP, SUTTIE JM. Effects of insulin-like growth factor 1 and testosterone on the proliferation of antlerogenic cells in vitro. J Exp Zool. 1999;284(1):82-90. [24] YANG J, CHEN Z, PAN D, et al. Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Combined Pluronic F127 Hydrogel Promote Chronic Diabetic Wound Healing and Complete Skin Regeneration. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:5911-5926. [25] 肖玉伟,孙倩,陆娜,等.烫伤创面大鼠模型制备及评价[J].临床军医杂志,2024,52(7):678-681. [26] 王燕,郭蕊.miR-20b-5p靶向VEGFA对深Ⅱ度烫伤创面组织的作用机制[J].临床皮肤科杂志,2024,53(3):151-156. [27] 崔允美,崔晶,李今子.皮肤无瘢痕愈合的研究现状[J].中国皮肤性病学杂志,2023,37(9):988-993. [28] 史敏,毕芳芳,张明雨,等.外泌体在组织修复及抗瘢痕治疗中的研究进展[J].中国美容医学,2021,30(11):179-182. [29] 刘紫微,时权,王思拓,等.间充质干细胞来源外泌体在皮肤损伤修复中的研究进展[J].解放军医学院学报,2022,43(8):896-900. [30] AGUAYO-MORALES H, COBOS-PUC LE, LOPEZ-BADILLO CM, et al. Collagen-polyurethane-dextran hydrogels enhance wound healing by inhibiting inflammation and promoting collagen fibrillogenesis. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2024;112(10):1760-1777. [31] JIA Y, HAN Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Multifunctional type lll recombinant human collagen incorporated sodium alginate hydrogel with sustained release of extra cellular vehicles for wound healing multimodal therapy in diabetic mice. Regen Ther. 2024;27:329-341. [32] AN R, SHI C, TANG Y, et al. Chitosan/rutin multifunctional hydrogel with tunable adhesion, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties for skin wound healing. Carbohydr Polym. 2024;343:122492. [33] SALAH NM, ELBEDAIWY HM, HELMY MW, et al. Topical amlodipine-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for enhanced burn wound healing: A repurposed approach. Int J Pharm. 2024;662:124484. [34] WILKINSON HN, HARDMAN MJ. Wound healing: cellular mechanisms and pathological outcomes. Open Biol. 2020;10(9):200223. [35] ZENG J, PAN Y, CHAKER SC, et al. Neural and Inflammatory Interactions in Wound Healing. Ann Plast Surg. 2024;93(2S Suppl 1): S91-S97. [36] WANG Y, ZHOU C, LI Z, et al. Injectable immunoregulatory hydrogels sequentially drive phenotypic polarization of macrophages for infected wound healing. Bioact Mater. 2024;41:193-206. [37] SHI X, LI Y, KANG S, et al. Dual-functional gallium/chitosan/silk/umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell exosome sponge scaffold for diabetic wound by angiogenesis and antibacteria. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;274(Pt 2):133420. [38] TENG L, MAQSOOD M, ZHU M, et al. Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Accelerate Diabetic Wound Healing via Promoting M2 Macrophage Polarization, Angiogenesis, and Collagen Deposition. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(18):10421. [39] PEÑA OA, MARTIN P. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of skin wound healing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024;25(8):599-616. [40] ZHANG L, SHANG Y, HAN C, et al. CD248 interacts with ECM to promote hypertrophic scar formation and development. Gene. 2024;927: 148730. [41] LIANG X, ZHANG L, WANG S, et al. Exosomes secreted by mesenchymal stem cells promote endothelial cell angiogenesis by transferring miR-125a. J Cell Sci. 2016;129(11):2182-2189. [42] BUECHLER MB, FU W, TURLEY SJ. Fibroblast-macrophage reciprocal interactions in health, fibrosis, and cancer. Immunity. 2021;54(5): 903-915. [43] DENG Z, FAN T, XIAO C, et al. TGF-β signaling in health, disease, and therapeutics. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024;9(1):61. [44] 陈端凯,岑小宁,包崇婵,等.MEBT/MEBO通过PTEN/AKT通路对慢性难愈合创面中基质金属蛋白酶表达的影响[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2020,40(4):459-464. [45] RONG S, LI C, LI S, et al. Genetically modified adipose-derived stem cells with matrix metalloproteinase 3 promote scarless cutaneous repair. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33(6):e14112. [46] WANG J, WU H, ZHAO Y, et al. Extracellular Vesicles from HIF-1α-Overexpressing Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Restore Diabetic Wounds Through Accelerated Fibroblast Proliferation and Migration. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021;16:7943-7957. [47] 王俊杰,高建萍,张扬,等.炭药提取液对小鼠皮肤伤口愈合过程中胶原组成的影响[J].生物学杂志,2023,40(6):88-93. [48] 李文华,伍伟明,刘筱,等.美洲大蠊提取液对慢性难愈合创面Ⅰ/Ⅲ型胶原蛋白调控研究[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2018,38(3): 250-253. [49] ZHANG J, GUAN J, NIU X, et al. Exosomes released from human induced pluripotent stem cells-derived MSCs facilitate cutaneous wound healing by promoting collagen synthesis and angiogenesis. J Transl Med. 2015;13:49. |
| [1] | Wu Yanting, Li Yu, Liao Jinfeng. Magnesium oxide nanoparticles regulate osteogenesis- and angiogenesis-related gene expressions to promote bone defect healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1885-1895. |
| [2] | You Huijuan, Wu Shuzhen, Rong Rong, Chen Liyuan, Zhao Yuqing, Wang Qinglu, Ou Xiaowei, Yang Fengying. Macrophage autophagy in lung diseases: two-sided effects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1516-1526. |
| [3] | Cao Wenqi, Feng Xiuzhi, Zhao Yi, Wang Zhimin, Chen Yiran, Yang Xiao, Ren Yanling. Effect of macrophage polarization on osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling in type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 917-925. |
| [4] | Yang Xiao, Bai Yuehui, Zhao Tiantian, Wang Donghao, Zhao Chen, Yuan Shuo. Cartilage degeneration in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: mechanisms and regenerative challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 926-935. |
| [5] | Xie Peisen, Guan Zhenpeng, Wei Xianjie, Zhang Keshi, Kang Qingyuan, Xiao Wentao, Guo Xiaoshuai. Cerium dioxide nanoparticles regulate expression of inflammatory factors in M1 macrophages and affect fibroblast co-culture system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 375-383. |
| [6] | Zhang Tingting, Li Yalong, Yue Haodi, Li Yanjun, Geng Xiwen, Zhang Yuwei, Liu Xiaozhuan. Protection of exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells of different mouse ages on radiation-induced lung injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 1-9. |
| [7] | Zuo Na, Tang Qi, Yu Meng, Tao Kai. Effect of miR-196b-5p in adipose-derived stem cell exosomes on burn wound healing in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 43-49. |
| [8] | Yu Manya, Cui Xing. Contribution and interaction of various cells in bone marrow microenvironment to exosomal circular RNA associated with multiple myeloma bone disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 101-110. |
| [9] | Liu Nian, Dong Xinyue, Wang Songpeng, Xu Yingjiang, Zhang Xiaoming. Stem cell exosomes and biomaterial-assisted exosomes in bone defect repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 175-183. |
| [10] | Lyu Ruyue, Gu Lulu, Liu Qian, Zhou Siyi, Li Beibei, Xue Letian, Sun Peng. Regulatory mechanisms of exosome secretion and its application prospects in biomedicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 184-193. |
| [11] | Liu Yu, Gong Senyi, Yang Lihua, Li Weifeng, Hu Yuwen, Yan Qinbiao, Guo Meijin. Isolation, identification, and application of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 194-203. |
| [12] | Luo Wenbin, Li Ruoyun, Pan Chaofan, Luo Changjiang. Engineered exosomes for repairing tissue damage: application potential, excellent biological stability, and targeting specificity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 204-217. |
| [13] | Li Zikai, Zhang Chengcheng, Xiong Jiaying, Yang Xirui, Yang Jing, Shi Haishan. Potential effects of ornidazole on intracanal vascularization in endodontic regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-7. |
| [14] | Wang Wentao, Hou Zhenyang, Wang Yijun, Xu Yaozeng. Apelin-13 alleviates systemic inflammatory bone loss by inhibiting macrophage M1 polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1548-1555. |
| [15] | Lou Guo, Zhang Min, Fu Changxi. Exercise preconditioning for eight weeks enhances therapeutic effect of adipose-derived stem cells in rats with myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1363-1370. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||